Hello! Pentesters, this article is about a brute forcing tool Hydra. Hydra is one of the favourite tools of security researchers and consultants. Being an excellent tool to perform brute force attack, it provides various other options which can make your attack more intense and easier to gain unauthorised access to system remotely. In this article, I have discussed each option available in hydra to make brute force attacks in the various scenario.
Table of Contents:
·
Introduction to Hydra
·
To guess password for specific username
·
Brute forcing Username and Password
·
Verbose and Debug Mode
·
NULL/Same as Login
or Reverse login Attempt
·
Saving output in disk
·
To Resume Brute Force Attack
·
Password generating using various set of characters
·
To attack on specific port rather than default
·
Attacking on Multiple Hosts
·
Using Combo Entries
·
Concurrent testing on Multiple Logins
·
HTTP Login Form Brute Force
·
Service module Usage information
·
Attacking on secured service connection
·
Proxy Support
Introduction to Hydra
Hydra - a very fast network logon
cracker which supports many different services. It is a parallelized login
cracker which supports numerous protocols to attack. New modules are easy to
add, besides that, it is flexible and very fast. This tool gives researchers
and security consultants the possibility to show how easy it would be to gain
unauthorized access from remote to a system.
Currently this tool supports: adam6500,
afp, asterisk, cisco, cisco-enable, cvs, firebird, ftp, ftps,
http[s]-{head|get|post}, http[s]-{get|post}-form, http-proxy,
http-proxy-urlenum, icq, imap[s], irc, ldap2[s], ldap3[-{cram|digest}md5][s],
mssql mysql(v4), mysql5, ncp, nntp, oracle, oracle-listener, oracle-sid,
pcanywhere, pcnfs, pop3[s], postgres, rdp, radmin2, redis, rexec, rlogin, rpcap,
rsh, rtsp, s7-300, sapr3, sip, smb, smtp[s], smtp-enum, snmp, socks5, ssh,
sshkey, svn, teamspeak, telnet[s], vmauthd, vnc, xmpp
For most protocols SSL is supported (e.g.,
https-get, ftp-ssl, etc.). If not, all
necessary libraries are found during compile time, your available services will
be less. Type "hydra" to see
what is available.
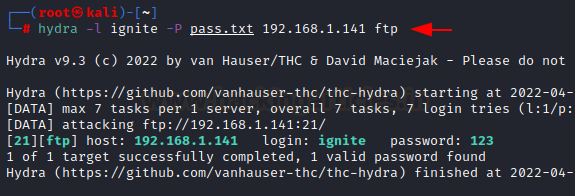
To guess Password for specific
username
If you have a correct username but
want to login without knowing the password, so you can use a list of passwords
and brute force on passwords on the host for ftp service.
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp
Here -l option is for username -P for
password lists and host ip address for ftp service.
For login ignite password 123 made
success.
To guess username for specific
password
You may have a valid password but no
idea what username to use. Assume you have a password for a specific ftp login.
You can brute force the field with correct username wordlists to find the
correct. You can use the -L option to specify user wordlists and the -p option
to specify a specific password.
hydra -L users.txt -p 123
192.168.1.141 ftp
Here, our wordlist is users.txt for
which -L option is used, and password is 123 and for that -p option is used over ftp.
Brute forcing Username and Password
Now if you don’t have either of
username or password, for that you can use brute force attack on both the
parameters username and password with wordlist of both and you can use -P and
-U parameters for that.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp
Users.txt is wordlist for username
and pass.txt is wordlist for password and the attack has displayed valid
credentials ignite and 123 for the host.
Verbose and Debug Mode
-V option is used for verbose mode,
where it will show login+pass combination for each attempt. Here, I have two
wordlists users.txt and pass.txt so the brute force attack was making
combinations of each login+password and verbose mode showed all the attempt.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp -V
Here the users.txt has 5 username and
pass.txt has 7 passwords so the number of attempts were 5*7= 35 as shown in
screenshot.
Now is the -d option used to enable
debug mode. It shows the complete detail of the attack with waittime, conwait,
socket, pid, RECV
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp -d
-d option enabled debug mode which,
as shown displayed complete detail of the attack.
NULL/Same as Login or Reverse login Attempt
Hydra has an option -e which will check 3 more
passwords while brute forcing. [n] for null, [s] for same i.e., as same as
username and [r] for reverse i.e., the reverse of username. As shown in the
screenshot, while brute forcing the password field, it will first check with
null option then same option and after that reverse. And then the list which I
have provided.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt 192.168.1.141 ftp -V
-e nsr
I have enabled verbose mode also so that we can get
detail information about the attempts made while brute forcing.
