Hello friends!!
Today we are going to discus advance option of Burpsuit pro for web penetration
testing; here we had used Bwapp lab which you can install from here and acunetix vulnerable web application which is available online for
making web application penetration practices.
Burp suite Advance
Usage
·
Burp Infiltrator
·
Macros
·
Burp Clickbandit
Burp Infiltrator
Burp Infiltrator is a tool used to target web applications in
order to test them using Burp Scanner.
Burp Infiltrator is used to target application so that Burp can detect cases
where its input can pass unsafe APIs on the server side.
Burp Infiltrator supports
applications which are written in:
- Java, Groovy, Scala, or other JVM
languages (JRE versions 1.4 - 1.8)
- C#, VB, or other .NET languages
(.NET versions 2.0 and later)
Let’s
start !!
First,
we need to enable the Burp Infiltrator from
the Burp tab in burpsuite where we
have to select the Burp Infiltrator
option. Then we will see a Burp Infiltrator box will appear where you have
to select the type of application you want to instrument as you shown in the
image
After that we need to select the folder where
we want the Infiltrator file to be saved, so that we can enable it later using
the terminal.
Next
we will give the path of the folder where the infiltrator file will be saved as
shown in the image.
Than
the Burp Infiltrator file will be saved as burp_infiltrator_java.jar.
Now
to enable the burp infiltrator file we will go to the path of the file using
the terminal, than to execute it we need to give the command java –jar burp_infiltrator_java.jar --non
interactive. Then Press Enter the
file will be executed.
We
have used --non interactive in our
command so that it will automatically configured the default settings else we
have to manually configure all the settings. Now we can intercept the request of any website
or application based on the supported parameters as shown in the image.
Turn off Intercept Tab. Select the Target Tab where we can see a Sub Tab
in it as Site Map as shown in the
image.
Then
select the Url you want to scan
using burp infiltrator, just Right click
on the Url then select option Actively
scan this host this will give all the issues related to the Website or
application we want to scan. All the Issues related to the Url scanned can be seen in the Issue
box as shown in the image.
Macros
Burp
suite has a new session handling ability which can be used to run macros,
according to session handling rules. A macro can be said as a predefined
sequence of one or more than one request. The cases in Macros may include:
·
Fetching a page such as a user's home page just to check whether
the current session is still valid or not.
·
By performing a login operation to obtain a new valid session.
·
A token or nonce obtained can be used as a parameter in another
request.
The Macros can be recorded using your
browser. When defining a macro, Burp suite displays the Proxy history, from
which you can select the requests to be used for the macro. You can select from
previously made requests, or record a fresh macro and select the new items from
the history. When you have recorded the macro, the macro editor shows the
details of the items in the macro, which you can review and configure as per
requirement.Let’s start!!
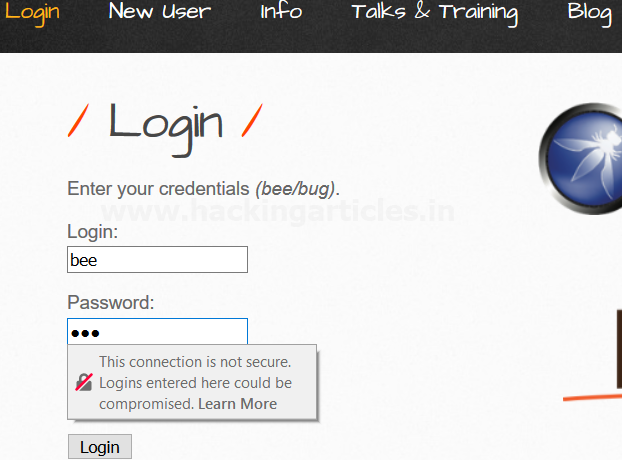
First we have intercepted the login request of Bwapp Lab where we have given the default username and password as shown in the image.
The request is captured in the Intercept Tab then Right Click anywhere around the captured request, next we need to select the option Do Intercept which has a sub option Response to this request. Click on it.
Then we have forward the captured request until we are successfully logged into the Bwapp Lab.
After that go to Project options Tab where we need to select the Sessions Tab as shown in the image.
