In order to protect online assets, web application security testing is an essential element of safeguarding them. Burp Suite has been a leader in this area for many years and it's still being used by safety professionals as well as Ethical hackers. One of those extensions that stands out in the web security testing community is "Autorize", which comes with a wide variety of additional features to improve its capabilities. A powerful set of features that simplify the authentication and authorization testing process is available with this extension.
Autorize = Authenticate + Authorize
Authorization includes any method by which a system grants
or revokes permission to access specific data or actions. Meanwhile, Authentication
is a process by which an individual or system authenticates themselves as being
who they claim to be.
·
Common vulnerabilities detected by Autorize
·
Understanding the Functionality
·
Installation and Setup
·
Navigation and Configuration options
·
Practical Demonstration of Autorize in Action
Common vulnerabilities detected by Autorize
It is primarily focused on identifying authorization-related
vulnerabilities. It can help to identify some of the main types of
vulnerabilities, such as:
·
Inadequate Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
It can uncover issues where user roles or permissions are not properly
enforced, allowing users to access functionality or data they shouldn't have
access to.
·
Broken Access Controls: It can identify
instances where access controls are not correctly implemented, leading to
unauthorized access to resources or actions.
·
Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR):
It can find situations where attackers can manipulate input to access other
users' data or perform actions they shouldn't be able to.
·
Forced Browsing: It can help identify
cases where an attacker can navigate directly to restricted areas of the
application by manipulating URLs.
·
Insufficient Authorization: It may detect
situations where user roles or permissions are not properly enforced, allowing
unauthorized actions to be performed.
·
Horizontal and Vertical Privilege Escalation:
It can find vulnerabilities that enable attackers to escalate their privileges
within the application, either by impersonating other users or gaining
additional permissions.
·
Business Logic Flaws: Autorize may
discover business logic vulnerabilities, where application workflows can be
manipulated in unintended ways, potentially leading to unauthorized actions or
data exposure.
Remember that the effectiveness of Autorize depends on how
well it is configured and your tests are carried out.
Understanding the working of Autorize
Let’s understand how Autorize works. Suppose, for instance, a
web application implements user-based roles and supports cookie-based authentication.
Normal User: has access to general functionality but is not
allowed to access admin functions and database (read-only access).
Admin User: has access to all functionality (read/write
access).
Capture the normal user cookies and add them to Authorize.
Re-log in with the Admin user access all the admin functionality and update
some data to the database.
What will Autorize be doing now? Autorize is capturing all
requests and changing the administrator cookie with your normal user's cookies
when you are browsing an application, then sending them to server. See the
server response, if the server behaves in the same way as legitimate Admin
(like 200 OK in response) and no errors have been detected. The request was
highlighted as a Red Bypass! Another request shows as a Green Enforced!.
For every request sent to the server from a client, it will
perform an automated test. With a large application, with over 30+ dynamic webpages,
it's going to ease our work. There are a lot of URLs you need to test manually,
so Autorize will do it for you.
Similarly, Autorize also detects an API endpoint problem in
the same way. The authentication method must be checked for the API. Let's say
an API uses a JWT token, you can control that by modifying its authorization
header and identifying the authentication bypass issues with the APIs.
Installation and Setup
From the Bapp Store, you can download and install the
extension. Select Bapp Store in Extensions. You can search for ‘Authorize’, or
you can just look down. Click on it, scroll down to the right side.
The extension is built in Python, you will see that 'Jython'
needs to be installed first.
Browse the below link and download ‘Jython Standalone’.
Refer this link: https://www.jython.org/download.html
After downloading go to Setting > Extension > on the
right side under Python Environment browser the Jython file. This environment
has been successfully set up for Jython.
Restart the Burp program and follow this path to install
Authorize on BApp Store. You'll notice that the install button is highlighted.
You can click on it and install it.
The Authorize tab will appear in the bar after successful
installation.
Navigating and Configuration Options
There are two tabs under the Authorize section, the first
one is Request/Response Viewers tab and the other one Configuration tab.
Request/Response Viewers: The Request/Response tab
will display complete information about the particular request you capture
within Authorize and choose. The manipulated request will be displayed under
the Modified Request section, the Original Request tab will display the original/unmodified
request, and the Unauthenticated request will display the unauth request.
