Today we are going to discuss how to Detect NMAP scan
using Snort but before moving ahead kindly read our privious both articles
releted to Snort Installation (Manually or using apt-respiratory)and its rule configuration to enable it as IDS for your network.
Basically
in this article we are testing Snort against NMAP various scan which will help
network security analyst to setup snort rule in such a way so that they become
aware of any kind of NMAP scanning.
Requirement
Attacker: Kali
Linux (NMAP Scan)
Target: Ubuntu
(Snort as IDS)
Optional: Wireshark (we have added it
in our tutorial so that we can clearly confirm all incoming and outgoing packet
of network)
Let’s Begins!!
Identify NMAP Ping Scan
As
we know any attacker will start attack by identifying host status by sending
ICMP packet using ping scan. Therefore be smart and add a rule in snort which
will analyst NMAP Ping scan when someone trying scan your network for
identifying live host of network.
Execute given below command in ubuntu’s terminal to open
snort local rule file in text editor.
sudo gedit /etc/snort/rules/local.rules
Now add given below line which will capture the incoming traffic
coming on 192.168.1.105(ubuntu IP) network for ICMP protocol.
alert icmp any any -> 192.168.1.105 any (msg:
"NMAP ping sweep Scan "; dsize:0;sid:10000004; rev: 1;)
Turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below command
in terminal:
sudo snort -A console
-q -u snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
Now using attacking
machine execute given below command to identify status of target maching i.e. host is UP or Down.
nmap -sP 192.168.1.105 --disable-arp-ping
If you will execute above
command without parameter “disable arp-ping” then will work as default ping sweep
scan which will send arp packets inspite of sending ICMP on targets network and
may be snort not able to capture NMAP Ping scan in that sinario, therefore we
had use parameter “disable arp-ping” in above command.
As I had
declaimed above why we are involving wireshark in this tutorial so that you can
clearly see the packet sends form attacker network to targets network. Hence in
given below image you can notice ICMP
request packet as well as ICMP reply packets both are part of network traffic.
Come back to over your target machine where
snort is capturing all in coming traffic here your will observe that it is
generating alert for NMAP Ping Sweep scan. . Hence you can block attacker’s IP
to protect your network from further scanning.
Now in order to connect with target network,
attacker may go with networking enumeration either using TCP Protocol or UDP
protocol. Let assume attacker may choose TCP scanning for network enumeration
then in that situation we can apply following rule in snort local rule file.
alert
tcp any any -> 192.168.1.105 22 (msg: "NMAP TCP Scan";
sid:10000005; rev:2; )
Above rule is only applicable for port 22 so if
you want to scan any other port then replace 22 from the port you want to scan
else you can also use “any” to analysis all ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as
done above.
Now again using attacker machine execute the given below
command for TCP scan on port 22.
nmap -sT -p22
192.168.1.105
From given below image you can observe wireshark has captured
TCP packets from 192.168.1.104 to 192.168.1.105
Here you
can confirm that our snort is absolutely working when attacker is scanning port
22 using nmap TCP scan and it is showing attacker’s IP from where traffic is
coming on port 22. Hence you can block this IP to protect your network from
further scanning.
As we know that TCP communication follows three
way handshake to established TCP connection with target machine but sometimes
instead of using SYN, SYN/ACK,ACK flag attacker choose XMAS scan to connect
with target by sending data packets through Fin, PSH & URG flags.
Let
assume attacker may choose XMAS scanning for network enumeration then in that
situation we can apply following rule in snort local rule file.
alert
tcp any any -> 192.168.1.105 22 (msg:"Nmap XMAS Tree Scan";
flags:FPU; sid:1000006; rev:1;)
Again above rule is only applicable for port 22
which will listen for incoming traffic
when packets come from Fin, PSH & URG flags .So if you want to scan any
other port then replace 22 from the port you want to scan else you can also use
“any” to analysis all ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as done above.
Now again using attacker machine execute the given below
command for XMAS scan on port 22.
nmap -sX -p22
192.168.1.105
From given below image you can observe that
wireshark is showing 2 packets from attacker machine to target machine has been
send using FIN, PSH, URG flags.
