What
is SNMP?
Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a protocol for network management. It is
used for collecting information from, and configuring, network devices, such as
servers, printers, hubs, switches, and routers on an Internet Protocol (IP)
network. It usually run on UDP port 161.
Create New
Virtual Machine using the VMware and change the Network Adapter to Bridged as shown in the given
screenshot.
The Default Login Credentials for Vyos are
Username: vyos
Password: vyos
The Initial Boot of Vyos will be as shown
below:
This is a
Live Boot of the vyos, so we will install the vyos to use it properly.
We will use
the iso image to install vyos. Type
the following command:
Command: install image
Enter “Yes” where it asks to continue.
Next it
will ask about the partition management.
Enter “Auto” where it asks about Partition.
It will
detect the drives in the Virtual System and ask you to select the particular
drive in which you want to install vyos.
Enter “sda” where it asks about the location
for installation.
Next it
will ask about the size for the root partition for the vyos.
You can
enter any size from 1000MB to 21474MB. But it is recommended to keep it maximum
i.e. 21474MB.
Next it
will ask about the name for the image.
By default
the name is set to the version number that is 1.1.8. You can either give a
personalised name or you can leave it default.
Next it
will ask about the location to copy the sda.
It is
recommended to keep it default.
After that
it will ask for the password to be kept for the administrator account.
By default
it is kept vyos. But from security point of view it is recommended to change it
to something complex which is difficult to guess or brute force.
Now it will
ask for the drive on which you want to setup GRUB Boot-loader? Again leave it default to “sda”.
After that
we have completed the vyos setup. Reboot using the command
Command: reboot
After
reboot it will ask for login credentials, Enter the credential that you entered
during the installation.
Now we will
configure the Network Interface. To do that, we will have to enter
configuration mode.
Command: configure
After
entering into configuration mode set up Network interface
Syntax: set interface ethernet [network interface]
address [Static IPv4 Address]
Command: set interface ethernet eth0 address
192.168.1.125/24
Now Commit
and Save the Configuration
Command: commit
Command: save
After that
type “exit” to get out of
configuration mode and then reboot the machine using “reboot” command
We are
rebooting because the configuration changes come in effect only after a reboot.
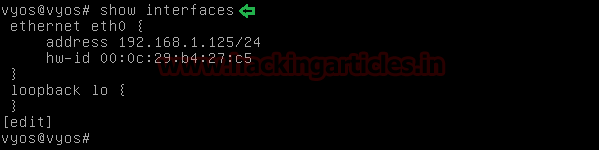
You can the
view interface which we configured by using the command
Command: show interfaces
Note: Above command will run in configuration mode.
Start
SNMP service
Now we will
set up the snmp service in the Vyos.
For that we
will enter configuration mode using command
Command: configure
Now to set
up a snmp service we will need to add a community string and give it an
authorization. To do that:
Syntax: set service snmp community [community-string]
authorization [auth-mode]
[community-string]:
It can be anything but normally it is either public or private. But from a
security point of view it is recommended to keep it that cannot be easily
guessed or bruteforced.
[auth-mode]:
It is the Authorization Mode. We have two options
1.
[ro]:
Read Only Authorization (It can only
be used to read or extract data, we can change it using this string)
2.
[rw]:
Read Write Authorization (It can be
used to change the data using the string)
Command: set service snmp community ignite123 authorization
ro
Command: set service snmp community ignite123
authorization rw
Now let’s
set a user for the system.
Firstly
Enter the Configuration Mode.
Command: configure
Now to add
a user we will use the following command,
Syntax: set system login user [username]
authentication plaintext-password [password]
Command: set system login user ignite
authentication plaintext-password ignite123
After this
commit the configuration and save it.
Also reboot the machine so that
changes may take effect.
We have
successfully completed snmp Lab in Vyos.
SNMP
Enumeration using Kali Linux
Now that we
have setup a snmp service let’s pentest it through kali linux inbuilt tools one
by one, where We can read and extract information using the community string that
have the authorization of reading only but to change the information we will
have to use the community string with the read and write authorization.
Nmap
Let’s check
using nmap in Kali Linux Machine which is running on the same network.
nmap –sU –p161, 162 192.168.1.125
[-sU]: UDP
Ports as SNMP service runs on UDP port
[-p]: Specify
Port Number; SNMP service runs on port 161 and 162
From given
below image you can observed that it has also shown port 161 is open.
Snmpwalk
snmpwalk is an SNMP application that uses SNMP
GETNEXT requests to query a network entity for a tree of information.
Command: snmpwalk -v1
–c ignite321 192.168.1.125
Here
[-v1]: Level of verbose mode
[-c]: Community String
From given below image you can observe all details that are specified
for “STRING”
Snmpset
We can
manipulate these details using the iso id, using another tool snmpset. Here we
are renaming the host string from vyos to hacked
Command: snmpset –v1 –c ignite321 192.168.1.125
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0.s Hacked
Let’s check
if the changes we implemented had an effect using snmpwalk
Command: snmpwalk –v1 –c ignite321
192.168.1.125
As
you can see that the we have successfully change the host name from vyos to
hacked.
We can
extract a number of information using snmpwalk
Command: snmpwalk –v1 –c ignite321
192.168.1.125 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.2
Command: snmpwalk –v1 -c ignite321
192.168.1.125 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.3
Command: snmpwalk –v1 –c ignite321
192.168.1.125 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.6.3.1.2
As the data
extracted by snmp walk is quite large we can extract that into a text file by
using command below
Command: snmpwalk –v1 -c ignite321
192.168.1.125 > snmpout.txt
We can use
gedit to view the extracted information
Command: gedit snmpout.txt
SNMP-Check
Like to snmpwalk, snmp-check allows you to enumerate the
SNMP devices and places the output in a very human readable friendly format. It
could be useful for penetration testing or systems monitoring.
Command: snmp-check
192.168.1.125 -p 161 -c ignite123
Here,
[-p]: To specify port
[-c]: To specify Community String
Braa
Braa is a
mass snmp scanner. The intended usage of such a tool is of course making SNMP queries
– but unlike snmpwalk from net-snmp, it is able to query dozens or hundreds of
hosts simultaneously, and in a single process. Thus, it consumes very few
system resources and does the scanning VERY fast.
Braa
implements its OWN snmp stack, so it does NOT need any SNMP libraries like
net-snmp.
Syntax: braa [Community-string]@[IP of SNMP
server]:[iso id]
Command: braa ignite123@192.168.1.125:.1.3.6.*
Metasploit
We can
enumerate SNMP using a Metasploit module called snmp_enum.
use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_enum
msf auxiliary(scanner/snmp/snmp_enum)
> set rhosts 192.168.1.125
msf auxiliary(scanner/snmp/snmp_enum)
> set community ignite123
msf auxiliary(scanner/snmp/snmp_enum)
> run
We have
fetched same result from metasploit as above.



































0 comments:
Post a Comment