What is threat hunting?
The process of threat hunting involves
proactively searching for malware or attackers that are hiding within a
network. Rather than simply relying on security solutions or services to detect
threats, threat hunting is a predictive element to a layered security strategy,
empowering organizations to go on the offensive looking for threats. Threat
hunting is typically carried out by highly skilled security professionals using
sophisticated toolsets to identify and stop hard-to-find malicious activities
on a network.
According to Microsoft, an attacker resides on a compromised network a
median time of 146 days before being discovered, making this kind of attack an Advanced
Persistent Threat (APT). In this amount of time, attackers residing on a
network in stealth can exfiltrate data, access applications to identify and use
business details to commit fraud, or laterally move through a network gathering
credentials for access to even more valuable data and resources.
Table
of content
·
Prerequisites
·
Credentials
·
Why is Threat Hunting
necessary?
·
Brute force detection via
different protocol
·
Alerts Attack based Tickets
·
Traffic Analysis
·
Deployment Status
·
OTX: Open Threat Exchange
·
Indicators of compromise (IoCs)
Prerequisites
·
Kali (Attacker Machine)
·
Ubuntu 20.04.1
·
Putty (for log-in in servers
via different protocols)
·
Root privileges
Credentials
·
AlienVault IP: - 192.168.1.70
·
Ubuntu Machine IP: -
192.168.1.9
·
Kali (Attacker Machine IP): -
192.168.1.12
Why
is threat hunting necessary?
·
A layered security strategy can
be effective in stopping the majority of cyberattacks. However, it should be
assumed that some small percentage of advanced attacks will evade detection by
traditional security solutions, giving cybercriminals access to an
organization’s network for as long as they deem necessary to carry out their
malicious activities.
·
Implementing a security posture
that prevents and detects attacks is defensive– as the idea is to attempt to
stop an attack before it happens.
·
Threat hunting is a predictive
and offensive tactic, based on the assumption that an attacker has already
successfully gained access (despite an organization’s best efforts).
·
Threat hunting uses a mixture
of forensics capabilities and threat intelligence to track down where attackers
have established footholds within the network and eliminate their access before
any damaging malicious actions can take place.
Brute
Force detection via different protocols
Brute Force simply can be defined as
attempting to log-in without knowing the username or password.
This type can be evaded or avoided by
using Brute force Detection by using different type of SIEM tools such as
AlienVault
Without of much theory Lets get started
with the detection scenario
Let’s take a look 🤔!!
We are going to perform Brute Force via
different protocols
To perform Telnet based Brute Force fire
up your KALI machine and run the following command:
hydra -L user.txt -P passwd.txt
192.168.1.11 telnet
Let’s see the Magic 🙃!!
Whoa 😱
as we can see it detected the multiple wrong login attempts.
Let’s perform one more Brute Force
attack Via FTP protocol to be ensured that it can detect all type of Brute
Force attacks by simply running the following command:
hydra -L user.txt -P passwd.txt
192.168.11 ftp
Let’s check the logs
As we can see it also detected multiple
wrong logins attempts with the host or source details.
It's quite informative to evade Brute
force attacks.
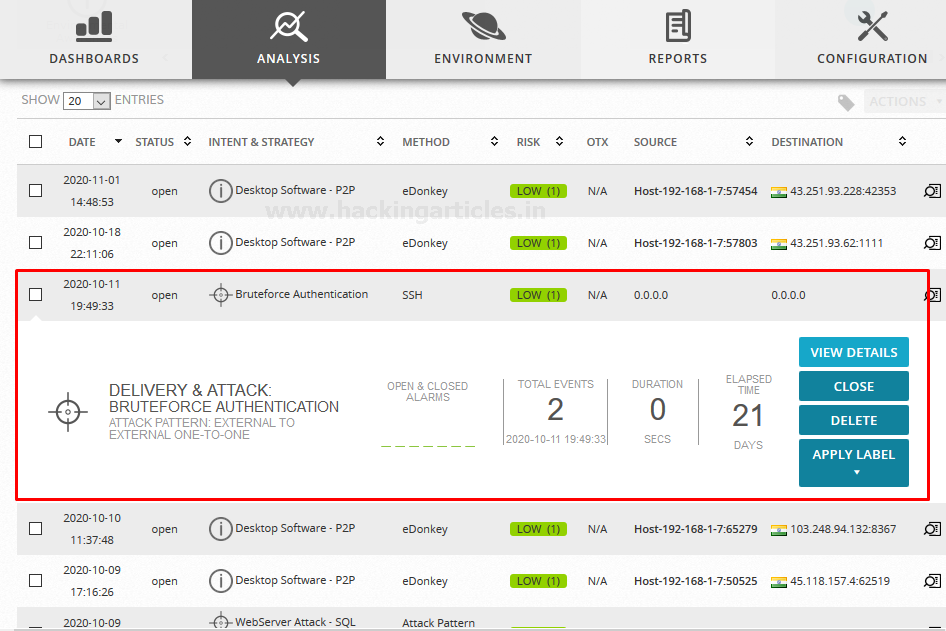
Similarly, I performed some attacks in
my network and yessss…. AlienVault detected all the threats and generated
Alarms smartly under Analysis > Alarms as shown below:
Let’s check the host details from where
or which type of attack were performed. As we can see the details of the Brute
Force attack that above we have performed.
You can make it more informative by
navigating to View Details.
Alerts
Attack based Tickets
It provides access to the OSSIM
Appliance management system. Tickets are helpful to provide workflow tracking
activity related to detected alarms such as vulnerabilities found in systems or
applications or other issues that you want to keep track of.
Here OSSIM generated some tickets on
behalf of performed automatic vulnerability scan or some on behalf of attack
vector as shown below
By default, the OSSIM appliance Web UI
displays a list of all tickets. Also, you can click the Create button
to create a new ticket of a specific type or category.