Saving output in Disk
This tool gives you an option to save
the result into the disk. Basically for record maintenance, better readability
and future preferences we can save the output of the brute force attack into a
file by using -o parameter.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt 192.168.1.141
ftp -o result.txt
I tried to use this option and got
success using the above command where the output is stored in result.txt file.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp -o result:json
I have used this option to store
result in json file format also, this type is unique thing provided by hydra.
To Resume Brute Force Attack
It may happen sometimes, that attack
gets halted/paused accidently due to some unexpected behaviour by hydra. So,
hydra has solved this problem by including -R option so that you can resume the
attack from that position rather than starting from beginning.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp
hydra -R
First, I started the attack using the
first command, then after that halted the attack by pressing CTRL + C and then
by using second command I have resumed the attack.
Password generating using various set
of characters
To generate passwords using various
set of characters, you can use -x option. It is used as -x
min:max:charset where,
Min: specifies minimum number of
characters in password.
Max: specifies maximum number of
characters in password.
Charset: charset can contain 1 for
numbers, a for lowercase and A for uppercase characters. Any other character
which is added is put to the list.
Let’s consider as example: 1:2:a1%.
The generated passwords will be of
length 1 to 2 and contain lowercase letters, numbers and/or percent signs and
dots.
hydra -l ignite -x 1:3:1 ftp://192.168.1.141
So, here minimum length of password
is 1 and max length is 3 in which it will contain numbers and for password 123
it showed success.
To make you understand better I have
used -V mode and it has displayed result in detail.
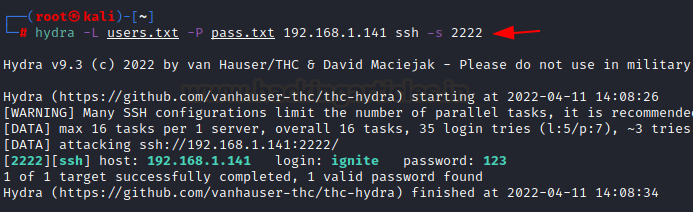
To attack on specific port rather
than default
Network admins sometimes change the
default port number of some services for security reasons. In the previous
commands hydra was making brute force attack on ftp service by just mentioning
the service name rather than port, but as mentioned earlier default port gets
changed at this time hydra will help you with -s option. If the service is on a
different default port, define it using -s option.
nmap -sV 192.168.1.141
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ssh -s 2222
So to perform, first I tried running
nmap scan at the host. And the screenshot shows all open ports where ssh is at
2222 port. So post that I tried executing the hydra command with -s parameter
and port number.
Here it found valid entries with user
ignite and password 123.
Attacking on Multiple Hosts
As earlier I performed brute force
attack using password file pass.txt and username file users.txt on single host
i.e., 191.168.1.141. But if there are multiple hosts, for that you can use -M
with the help of which brute force is happening at multiple hosts.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt -M
hosts.txt ftp
First, I have created a new file hosts.txt
which contains all the hosts. Then the result is showing 2 valid hosts,
username and password with success.
Now in above command I have used -M
option for multiple hosts so, it is very time consuming to display all the
attempts taking place while the attack, for that medusa has provided -F option
such that attack will exit after the first found login/password pair for any
host.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt -M
hosts.txt ftp -F
Using Combo Entries
This tool gives you a unique
parameter -C for using combo entries. First you need to create a file which has
data in colon separated "login:pass" format, and then you can use -C option mentioning file
name and perform brute force attack instead
of using -L/-P options separately. In
this way, attack can be faster and gives you desired result in lesser time.
cat userpass.txt
hydra -C userpass.txt 192.168.1.141
ftp
So, I have created a userpass.txt
file using cat command and entered details in “login:pass” format. Then I used
-C option in the hydra command to start the attack.
Concurrent Testing on Multiple Logins
If you want to test multiple logins
concurrently, for that you can use -t option by mentioning the number and hence
hydra will brute force concurrently.
hydra -L users.txt -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp -t 3 -V
As shown in the screenshot, three
attempts are made concurrently, three passwords are concurrently checking with
user ignite at host 192.168.1.141, as you can observe child changes 0, 1,2 that
means it is concurrently making three attempts and printed 3 of them
simultaneously.