Identify NMAP FIN Scan
Instead of using SYN, SYN/ACK and ACK flag to established
TCP connection with target machine may attacker choose FIN scan to connect with
target by sending data packets through Fin flags only.
Let assume
attacker may choose FIN scanning for network enumeration then in that situation
we can apply following rule in snort local rule file.
alert tcp any any
-> 192.168.1.1045 22 (msg:"Nmap FIN Scan"; flags:F; sid:1000008;
rev:1;)
Again above rule is only applicable for port 22 which will
listen for incoming traffic when packets come from Fin Flags. So if you want to
scan any other port then replace 22 from the port you want to scan else you can
also use “any” to analysis all ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as done above.
Now again using attacker machine execute the given below
command for FIN scan on port 22.
nmap -sF -p22
192.168.1.105
From given below image you can observe that wireshark is showing 2
packets from attacker machine to target machine has been send using FIN flags.
Come back to over your target machine where snort is
capturing all in coming traffic here your will observe that it is generating
alert for NMAP FIN scan. Hence you can block attacker’s IP to protect your
network from further scanning.
Instead of using
SYN, SYN/ACK and ACK flag to established TCP connection with target machine may
attacker choose NULL scan to connect with target by sending data packets
through NONE flags only.
Let assume attacker may choose FIN scanning
for network enumeration then in that situation we can apply following rule in
snort local rule file.
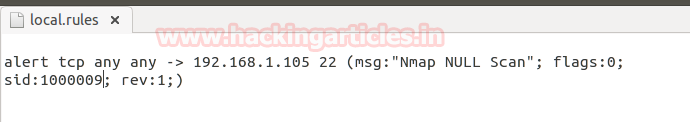
alert tcp any any -> 192.168.1.105 22 (msg:"Nmap NULL
Scan"; flags:0; sid:1000009; rev:1;)
Again above rule is
only applicable for port 22 which will listen for incoming traffic when packets
come from NONE Flags. So if you want to scan any other port then replace 22
from the port you want to scan else you can also use “any” to analysis all
ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as done above.
Now again using attacker machine execute the given below
command for NULL scan on port 22.
nmap -sN -p22
192.168.1.105
From given below image you can observe that wireshark is showing 2
packets from attacker machine to target machine has been send using NONE flags.
Come back
to over your target machine where snort is capturing all in coming traffic here
your will observe that it is generating alert for NMAP Null scan. Hence you can
block attacker’s IP to protect your network from further scanning.
In order to Identify open UDP port and running
services attacker may chose NMAP UDP scan to establish connection with target
machine for network enumeration then in that situation we can apply following
rule in snort local rule file.
alert UDP
any any -> 192.168.1.105 68 (msg:"Nmap UDPScan"; sid:1000010;
rev:1;)
Again above rule is only applicable for port 68
which will listen for incoming traffic when packets come from NONE Flags. So if
you want to scan any other port then replace 68 from the port you want to scan
else you can also use “any” to analysis all ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as
done above.
In order to Identify open UDP port and running
services attacker may chose NMAP UDP scan to establish connection with target
machine for network enumeration then in that situation we can apply following
rule in snort local rule file.
alert UDP
any any -> 192.168.1.105 68 (msg:"Nmap UDPScan"; sid:1000010;
rev:1;)
Again above rule is only applicable for port 68
which will listen for incoming traffic when packets come from NONE Flags. So if
you want to scan any other port then replace 68 from the port you want to scan
else you can also use “any” to analysis all ports. Enable NIDS mode of snort as
done above.
Now again using attacker machine execute the given below
command for NULL scan on port 22.
nmap -sU -p68
192.168.1.105
From given below image you can observe that wireshark is
showing 2 packets from attacker machine to target machine has been send over
UDP Port.
Come
back to over your target machine where snort is capturing all in coming traffic
here your will observe that it is generating alert for NMAP UDP scan. Hence you
can block attacker’s IP to protect your network from further scanning.

































0 comments:
Post a Comment