Click on Add Button under the Session Handling Rules which will open a Session handling rule editor window where we have given a name to the Rule under the Rule description as shown in the image.
Click on Add Button under Rule Action then select Check session is valid option which will open a window for Session handling action editor then give a expression you want the burp suite to look up in the Url like we have given login.php and Tick the option If session is invalid, perform the action below as shown in the image.
Click on Add Button under Select Macro which open a window of Macro Recorder where we will select the item from the proxy history that we want to include in the Macro as shown in the image, Click Ok.
Next the Macro Editor window will open where we will give a name to the macro in the Macro description field as shown in the image. Click Ok.
After this we will get back to Session handling rule editor where we will click on the Scope tab then we need to tick the options Extender, Proxy under Tools Scope and Include all URL’s under URL Scope, Click Ok now the macro will be running in the background.
As you can see in the image we are on the login page of the Bwapp Lab where we have not given any login details.
We made a simple change in the URL we replaced login.php with portal.php as shown in the image.
This has successfully logged us into Bwapp Lab without giving any login details.
Burp Clickbandit
Burp Clickbandit option
in burp suite is a tool used for generating clickjacking attacks. When you know a web page that is vulnerable
to clickjacking, we can use Burp Clickbandit to create an attack, and to
confirm the vulnerability can be successfully exploited. When running Burp
Clickbandit on untrusted websites. Malicious JavaScript from the target site
can take the authority of the HTML output that is generated by Burp
Clickbandit. There are two modes in Burp Clickbandit as follows:
Record
Mode
Burp Clickbandit
first opens in record mode. Then we need to perform one or more mouse clicks to
record your clickjacking attack, as this will involve performing the mouse
clicks that the victim user needs to perform for making some desired action. We
can also use the "disable click actions" checkbox to record clicks
without the target page handling them. When you have finished recording, click
the "Finish" button to enter review mode.
Review
Mode
When you have
finished recording your clickjacking attack, Burp Clickbandit enters into review
mode. This lets you review the generated attack, with the attack user interface
over the original page UI. You can click the buttons on the attack UI to verify
that the attack works.
List of commands that
are available in review mode:
- + And - buttons are used to zoom
in and out.
- The "toggle
transparency" button allows you to show or hide the original page UI.
- The "reset" button
restores the generated attack, as it was before any further clicks were
made.
- The "save" button is
used to save an HTML file containing the attack. This can be used as a
real-world exploit as clickjacking vulnerability.
- You can use the keyboard arrow
keys to reposition the attack UI over the original page UI, if not
correctly aligned with the original page UI.
Let’s
start!!
Burp Clickbandit
runs on browser using JavaScript. It can work on all latest browsers except for
Microsoft IE and Edge.
To run
Clickbandit, go to the Burp menu and select "Burp Clickbandit".
Click the "Copy
Clickbandit to clipboard" button. This will copy the Clickbandit script to
your clipboard.- In your browser, visit the web
page that you want to test, in the same way we regularly do. Then in your
browser, open the web developer console. This might also be called
"developer tools" or "JavaScript console". Paste the
Clickbandit script by editing allow
pasting before pasting copied code into the web developer console, and
press enter.
- The Burp Clickbandit Logo will
appear at the top of the browser window and the original page will be
loaded with in the frame which ready for the attack to be performed, this
is said to be the record mode of burp clickbandit. Then we need to perform
one or more mouse clicks to record your clickjacking attack, as this will
involve performing the mouse clicks that the victim user needs to perform
for making some desired action. We can also use the "disable click
actions" checkbox to record clicks without the target page handling
them. When you have finished recording, click the "Finish"
button to enter review mode.
·
When you have
finished recording your clickjacking attack, Burp Clickbandit enters into
review mode. This lets you review the generated attack, with the attack user
interface over the original page UI.
·
Click on Save Button, allows you to save an html
file containing the attack. This can
be used as a real-world exploit as clickjacking vulnerability.
·
We have opened
the saved html file which shows a transparent UI we have created over the
original UI with a click button in the red box appearing on the page.
·
We can click the
buttons on the attack UI to verify that the attack works. A message will appear
the, you’ve been Clickjacked as shown in the image.