Hello
friends!! Today we are discussing about how to read hexadecimal bytes from an
IP Packet that help a network admin to identify various types of NMAP scanning.
But before moving ahead please read our previous both articles “Network packet forensic” and “NMAP scanning with Wirehsark” it will
help you in better understanding of this article.
Requiremnt
Attacking tool: Namp
Analyis tool: wireshark
We are going to calculate
hexadecimal bytes of wireshark using given below table and as we know wireshark
capture network packet mainly of 4 layers which is describd below in table as
per OSI layer model and TCP/IP layer model.
NMAP ARP Scanning
Hopefully reader must be
aware of basic NMAP scanning techniques if not then read it from here, now
open the terminal and execute given below command which known as “HOST SCAN” to
idenfiy live host in network.
nmap -sn 192.168.1.100
Nmap uses the
–sP/-sn flag for host scans and broadcast ARP request packet to identify which
IP is allocated to particular host machine. From given below image you can
observe that “1 host up” message.
Working of ARP
Scan for Live Host
i.
Send ARP
request for MAC address
ii.
Receive MAC
address though ARP Reply packet
Step to Identify NMAP
ARP Scan
- Collect
Ethernet Header details
Here we used wireshark to capture the network packet
coming from victim’s network and in order to analysis only ARP packet we have
applied filter “ip.addr == VICTIM IP ||
arp” as shown in given below image. Here you will find 2 arp packets,
basically the 1st arp packet is broadcasting IP for asking MAC address of that
network and the 2nd packet is unicast contains Answer of IP query.
Now let’s read Hex value of Ethernet header for identifying
source and destination Mac addresses along with that we can also enumerated the
bytes used for encapsulated packet, in order to identifying Ether type is being
used here.
There should’nt be any uncertainty
in conercn with source Mac address who is responsible for sending packet but if
we talk about Destination Mac address then we got ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff which means exact
Destination is machine is not available here. Further moving ahead we found Ether type 0x0806 highlighted in yellow color is used for ARP protocol.
Hence from Ethernet
header we can conclude it as ARP broadcast packet asking for destination Mac
address.
In order to identify ARP scan you need to investigate
some important parameters which could help a network admin to make correct
assumption in concern of ARP scann.
Try to collect following details as given below:
·
Opcode
(Request/Reply)
·
Source Mac
·
Source IP
·
Destination MAC
·
Destination IP
Now with help of
following table you can read the hex value highlighted in above and below image
for ARP Request and Reply packets
respectively.
Now execute
given below command which known as “HOST SCAN” to identify live host in network
by sending Ping request with the
help of ICMP packet.
nmap -sn 192.168.1.100 –disable-arp-ping
Now
above command will send ICMP request packet instead of ARP request for
identifying live host in network.
Working
of NMAP ICMP Ping when host is live:
i.
Send
ICMP echo request packet.
ii.
Receive
ICMP echo reply.
iii.
Send TCP SYN packet on any TCP port (this
port must be rarely blocked by network admin).
iv.
Receive TCP RST-ACK from target’s Network.
As a result NMAP give “HOST UP” message as
shown in given below image.
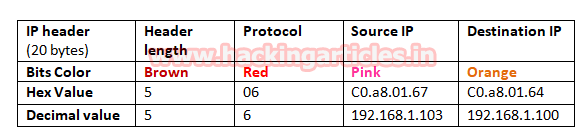
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our
previous article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether
type for IPv4 is 0x0800
Since we know ICMP is Layer 3 protocol
according to OSI model therefore we need to focus on following details for ICMP
forensic with help of IP Header of a packet.
Try to collect
following details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (01 for
ICMP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
From given below image you can observe
Hexadecimal information of IP header field and using given table you can study
these value to obtain their original value.
The IP header length is always given in form of bit and here it is 5 bit which is also minimum IP header length and to make it 20 bytes multiple 5 with 4 i.e. 5*4 bytes =20 bytes.
Now we had discussed
above according to Nmap ICMP scanning technique the 1st packet is should be ICMP
echo request packet and 2nd packet
is should be of ICMP echo reply
packet.
Now with help of following
table you can read hex vaule highlighted in above and below image for ICMP
Request and Reply packets respectively.
- Identify TCP Flags
AS discussed above after ICMP reply, the 3rd packet should be of TCP-SYN packet and 4th should be of TCP-RST/ACK. We had seen in our previous article the hex
value of all TCP-Flags are different from each other, so if we are talking for
TCP-SYN flag then its Hex value should 0x02.
From given below table you can observe the sequence of
TCP flag and how bits of these flag are set for sending packet to destination
port.
For example if you found TCP SYN packet then the bit for SYN flag is set 1 for which the binary value will be 000000010 and its hexadecimal will be 0x02.
