Universal Serial Bus flash drives,
commonly known as USB flash drives are the most common storage devices
which can be found as evidence in Digital Forensics Investigation. The digital
forensic investigation involves following a defined procedure for investigation
which needs to be performed in such a manner that the evidence isn’t destroyed.
So, let us get started with the Forensics Investigation of USB.
Table of Contents
·
Detecting last attached USB flash drives in the Windows
system
§
Using Registry Editor
§
Using PowerShell
§
Using USBDeview
·
Detecting last attached USB flash drives in Linux system
·
Investigating USB flash drives for deleted files
§
Creating Disk Image
§
Analysing Disk Image
Detecting last attached USB flash
drives in the Windows system
The
usage of USB drives in place of work may let nasty employees remove sensitive
or confidential information from a system without any authorization. To resolve
this issue, forensic examination of systems comes into the picture. So, let’s
start investigating;
To detect the artifacts of the USB in
the windows machine, we can use the manual as well as automated methods.
Using Registry Editor
It is
a manual method to easily list the information of the last plugged in USB
storage devices. Press ‘Windows+R’ and type Registry Editor.
This
information can be found in the Windows registry at:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR
The
details like last plugged in USB devices, the vendor of the USB, name of the
product, serial number, and version name can be seen.
Using PowerShell
This a manual method to find
artifacts. The same path can be used in the PowerShell to get the information
on last plugged in USB, with the following command;
Get-ItemProperty -Path
HKLM:\SYStem\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR\*\* | Select FriendlyName
Using USBDeview
To
use an automatic method to find artifacts, you can download USBDeview.
This tool gives you an automated and a graphical representation understanding
of what USB devices were connected to the system.
Detecting last attached USB flash
drives in Linux system
When the USB flash drives history need to be
investigated remotely, we can make use of modules in Metasploit in the Kali
Linux This module will enumerate USB Drive history on a target host. To use
this module, switch on your Linux machine, start msfconsole, and type
command;
use post/windows/gather/usb_history
Set the
session number and exploit. Here you will be able to see a history of various
USB connected previously.
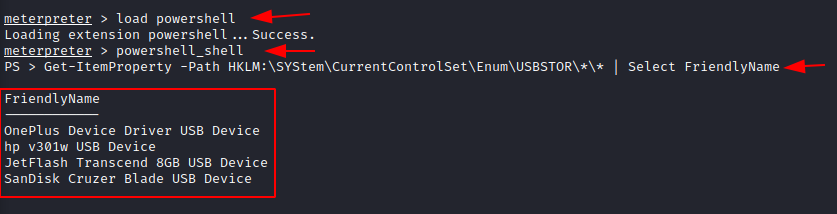
Now
you have also obtained the meterpreter session, so in order to use the powershell
remotely to get the history of USB flash drives connected you can use the
following command;
load powershell
Once
the PowerShell is loaded, you can type,
Get-ItemProperty -Path
HKLM:\SYStem\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR\*\* | Select FriendlyName
You
can hence see the list of USB Flash drives connected to the system remotely.
Investigating USB flash drives for deleted files.
After we have detected all the USB
connected to the system and if the USB Flash drive is available at the scene of
crime. It can be carefully collected in Faraday Bag and now the forensic
investigator can investigate the evidence.
At first, it is important to create an image
of the USB flash drive that was retrieved from the crime scene. To create an
image and to analyse, we can use FTK® Imager, which can be
downloaded from here.
Creating Disk
Image
Step 1: Install
and run AccessData FTK imager
Step 2. Create a disk image of the USB Drive
A disk image is a bit-by-bit or a sector-by-sector copy of a
physical storage device like USB Flash drive, which includes all files, folders
and unallocated, free and slack space etc.
Step
3: As it as USB Flash drive, select Physical Drive and its source to create
image and click on finish.
Step
4: Add the destination of the image file, check the box which say verify images
that are created
.
Step 5: After adding the destination
of the image file to be create, type the name you want to give to the image
file and click on finish.
Step 6: You can see that the image destination is
ready, then click on Start to begin imaging.
Step 7: You see that the image of
your USB flash Drive is being created.
Step
8: After the imaging is completed, you will be prompted with MD% image
verification details where a compared and verified hash is generated.
Here the imaging part is over, so we
can now move to analysis of the USB Flash Drive.
Analysing Disk Image
Note: Investigation is to be
performed only on the Disk image of the original evidence.
Step 9: Click on add evidence item
and add the source of the created image file.
Step 10: Here you see that an
evidence tree is created and the root folder has deleted folders. Here we will
try to retrieve them by clicking on ‘Export files’
Step 11: You see that the deleted
folder and the contents of the deleted folder have been retrieved.




























0 comments:
Post a Comment