In this article you will learn how to capture network packet using Wireshark when attacker is scanning target using NMAP port scanning method. Here you will notice that how Wireshark captured different network traffic packet for open and close ports.
Lets start!!!
TCP SCAN
Tcp scan will scan for TCP port like port 22, 21, 23, 445 etc and ensure for listening port (open) through 3-way handshake connection between source and destination port. If port is open then source made request with SYN packet, as response destination sent SYN, ACK packet and then source sent ACK packets, at last source again sent RST, ACK packets.
Lets start!!!
TCP SCAN
Tcp scan will scan for TCP port like port 22, 21, 23, 445 etc and ensure for listening port (open) through 3-way handshake connection between source and destination port. If port is open then source made request with SYN packet, as response destination sent SYN, ACK packet and then source sent ACK packets, at last source again sent RST, ACK packets.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sT -p 445 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 445 is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 445 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark.
You will notice that it has captured same sequence of flag as described above:
You will notice that it has captured same sequence of flag as described above:
- Source sent SYN packet to destination
- Destination sent SYN, ACK to source
- Source sent ACK packet to destination
- Source again sent RST, ACK to destination.
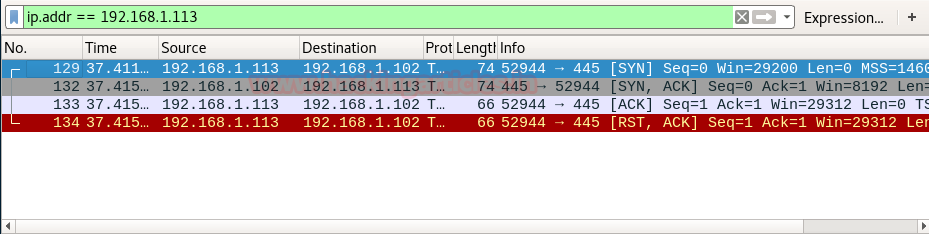
Let’s figure out network traffic for close port. According to given image it is showing if scanning port is closed then 3-way handshake connection would be not possible between source and destination.
Source sent SYN pack and if port is close the receiver will sent response through RST, ACK.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start Wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sT -p 3389 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is closed.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark.
You will notice that it has captured same sequence of flag as described above:
- Source sent SYN packet to destination
- Destination sent RST, ACK packet to source
Stealth Scan
SYN scan is the default and most popular scan option for good reasons. It can be performed quickly, scanning thousands of ports per second on a fast network not hampered by restrictive firewalls. It is also relatively typical and stealthy since it never completes TCP connections.
The port is also considered open if a SYN packet (without the ACK flag) is received in response.
This technique is often referred to as half-open scanning, because you don't open a full TCP connection. You send a SYN packet, as if you are going to open a real connection and then wait for a response. A SYN, ACK indicates the port is listening (open)
SYN scan is the default and most popular scan option for good reasons. It can be performed quickly, scanning thousands of ports per second on a fast network not hampered by restrictive firewalls. It is also relatively typical and stealthy since it never completes TCP connections.
The port is also considered open if a SYN packet (without the ACK flag) is received in response.
This technique is often referred to as half-open scanning, because you don't open a full TCP connection. You send a SYN packet, as if you are going to open a real connection and then wait for a response. A SYN, ACK indicates the port is listening (open)
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sS-p 22 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent SYN packets to destination
- Destination sent SYN, ACK packets to source
- Source sent RST packets to destination
Now figure out traffic for close port using stealth scan. When source sent SYN packet on specific port then if port is closed then destination will reply by sending RST packet.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sS -p 3389 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is closed.
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is closed.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent SYN packets to destination
- Destination sent RST, ACK packets to destination
Fin Scan
A FIN packet is used to terminate the TCP connection between source and destination port typically after the data transfer is complete. In the place of a SYN packet, Nmap start a FIN scan by using a FIN packet. If port is open then no response will come from destination port when FIN packet is sent through source port.
A FIN packet is used to terminate the TCP connection between source and destination port typically after the data transfer is complete. In the place of a SYN packet, Nmap start a FIN scan by using a FIN packet. If port is open then no response will come from destination port when FIN packet is sent through source port.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sF -p 22 192.168.1.102From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent FIN packets to destination
- Destination sent no reply to source
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sF -p 3389 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
Null Scan
A Null Scan is a series of TCP packets which hold a sequence number of “zeros” (0000000) and since there are none flags set, the destination will not know how to reply the request. It will discard the packet and no reply will be sent, which indicate that port is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent SYN packets to destination
- Destination sent RST packets to destination
A Null Scan is a series of TCP packets which hold a sequence number of “zeros” (0000000) and since there are none flags set, the destination will not know how to reply the request. It will discard the packet and no reply will be sent, which indicate that port is open.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sN -p 22 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent Null packets to destination
- Destination sent no reply to source
If the port is closed, the Destination will send an RST, ACK packet in response when source send null packets on specific port.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sN -p 3389 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent Null (none) packets to destination
- Destination sent RST, ACK to source
UDP Scan
UDP scan works by sending a UDP packet to every destination port; it is a connection less protocol. For some common ports such as 53 and 161, a protocol-specific payload is sent to increase response rate, a service will respond with a UDP packet, proving that it is open. If no response is received after retransmissions, the port is classified as open|filtered. This means that the port could be open, or perhaps packet filters are blocking the communication.
UDP scan works by sending a UDP packet to every destination port; it is a connection less protocol. For some common ports such as 53 and 161, a protocol-specific payload is sent to increase response rate, a service will respond with a UDP packet, proving that it is open. If no response is received after retransmissions, the port is classified as open|filtered. This means that the port could be open, or perhaps packet filters are blocking the communication.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sU -p 161 192.168.1.119
From given image you can observe the result that port 161 is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 161 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through Wireshark
- Source sent UDP packets to destination
- Destination sent UDP packet with some data to the source
Similarly if source sent UDP packet on a close port to the destination then destination sent reply with ICMP packet port unreachable with appropriate error
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start Wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sU -p 53 192.168.1.119
From given image you can observe the result that port 53 is close.
From given image you can observe the result that port 53 is close.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent UDP packets to destination
- Destination sent ICMP packet port unreachable to the source
Xmas Scan
These scans are designed to manipulate the PSH, URG and FIN flags of the TCP header, Sets the FIN, PSH, and URG flags, lighting the packet up like a Christmas tree. When source sent FIN, PUSH, and URG packet to specific port and if port is open then destination will discard the packets and will not sent any reply to source.
These scans are designed to manipulate the PSH, URG and FIN flags of the TCP header, Sets the FIN, PSH, and URG flags, lighting the packet up like a Christmas tree. When source sent FIN, PUSH, and URG packet to specific port and if port is open then destination will discard the packets and will not sent any reply to source.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sX -p 22 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
From given image you can observe the result that port 22 is open.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent FIN,PUSH and URG packets to destination
- Destination sent no reply to source
Similarly if source sent FIN, PUSH and URG packets to specific port and if port is closed then destination will sent RST, ACK packets to source.
Type following NMAP command for TCP scan as well as start Wireshark on other hand to capture the sent Packet.
nmap -sX -p 3389 192.168.1.102
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
From given image you can observe the result that port 3389 is close.
Look over the sequence of packet transfer between source and destination captured through wireshark
- Source sent FIN,PUSH and URG packets to destination
- Destination RST, ACK packet to source














































0 comments:
Post a Comment