Configuration: Under the configuration tab you will
see Autorize is off by default, when you are ready to capture the request first
put Autorize on. There are also some configurations for capturing a request and
server status code. Depending on your preference, you can select it.
Here, under the Temporary header box; you need to put the
normal user token/cookies/header value that you want to replace within the
actual request i.e. if any application is using a JWT token for auth mechanism
you need to put that value here.
Either you can manually add the auth value or below is the
option to fetch it from the last request. If you want to add the cookies header
from the last request – click on ‘Fetch Cookies header’ or If you want to add
Authorization header – click on ‘Fetch Authorization header’.
Generally, the session cookies are under Cookies Header and
the auth token comes under Authorization Header.
Once the session cookies are loaded, it is essential to
instruct Authorize on which requests to intercept and establish the standard
behavior for the application when dealing with unauthorized requests or those
with insufficient permissions.
Commencing with the Enforcement Detector, input a
characteristic of the application's response that can be anticipated when a
user with limited privileges tries to perform an action they lack sufficient
permissions. In my practice, I've found that utilizing the "Body (simple
string): enforced message body contains" option is the simplest to set up
and functions effectively. Choose the type and content that aligns with your
specific needs and remember to click the "Add filter" button.
Moreover, it is necessary to understand that it
automatically sets the default comparison to "And" when assessing
multiple filters. Therefore, if the application generates distinct error
messages, such as one for trying to read a file and another for attempting to
access administrative features, you should create a filter for each scenario
and switch the "And" to "Or."
Follow the same procedure for the Unauthenticated Detector
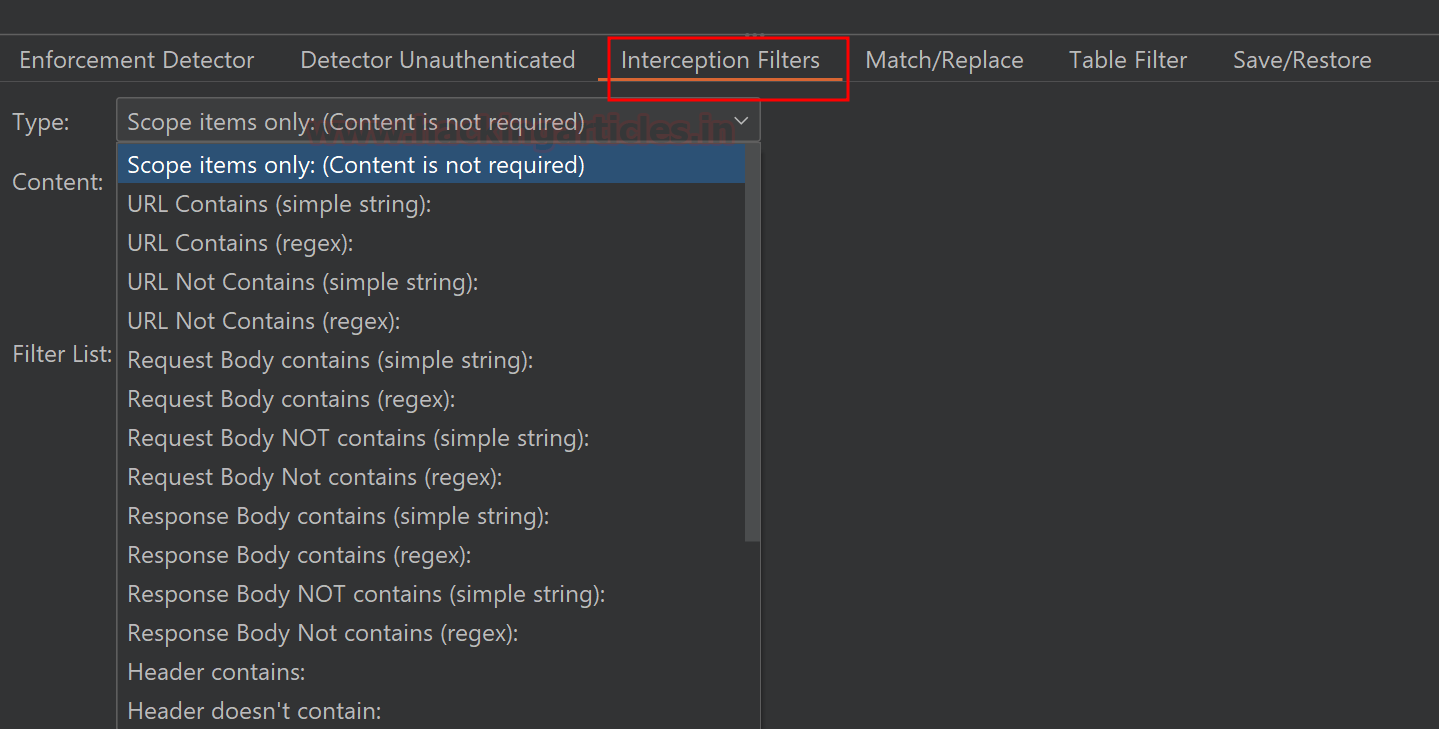
The interception filter will intercept “Scope items only”
regardless of content and from those requests, it will ignore spider requests
and URLs containing image extensions. You may select on your preference and
click “Add filter” when type is selected.
