There have been many Red Team scenarios,
Capture the Flag challenges where we face the Windows Server. After exploiting
and getting the initial foothold in the server it is very difficult to extract
the data and as well as there are scenarios where we couldn’t get onto the
server per se. But using the SMB we can execute commands remotely on the
server. This was visualized by the SecureAuth and they gave us one of the most
amazing collection of Python classes for working on different protocols. This
collection is named Impacket.
Official GitHub Repository: SecureAuthCorp /impacket
Table of Contents
·
Introduction to SMB
·
Introduction to MSRPC
·
Configurations Used in
Practical
·
Impacket Categories
·
Installation
·
smbclient.py
·
lookupsid.py
·
reg.py
·
rpcdump.py
·
samrdump.py
·
services.py
·
ifmap.py
·
opdump.py
·
getArch.py
·
netview.py
·
Conclusion
Introduction to SMB
The SMB is a network protocol which is also
know as Server Message Block protocol. It is used to communicate between a
client and a server. It can be used to share the files, printers and some other
network resources. It was created by IBM in the 1980s.
Introduction to MSRPC
MSRPC or Microsoft Remote Procedure Call is
a modified version of DCE/RPC. It was created by Microsoft to seamlessly create
a client/server model in Windows. The Windows Server domain protocols are
entirely based on MSRPC.
Configurations Used in Practical
o Attacker Machine
o OS: Kali Linux 2020.1
o IP Address: 192.168.1.112
o Target Machine
o OS: Windows Server 2016
o IP Address: 192.168.1.105
Impacket Categories
·
Remote Execution
·
Kerberos
·
Windows Secrets
·
Server Tools/MiTM Attacks
·
WMI
·
Known Vulnerabilities
·
SMB/MSRPC
o
smbclient.py
o
lookupsid.py
o
reg.py
o
rpcdump.py
o
samrdump.py
o
services.py
o
ifmap.py
o
opdump.py
o
getArch.py
o
netview.py
·
MSSQL / TDS
·
File Formats
·
Other
Installation
Before
using the Impacket tool kit on our system, we need to install it. Installation
process is quite simple. First, head to the GitHub Repository by clicking here. Then using the git
clone command, we clone the complete repository to out Attacker Machine. After cloning
we can see that there is a setup.py file, let us install it. After installation,
we will head to the examples directory and use the scripts as per our convenience.
cd
impacket/
ls
python
setup.py install
smbclient.py
There are moments where we needed to perform
multiple actions between the attacker machine and the target machine. It can be
listing shares and files, renaming some file, uploading the binaries or
downloading files from the target machine. There are some situations where we
even need to create a folder or two on the target machine. Performing such
actions can get tricky while working with a shell that can be detected or can
close at any time. The smbclient.py script helps us in these situations. It can
connect to the Target Machine with the help of bunch of attributes.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password
Hash
o Target
IP Address
When we provide the following parameters to
the smbclient in such a format as shown below and we
will get connected to the target machine and we have a smb shell which can run
a whole range of commands like dir, cd, pwd, put, rename, more, del, rm, mkdir,
rmdir, info, etc
Syntax:
smbclient.py [domain]/[user]:[password/password
hash]@[Target IP Address]
Command:
smbclient.py
ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105
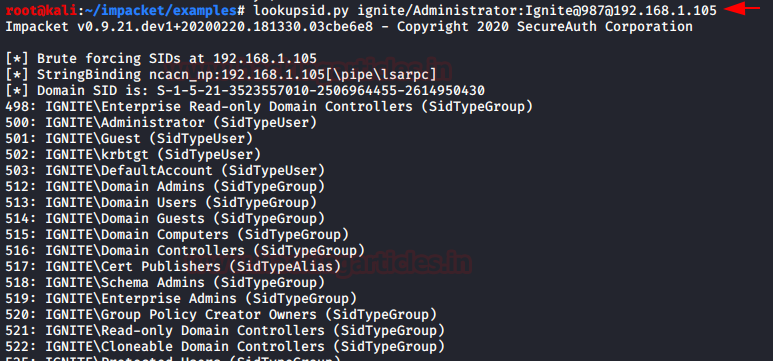
lookupsid.py
A Security Identifier (SID) is a unique
value of variable length that is used to identify a user account. Through a SID
User Enumeration, we can extract the information about what users exist and
their data. Lookupsid script can enumerate both local and domain users. There
is a Metasploit module too for this attack. If you are planning on injecting a target
server with a golden or a silver ticket then one of the things that are
required is the SID of the 500 user. Lookupsid.py can be used in that scenario.