In the Filters section at the top of the
Tickets page, you can choose criteria to filter the ticket results. You can
choose additional criteria to filter ticket results by clicking the Switch
to Advanced option.
From the Ticket summary list, you can
click on a specific ticket to open the ticket and display the entire details of
the ticket on a new page. From this ticket detail display, you can perform
various actions such as editing fields in the ticket, assigning the ticket,
adding notes and attachments, and changing the status and priority of a ticket,
depending on whatever method or process you want to use to track resolution of
issues.
Traffic
Analysis
This option allows users to monitor or
manage remote traffic capture through the OSSIM sensor.
There are few capture options available
as shown below
·
Timeout
·
Filtering packet size
·
Sensor name
·
Packet source and destination
Let’s check out how AlienVault perform
Traffic Analysis
To perform Traffic Capture, navigate to “Environment
> Traffic Capture” apply the filters as per your own in my case I choose
timeout value 90 seconds and selected the source as shown below
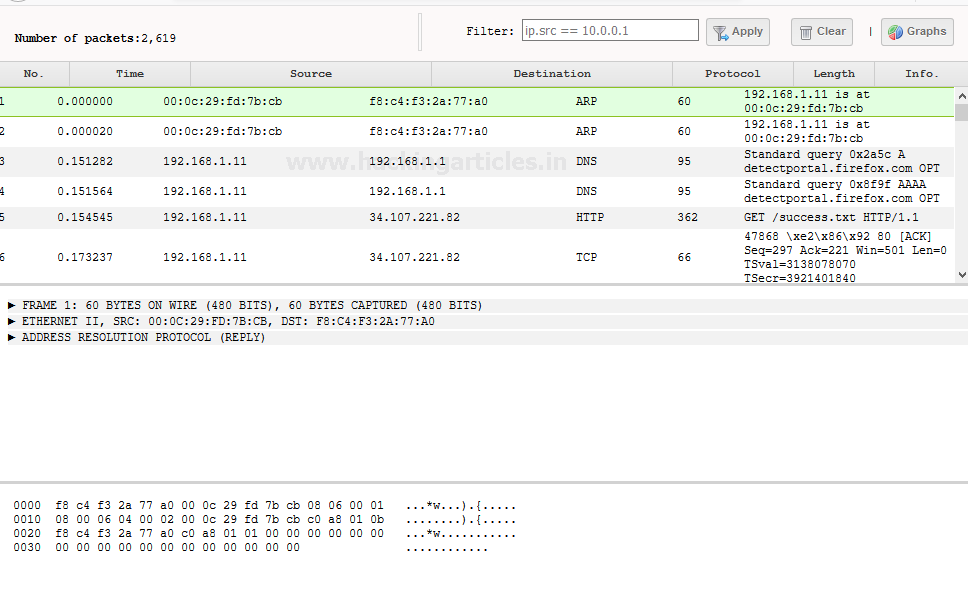
After Launching the traffic capture it
saves the results in the upper section as shown below
As you can see it save the report in PCAP
format you can see it directly by selecting the interface icon
As we can see it capture different type
of packets such as UDP or TCP.
Similarly, you can monitor your whole
network.
Deployment
status
The default “Configuration >
Deployment” provides status and resource information for different OSSIM
Appliance instance components also it provides options to configure and manage
OSSIM Appliance components such as:
·
AlienVault sensors
·
OSSIM appliance servers
·
OSSIM Appliance loggers
So that you can view and change
configuration settings for existing components as shown below:
OTX:
Open Threat Exchange
OTX is an open information-sharing
and analysis network that provides access to real-time information about issues
and attack threats that may impact your organization, allowing you to learn
from and work with others who have already experienced such
attacks. AT&T Alien Labs™ and other security researchers
constantly monitor, analyze, reverse engineer, and report on sophisticated
threats including malware, botnets, phishing campaigns, and more.
Navigate to “Configuration > Open
Threat Exchange option”, OSSIM Appliance displays the
following page.
Indicators
of compromise (IoCs)
Threat hunting generally begins with
security analysts working through threat intelligence, understanding of the
environment they secure, and other security data sources to postulate about a
potential threat. Threat hunters then look for indicators of compromise (IoCs)
found in forensic “artifacts” to identify threatening activity that aligns with
the hypothesized threat activity.
These artifacts are bits of data from
server logs, network traffic, configurations, and more that help threat hunters
determine if suspicious activities have taken place. Artifacts include:
·
Network-based artifacts –
Monitoring listening ports of internet-facing systems, threat hunters can
monitor traffic as well as look through packet session recordings, looking for
unusual outbound traffic, abnormal communication geographies, irregular amounts
of inbound or outbound data, etc.
·
Host-based artifacts –
Changes in file systems and the Windows registry are two places threat hunters
can find anomalous settings and content. Scanning registry values and
monitoring changes made to file systems are common threat hunting activities.
·
Authentication-based
artifacts – Monitoring or reviewing the login (or attempted login) of
privileged accounts on endpoints, servers, and services can be useful for a
threat hunter to follow the trail used by an attacker to identify which
accounts have been compromised and need to be remediated.
You can perform Threat hunting on behalf
of OTX IoCs by opening them “View in OTX” as shown below:
The path taken during the “hunt” is only defined by the details discovered. For example, spotting anomalous outbound network traffic would lead a threat hunter to take a closer look at the endpoint transmitting that traffic. Thus, there’s no one established threat hunting process that applies to every hunt.
Let’s end up here.
Reference: - Source: - AlienVault AT&T Cybersecurity





















0 comments:
Post a Comment