Splunk Inc. is an American public multinational corporation based
in San Francisco, California, that produces software for searching,
monitoring, and analyzing machine-generated big data via a Web-style interface.
Splunk (the product) captures, indexes,
and correlates real-time data in a searchable repository from which it can
generate graphs, reports, alerts, dashboards, and visualizations.
Table of Content
§
What is Splunk
§
Splunk Features
§
Splunk Architecture
§
Prerequisites
§
Splunk Environment
§
Download and Install Splunk
§
Adding a task
§
Creating a Dashboard
§
Log Monitoring
What is Splunk
Splunk is a software that is used to
search, and analyze machine data generated by various CPU running on web or
local servers, IoT devices, mobile apps, sensors, or data created by the user.
It completes the needs of IT infrastructure by analyzing the logs generated by
systems in various processes in a structured or semi-structured format with
proper data modelling and then it allows users to create Reports, Alerts, Tags,
and Dashboards on these data.
Splunk
Features
Data searching: - searching in Splunk involves the pattern of creating metrics or
indexes on Dashboards.
Data ingestion: - Splunk ingest data in various formats like XML, JSON, and
unstructured machine data such as logs of CPU running on web servers.
Data Indexing: - Splunk auto index the ingested data of various machines for the
faster searching on various conditions.
Alerts: - Splunk alert used for triggering emails or other feeds when some
unusual suspicious activity found in data is being analysed.
Dashboards: - it shows the search results in form of pivots, area mapping, pie
charts, reports, etc.
Splunk
Architecture
There are three main components of
Splunk: -
·
Splunk Forwarder
·
Splunk Indexer
·
Splunk Head
Prerequisites
To configure Splunk in your Ubuntu
platform, there are some prerequisites required for installation.
§ Ubuntu 20.04.1 with minimum 4GB RAM and 2 CPU
§ SSH Access with Root Privileges
§ Firewall Port: - 8000
Splunk
Environment
In this blog, we will target to install an enterprise version that is
available free for 60 days with all features enabled. You can download Splunk
by following the below link.
Linux version
Create a Splunk Account and download
Splunk for Linux version by the given above link. We choose .deb Package
for the installation in Ubuntu.
We can
directly install it via terminal by copying wget snippet
Download and
install Splunk
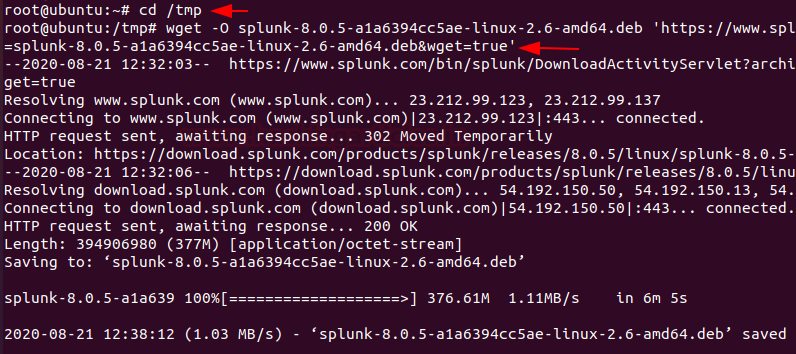
Now, Hit the terminal and download the Splunk into the tmp directory by
entering the following command.
cd /tmp
wget -O splunk-8.0.5-a1a6394cc5ae-linux-2.6-amd64.deb
'https://www.splunk.com/bin/splunk/DownloadActivityServlet?architecture=x86_64&platform=linux&version=8.0.5&product=splunk&filename=splunk-8.0.5-a1a6394cc5ae-linux-2.6-amd64.deb&wget=true'
Next,
we run the dpkg command to extract and install the Splunk server. To extract
.deb package enter the following command
dpkg
-i splunk-8.0.5-a1a6394cc5ae-linux-2.6-amd64.deb
Secondly,
we need to create the init.d script so we can easily start or stop Splunk
service. Change your binary directory at /opt/splunk/bin/ and run the following
command to start the Splunk with system boot.
cd
/opt/splunk/bin/
./splunk
enable boot-start
During
this process press the spacebar to go through the license agreement and then
type “Y” to accept it and then provide the username and password that
you created on the official website of Splunk. Finally, we can start Splunk
service with the below argument.
service
splunk start
Now,
you need to make sure port 8000 is open on your server firewall and then you
can access Splunk on web interface at
or
And
then, enter the login credentials that you created during the installation
process to access the GUI interface. Once you logged in then you will have your
Splunk Dashboard ready to set fire on the logs 😊.
Adding a task
On the
Splunk web interface, there are various categories listed over on the homepage
you can choose your own to start Splunking.
I’m
adding an example for a task which is been added to the Splunk system. My task
is to add or forward system logs to Splunk dashboard.
To
forward logs to Splunk monitoring console just open the terminal and hit the
following commands in the Splunk installed directory with the below arguments.
cd
/opt/splunk/bin
./splunk
add forward-server 192.168.205.135:9997 -auth splunk:Splunk@123
./splunk
add monitor /var/log -sourcetype linux_logs -index remotelogs
./splunk
restart
And
then open Splunk search and reporting console and then run a query in the search
bar.
index=remotelogs
* host-ubuntu
You
can also directly add this task by your Splunk Dashboard by following the below
steps.