When we provide the following parameters to the Lookupsid in such a format as shown below.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password
Hash
o Target
IP Address
Syntax:
lookupsid.py [domain]/[user]:[password/password
hash]@[Target IP Address]
Command:
lookupsid.py
ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105
reg.py
This Impacket script is ripped straight out
of the reg.exe of the Windows OS. Reg.exe is an executable service that can
read, modify and delete registry values when used with eh combination of query,
add, delete keywords respectively. We can even begin to express the importance
of the access of the registry. Registry controls each and every aspect of the
system. It can be used to gain information about the various policies, software
and also alter some of those policies.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password Hash
o Target
IP Address
o
Registry Key Name
Syntax:
reg.py
[domain]/[user]:[password:password hash]@[Target IP Address] [action] [action
parameter]
Command:
reg.py
ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105 query -keyName
HKLM\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows -s
rpcdump.py
RPC or Remote Procedure Call is when a
computer program causes a procedure to execute in different address space which
is coded as a normal procedure call. This script can enumerate those endpoints
for us. It also matches them to some of the well-known endpoints in order to
identify them.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password Hash
o Target
IP Address
Syntax:
rpcdump.py
[domain]/[user]:[Password/Password Hash]@[Target IP Address]
Command:
rpcdump.py ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105
samrdump.py
Samrdump is an application that retrieves
sensitive information about the specified target machine using Security Account
Manager (SAM). It is a remote interface that is accessible under the Distributed
Computing Environment / Remote Procedure Calls (DCE/RPC) service. It lists out
all the system shares, user accounts, and other useful information about the
target’s presence in the local network. The image clearly shows us all the user
accounts that are held by the remote machine. Inspecting all the available
shares for sensitive data and accessing other user accounts can further reveal
valuable information.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password Hash
o Target IP Address
Syntax:
samrdump.py
[domain]/[user]:[Password/Password Hash]@[Target IP Address]
Command:
samrdump.py
ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105
services.py
The services script of the Impacket communicates
with Windows services with the help of MSRPC Interface. It can start, stop,
delete, read status, config, list, create and change any service. While working
on Red Teaming assignments there were so many tasks that could have been
simplified if only, we have the access to the services of the Target machine.
This makes it all a simple task.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Username
o Password/Password Hash
o Target IP Address
o Action
Syntax:
services.py
[domain]/[user]:[Password/Password Hash]@[Target IP Address] [Action]
Command:
services.py ignite/Administrator:Ignite@987@192.168.1.105
list
ifmap.py
Ifmap scripts initially binds to the MGMT
interface of the Target machine. Then it fetches a list of interface IDs. Then
it adds those IDs to another large list of UUIDs it already has in its database.
Then it tries to bind each of the interface and reports the status of the
interface. The status can be listed or listening. Its ability to gather
information is unmatched. There is a Metasploit Module that works quite similar
to this script is “auxiliary/scanner/dcerpc/endpoint_mapper” The list of UUIDs
(Universal Unique Identifier) which are running endpoint-mapper mapped to the
unique services. After getting these services, an attacker can search on the
internet to find if any of these services are vulnerable to Overflow over RPC.
Requirements:
o Target IP Address
o Target Port
o Hostname (Optional)
Syntax:
ifmap.py [Target IP Address] [Target
Port]
Command:
ifmap.py 192.168.1.105 135
opdump.py
This script binds to the given
hostname:port and connects to the DCERPC (Distributed Computing Environment/
Remote Procedure Calls) interface. After connecting, it tries to call each of
the first 256 operation numbers in turn and reports the outcome of each call.
This generates a burst of TCP connections to the given host:port!
It gives the output as following:
op 0 (0x00): rpc_x_bad_stub_data
op 1 (0x01): rpc_x_bad_stub_data
op 2 (0x02): rpc_x_bad_stub_data
op 3 (0x03): success
op 4 (0x04): rpc_x_bad_stub_data
ops 5-255: nca_s_op_rng_error
rpc_x_bad_stub_data, rpc_s_access_denied,
and success generally means there's an operation at that number.
Requirements:
o IP Address
o Hostname (Optional)
o Port Interface Version
Syntax:
opdump.py [Target IP Address] [Port Interface
Version]
Command:
opdump.py 192.168.1.105 135
99FCFEC4-5260-101B-BBCB-00AA0021347A 0.0
getArch.py
All PDUs (Protocol Data Unit) encoded with
the NDR64 transfer syntax must use a value of 0x10 for the data representation
format label. This value is used only in the transfers of the x64 bit systems.
This scripts when provided with a target tried to communicate with the target
system and collects the value of the data representation format label. Then it
matches it to the NDR64 syntax stored in its code. Then it can provide the
information to the attacker if the Operating System is a 64 bit or 32-bit
system. We can also provide a list of targets and it can work simultaneously on
all the targets.
Requirements:
o Target IP Address
Syntax:
getArch.py -target [Target IP Address]
getArch.py -targets [Target List]
Command:
getArch.py -targets
/root/Desktop/target.txt
netview.py
It is an enumeration tool. It requires the
domain name to enumerate hosts. It can also be provided a list of hosts or
targets. Once a list is gathered then netview checks each of the following:
o IP addresses
o Shares
o Sessions
o Logged On Users
Once finding the information it doesn’t
stop. It keeps looping over the hosts found and keep a detailed track of who
logged in/out from remote servers. It keeps the connections with the target
systems and it is very stealthy as it just sends few DCERPC packets. This
script requires that the attacker machine is able to resolve the domain
machine’s NetBIOS names. This can be achieved by setting the DNS on the
attacker machine to the domain DNS.
Requirements:
o Domain
o Target IP Address
o Username
Syntax:
netview.py [domain]/[User] -target
[Target IP Address] -users [User List]
netview.py [domain]/[User] -targets
[Target List] -users [User List]
Command:
netview.py ignite/Administrator -targets
/root/Desktop/target.txt -users /root/Desktop/user.txt
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the scripts in
the Impacket Toolkit that can interact with the SMB/MSRPC services on a target
system. Impacket has many categories which will further explore in due time.




















0 comments:
Post a Comment