NS
|
CWR
|
ECE
|
URG
|
ACK
|
PSH
|
RST
|
SYN
|
FIN
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
Sometime you will get combination of two or more flag in
TCP header, so in that scenario take the help of following table to read the
Hex value of such packet to identify TCP flags bits are being set 1.
For example if you found TCP SYN/ACK packets then indicates that SYN & ACK flags are set
1 for which the binary value will be 000010010
and its hexadecimal will be 0x12
NS
|
CWR
|
ECE
|
URG
|
ACK
|
PSH
|
RST
|
SYN
|
FIN
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
The image given above contains
the hex value of TCP-SYN packets and
the image given below contains the hex value of TCP-RST/ACK packet from which we can calculate the source port and
the destination port of the packet respectively like one given below.
Conclusion! So as stated above regarding the working of NMAP ICMP scan we had obtain the hex value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for
every packet in such sequence gives indication to the Penetration tester that Someone
has Choose NMAP ICMP scan for Network enumeration.
Default NMAP Scan (Stealth Scan)
Here we are going with default scan method to enumerate “open”state
of any specific port
nmap -p 80 192.168.1.100
Working of Default Scan
for open port:
i.
Send TCP-SYN
packet
ii.
Receive
TCP-SYN/ACK
- Send TCP-RST packet
It is also known as half Open
TCP Scan as it does not send ACK packet after receive SYN/ACK packet .
Step to
Identify NMAP Default Scan (Stealth Scan)
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800.
Try to collect following
details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (6 for
TCP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
From given below image you can observe Hexadecimal
information of IP header field and using given table you can study these value
to obtain their original value.
- Analysis TCP Header Details
Since from above image we had obtain Source and
Destination IP and protocol used for communication i.e. TCP, now we need to
identify source and Destination port and TCP Flag used for establishing
connection between two system.
In image we have highlighted source port in “Light brown”
color and destination port in “yellow color”, you can use given below table to
read the hex value of given image.
So we come to know that here TCP-SYN packet is used for sending connection request on Port 80.
Again we read next packet
then here we found hex value 12
indicates that TCP-SYN/ACK has been
send from port 80.
Take the help given above table to read the hex vaule of given image. Hex value 12 for TCP flag is used for SYN + ACK as explained above, and we get 0x12 by adding Hex value “ 0x02 of SYN” and “0x10 of ACK”.
In the image given below we come to know that TCP-RST packet is used for sending Reset
connection to Port 80.
Conclusion!
So as declared above regarding the working of NMAP default scan or NMAP stealth
scan we had obtain the hex value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for
every packet in such sequence gives indication to the Penetration tester that Someone
has Choose NMAP Default scan for Network enumeration.
NMAP TCP Scan
Here we are going with TCP scan to enumerate state of any
specific port
nmap -sT -p 80 192.168.1.100
Working of Default Scan
for open port:
i.
Send TCP-SYN
packet
ii.
Receive
TCP-SYN/ACK
- Send TCP-ACK packet
- Send TCP-RST/ACK packet
Step to
Identify NMAP TCP Scan
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800.
Try to collect following
details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (06 for
TCP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
It is quite similar as NMAP stealth Scan and using given
table you can study these values to obtain their original value.
- Analysis
TCP Header Details
NMAP TCP Scan follow 3 way handshak of TCP connection for
enumeration open port. Identfying source and destination port along with Flag
hex value (TCP-SYN) is similar as
above.
So we come to know that here TCP-SYN packet is used for sending connection request on Port 80.
Again we read next packet
then here we found hex value 12 indicates that TCP-SYN/ACK has been send via port 80.
The only difference between
Stealth Scan and TCP scan is that here packet of ACK flag is send by source machine
who intiate the TCP communication. Again
we read next packet then here we found hex value 0x10 indicates that TCP- ACK has been send via port 80.
Conclusion! So as stated above regarding the working of NMAP TCP scan we had obtain the hex value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for
every packet in such sequence gives indication to the Penetration tester that Someone
has Choose NMAP Default scan for Network enumeration.
NOTE: For packet TCP-RST/ACK the hex value will be “
0x14” send by the attacker machine
NMAP FIN Scan
Here we are going with TCP-FIN scan to enumerate “OPEN” state
of a particular port in any Linux based system therfore excute given below
command.
nmap -sF -p 22 192.168.1.104
Working of FIN Scan for
open port: Send 2 packets of TCP-FIN on a
specific port
FIN is part TCP flag and
NMAP used FIN flag to intiat TCP communication instead of following three way
handshak communication.
Step to
Identify NMAP FIN Scan
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800
Try to collect following
details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (06 for
TCP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
It is quite similar as NMAP above Scan and using given below
table you can study these values to obtain their original value.
- Analysis TCP Header Details
Now lets Identfying source
and destination port along with Flag hex value (TCP-FIN) is similar as above.