Step
1.
Fire
up the Splunk web interface on your favourite browser and choose the “Add
Data” option to start with.
Step
2.
The “Add
Data” opens up with three options: Upload, Monitor, and Forward each option
have self-explanatory with a short description. Our task is to monitor system
logs we go with the option of “Monitor”.
In the
monitor option, there are four categories as shown below
Files
& Directories:
To monitor files and folders
HTTP
Event Collector:
To Monitor Data streaming over HTTP
TCP/UDP: To monitor network Traffic over
TCP/UDP ports
Scripts: To monitor Scripts and commands
Step
3.
As per
our purpose we choose and go with the “Files & Directories” option.
And
then we are going to browse the path where system logs are stored.
Now,
we’re going to browse the exact path /var/log that’s from the server to
monitor. Once you had done then select the next option.
After
selecting the system files to monitor select the next option.
Also,
you can whitelist or blacklist specific directories that you don’t want to
monitor on a given dialogue box and then review your settings and hit submit
button.
Congrats!
Finally, you have successfully added the task to the Search & Reporting
console now Start Searching.
Step
4.
Now
you’ve successfully added data source to Splunk for monitoring. You can search
and monitor logs file as required just run the search query
source="/var/log/*"
host="ubuntu"
Creating a Dashboard
And
then now you can save these logs directory on your dashboard or also you can
create an alert that is used for triggering emails or
other feeds when some unusual suspicious activity found in data is being analysed.
To add
this search and reporting console on your Dashboard simply follow the steps as
described below.
Step
5.
Just
locate “Save As” option on above of the Search & Reporting console
and select “Dashboard Panel”
By
selecting option Dashboard panel, it will prompt a Save As panel. Enter the
Title of Dashboard panel and descriptions then save it.
Great!
You have successfully created your dashboard panel. Now you can directly monitor your
system logs by heading system logs under Dashboards panel.
Just
select options available on your dashboard that you want to monitor in my case
I’m watching the server logs that I saved in my dashboard. Now You can watch as
many files of your server by simply adding it into the dashboard panel.
Log Monitoring
This one is a little bit special, as we can go into the “Dashboard” tab
select the options that you want to monitor
For example, I’m going to take access to my server by different
protocol’s as described below
·
SSH
·
Telnet
·
Vsftpd
SSh logs
I use putty to take SSH access to my server machine
After setting host or port open the SSH prompt login into the server
After getting the access of the server get back to your dashboard and
narrow down the logs to SSH on the server by running a query sshd.
Now, we can see SSH access of the server machine in Dashboard under
saved panel named system logs.
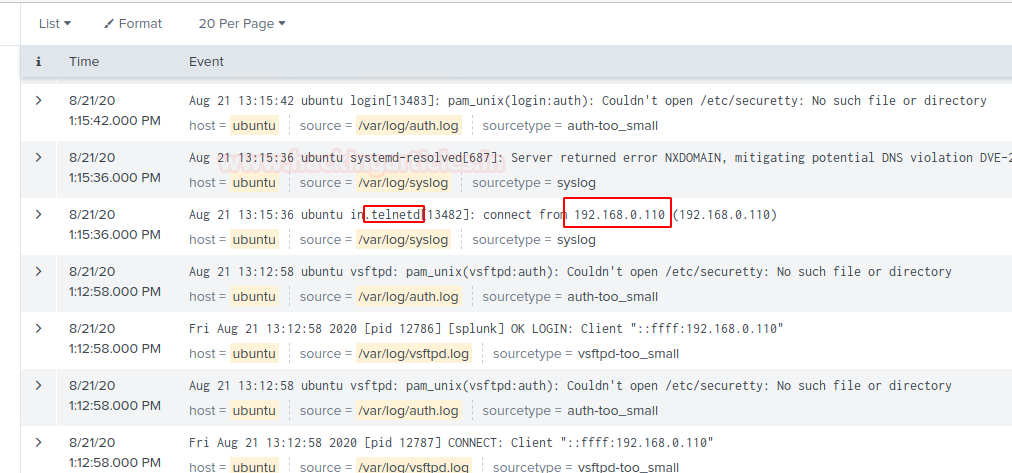
Telnet
I used the same puttygen to take telnet access of my server machine use
your credentials to log in to your server.
Let’s check what happened to the Splunk dashboard. After getting the access
of the server get back to your dashboard and narrow down the logs to telnet on
the server by running query telnet.
Now, we can see Telnet access logs of the server machine in Dashboard
under the same panel.
Hang on! This is not enough.
VSFTPD
I took
the vsftpd access of my server machine by using winscp or you can use
your desired applications.
Narrow
down your search by running a query vsftpd and then successfully you will be
able to see your server vsftpd logs.
You
can run more search queries to drill down it deeper.
The
more will be discussed in part 2.
Coming
soon!




































0 comments:
Post a Comment