This is another additional feature Match/Replace. You can
select it from this site if you need to change any specific header or body
parameter on the Autorize request. Suppose there is a parameter name 'u.name'
on the request body, and it has to be replaced by an Admin EID i.e.:=”a.name”)
for proper access circumvention. You can tell Autorize via adding here.
You can select the type of requests that you want to see
under the Table Filter bar,
·
bypassed!: the endpoint may be vulnerable to
IDOR,
·
Is enforced!: endpoint seems to be protected but
re-check once,
·
Enforcing!: against IDOR, the endpoint is
clearly protected.
You can save and export the data for further analysis under
the Save/Restore tab.
Practical Demonstration of Autorize in Action
Let's do a quick demonstration to understand in an easy way,
to perform this practical we are going to use a pre-setup Port Swigger lab “Method-based
access control can be circumvented”. Click on access the lab and browser the
application.
This will show a Broken Access Control vulnerability with
two users that have different role higher and lower privilege users. The same
concept can be applied to same-level users.
First, we have to capture the cookies for low privileged
user (normal user). We are using the default normal user credentials,
Wiener:peter
And logged into the application to capture session cookie.
Updated some more details.
You will see the below capture session cookie in to the
login request. Now copy this cookie header.
Add this cookie header value to Autorize tab as shown below,
And keep Autorize on.
In order to, check the auth bypass now we have to log in
with high privilege (admin user). Go to login page again and use admin
credentials to log in,
Administrator:admin
After successfully logging in and browsing the all admin-only
URLs. You can see under the Autorize tab some highlighted requests
The Authz. Status indicates which endpoints are
accessible to wiener (normal user).
The Unauth. Status pertains to unauthorized users,
effectively eliminating the cookie and all authorization headers. You can opt
to disable this feature by deselecting the "Check unauthenticated"
option in the Autorize configuration tab.
Red [Bypassed!] : endpoint could be vulnerable to
access control/IDOR issues.
Orange [Is enforced!] : endpoint seems to be
protected but cross-check manually by replacing the cookies value.
Green [Enforced!] : endpoint is clearly protected
against access control/IDOR issues.
As visible in above image, request 1, 2, 6, and 7 are having
Broken access control issue.
Keep in mind that do not blindly follow the Autorize
result, The Red highlight requests do
not mean that all endpoints are vulnerable or bypassed. There may be false
positives; You must do a cross-check.
Some other possible scenarios, Suppose you are testing auth issues with the two same level of users. As a result, you will see Authz. Status shows Bypassed! And Unauth. Status shows Enforced! In that case improper authorization can be found on the request which shows that the specific endpoint can be accessed by the 2nd user but has correctly implemented authorization for any unauthorized users.
When you select any highlighted request, on the right side
you will see the detailed information about modified, original &
unauthenticated request and responses.
That's a wrap for now. Cheers!
Conclusion
For carrying out comprehensive security reviews, the
"Autorize Burp" extension is an essential tool. By automating
authentication and enabling the testing of restricted areas, it enhances the
efficiency and effectiveness of security assessments. This extension is an
indispensable tool for conducting comprehensive tests and identifying potential
vulnerabilities that may only be accessible to authenticated users.





























0 comments:
Post a Comment