HTTP Login Form Brute Force
The hydra form can be used to carry
out a brute force attack on simple web-based login forms that requires username
and password variables either by GET or POST request. For testing I used dvwa
(damn vulnerable web application) which has login page. This page uses POST
method as I am sending some data.
hydra
-l admin -P pass.txt 192.168.1.150 http-post-form
“/dvwa/login.php:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^&Login=Login:Login
failed”
Here
I have given the username admin and provided file for passwords and used http-post-form
module to perform brute force attack on 192.168.1.150 host.
So, for password: password it gave
success and bypassed the login page. Now I had performed brute force on username
and password field mentioned having security level as “low”. And by using
cookie editor plugin I found out the cookie PHPSESSID and used its value in the
command.
hydra 192.168.1.150 -l admin -P
‘pass.txt’ http-get-form “/dvwa/vulnerabilities/brute/:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^&Login=Login:F=Username
and/or password incorrect.:H=Cookie:PHPSESSID=13f2650bddf7a9ef68858ceea03c5d;
security=low”
I had viewed page source and from
that I found out that page uses GET method, and so http-GET-form module as
mentioned in above command.
As in the screenshot, command is
successfully executed, and I got correct username and password.
Service module Usage information
As discussed earlier in introduction
all the supported services by hydra, if you want check once just type hydra -h
and you will get list of services supported by hydra. So, to get the detailed
information about the usage hydra provides -U option.
hydra http-get-form -U
Here http-get-form is one of the
services supported by hydra and -U option helped to get detailed information.
Attacking on secured service
connection
While performing attack on ftp
connection, you just mention the service name along with appropriate options,
but if the host has ftp port open but and ftp is secured, so if you use
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
ftp://192.168.1.141
This command will not execute
properly and hence 0 valid password found. So in order to perform attack on
secured ftp connection, then run this command.
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
ftps://192.168.1.141
And this command worked well and
showed 1 valid password found.
This is one way to attack on secured
ftp, hydra provides one more way to attack on secured service.
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt 192.168.1.141
ftp
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftps
The first did not worked as the host
192.168.1.141 has secured ftp, but second worked and showed us valid password
found. In this way you can perform brute force attack on hosts which have
secured services open.
Proxy Support
Now let’s discuss how hydra attacks
on hosts having proxy enabled. I first tried to same command with -l -p
parameters on host 192.168.1.141 on ftp service and found that no password was
found. Hence, I started nmap scan for the host and found list of services and
ports open. So, at port 1080 a proxy “socks5” was set without any
authentication.
Unauthenticated Proxy
Hydra provides two different ways for
proxy support. I have tried both the ways. Use screenshot for better
understanding. Let’s discuss the first way
1. Export Environment
To enable proxy I used this command
export
HYDRA_PROXY=socks5://192.168.1.141:1080
And then used the following command
and got 1 valid password
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt 192.168.1.141
ftp
2. Proxychains
I have opened the
/etc/proxychains4.conf using cat command and added the proxy details with host
and port. And then with the help of proxychains brute force is performed
cat /etc/proxychains4.conf
proxychains hydra -l ignite -P
pass.txt 192.168.1.141 ftp
Authenticated Proxy
I got the desired password 123 for
the host. In the above attack there was not any authentication enabled. Now I
tried on proxy that has authentication enabled.
1. Proxychains
I tried to brute force the target
using proxychains but it denied, because authentication was enabled on proxy.
proxychains hydra -l ignite -p
pass.txt 192.168.1.141 ftp
So, I added username and password in
/etc/proxychains4.conf file using cat command.
cat /etc/proxychains4.conf
Just observe screenshot for better
understanding. Then with the help of proxychains I started attack using below
command
proxychains hydra -l ignite -P
pass.txt 192.168.1.141 ftp
2. Export Environment
export
HYDRA_PROXY=socks5://raj:1234@192.168.1.141:1080
Here “raj” is username, “1234@” is
password for proxy and “192.168.1.141” is host and “1080” is the port on which
proxy is enabled. After that I used the command
hydra -l ignite -P pass.txt
192.168.1.141 ftp
And for this it showed valid password
for the host 192.168.1.141
Note:
For setting up the proxy I took reference from https://www.hackingarticles.in/penetration-testing-lab-setup-microsocks/
Author: Divya Adwani is a
researcher and technical writer who is very much keen to learn and enthusiastic
to learn ethical hacking. Contact here









































0 comments:
Post a Comment