So through given below image and with help of table we came to know that here TCP-FIN packet is used for sending connection request on Port 22.
Conclusion!
So as declared above regarding the working of NMAP FIN scan we had obtain the
hex value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for
every packet in such sequence gives indication to the Penetration tester that Someone
has Choose NMAP FIN scan for Network enumeration.
NOTE: If you found 1st FIN packet (0x01) and 2nd
RST packet (0x04) then indicates “Closed Port” on tagered network.
NMAP NULL Scan
Here we are going with TCP Null scan to enumerate “OPEN” state
of any specific port in any Linux based system.
nmap -sN -p 22 192.168.1.104
Working of Null Scan for
open port: Send 2 packets of TCP-NONE on
specific port
Here NMAP used NONE flag
(No flag) to initiate TCP communication and bit of each flag is set
“0”instead of following three-way handshake communication.
Step to
Identify NMAP Null Scan
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800
Try to collect following details
as given below:
·
Ip header length
20 Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (06 for
TCP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
It is quite similar as NMAP above Scan and using given
table you can study these values to obtain their original value.
- Analysis TCP Header Details
Now lets Identfying source
and destination port along with Flag hex value (TCP-NONE) is similar as above.
So through given below image and with help of table we come to know that here TCP-NONE packet is used for sending connection request on Port 22.
Conclusion! So
as stated above regarding the working of NMAP NONE scan we had obtain the hex
value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for every packet in such sequence
gives indication to the Penetration tester that someone has Chosen NMAP NONE
scan for Network enumeration.
NOTE: If you found 1st NONE packet (0x00) and 2nd
RST packet (0x04) then indicates “Closed Port” on tagered network.
NMAP XMAS Scan
Here we are going with XMAS scan to enumerate “OPEN” state
of any specific port in any Linux based system
nmap -sX -p
22 192.168.1.104
Working of XMAS Scan for open port: Send 2 packets of TCP Flags in combination
of FIN, PSH, URG on specific port.
Here NMAP used 3 TCP flags (FIN, PSH, and URG) to initiate
TCP communication and bit of each flag is set “1”instead of following three way
handshake communications.
Step to
Identify NMAP XMAS Scan
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800
Try to collect following
details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (06 for
TCP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
It is quite similar as NMAP above Scan and using given
table you can study these values to obtain their original value.
- Analysis TCP Header Details
Now lets Identfying source
and destination port along with Flag hex value (TCP-XMAS) is similar as above.
So through given below image and with help of table we come to know that here TCP flags {FIN,PSH,URG} packet is used for sending connection request on Port 22.
Conclusion! So
as stated above regarding the working of NMAP XMAS scan we had obtain the hex
value for every packet in same sequence.
Obtaining the hex value for every packet in such sequence
gives indication to the Penetration tester that someone has Choose NMAP XMAS scanned
for Network enumeration.
NOTE:
·
If you found 1st {FIN, PSH, URG} packet (0x29)
and 2nd RST packet (0x04) then indicates “Closed Port” on targeted network.
·
NMAP FIN, NMAP NULL and NMAP XMAS scan are only
applicable on Linux based system
NMAP UDP Scan
Here we are going with XMAS scan to enumerate state of any specific
port in any Linux based system
nmap -sU -p 68 192.168.1.104
Working of XMAS Scan for
open port: Send 2 packets of UDP on specific port
It is quite different from TCP communication process
because here no Flag are used for establishing connection or initiate
connection request with target’s network.
Step to
Identify NMAP UDP Scan
1. Collect IP
Header Details for Protocol Version
For reading data of Ethernet head visit to our previous
article “Network
packet forensic”.
NOTE: Ether type
for IPv4 is 0x0800
Try to collect following
details as given below:
·
Ip header length 20
Bytes (5bits*4=20 bytes)
·
Protocol (11 for
UDP)
·
Source IP
·
Destination IP
It is quite similar as NMAP above Scan as “IP header” and
“Ethernet header” information will be same either is TCP communication or UDP
communication and using given table you can study these values to obtain their
original value.
Basically 11 is hex value use for UDP protocol which is
quite useful in identify NMAP UDP scan from remanding scanning method.
- Analysis UDP Header Details
Now lets Identfying source
and destination port a as done above inTCP Scanning.
Conclusion! Obtaining the hex value for every packet in such sequence gives indication to the Penetration tester that Someone has Choose NMAP UDP scan for Network enumeration.
NOTE: If you found 1st UDP packet and 2nd UDP
with ICMP Message Port is unreachable then indicates “Closed Port” on tagered
network.
































































0 comments:
Post a Comment