In our previous article we
had discussed “ICMP protocol with Wireshark”
where we had seen how an ICMP protocol work at layer 3 according to OSI model
and study its result using wireshark. Today we are going discuss to ICMP
penetration testing by crafting ICMP packet to test our IDS “Snort” against all
ICMP message Types using Cat Karat tool, you can download it from http://packetbuilder.net link.
For configuring Snort as IDS read our previous article “Configure snort in Ubuntu”
it will automatically install snort in your system with predefine set of rules
that will help in packet capturing of your network.
Let’s start!!
Basically we will perform this practical in three phases
as describe below:
Packet crafting:
In this phase we will craft each ICMP packet with different type ICMP message
using Cat Karat. For more detail about Packet crafting process read our previous
article.
Packet Capturing:
In this phase we will capture the ICMP packet and receive an alert when it will
enters into target’s network using snort as IDS.
Packet Analysis:
In this phase we will investigate captured packet using wireshark.
Brief Introduction on ICMP protocol
ICMP message contains two types of codes i.e. query and
error.
Query: The
query messages are the information we get from a router or another
destination host.
For example given below message types are some ICMP query
codes:
·
Type 0 = Echo Reply
·
Type 8 = Echo Request
·
Type 9 = Router Advertisement
·
Type 10 = Router Solicitation
·
Type 13 = Timestamp Request
·
Type 14 = Timestamp Reply
Error: The
error statement messages reports problem which a router or a destination host
may generate.
For example: given below message types are some of the
ICMP error codes:
·
Type 3 = Destination Unreachable
·
Type 4 = Source Quench
·
Type 5 = Redirect
·
Type 11 = Time Exceeded
·
Type 12 = Parameter Problems
Now when you will run the installed application “Cat
KARAT” you will observe three important sections “Interfaces”, “Packet flow”
and Packet view which in their default state as shown in given below
image.
Message TYPE 0 ICMP
Packet Crafting
So as we know in Packet
Crafting Operation “Packet Assembly” is
1st phase where we need to decide protocol for crafting any packet, which is
quite easy to select with this tool. Only enable the radio button for selecting
protocol and direction flow of packet. Here I had enable radio buttons for
“IPv4” and “ICMP” without disturbing remaining default packet flow as shown
given below image.
Next we need to select the “interface” which you can
select from the Interfaces by double-Click on it.
Now next is “packet Editing” phase where you
need to specify source IP address such as: 192.168.1.2 from
which packet will be sent and Destination IP address such as: 192.168.1.107 on
which packet is received. Moreover you can also make some changes in your
packet such as Time to live (TTL), Data length and also can go with packet
fragmentation.
From given below image you can observe I had added source and
destination IP in packet under the third section protocol
view -> Ipv4
Under 3rd section protocol view in cat Karat
explore ICMP tab and select “0-Echo
Response” option which is generate type 0 ICMP message. Once everything is
edited then your packet is ready to send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for sending packet on target’s
network which known as “packet playing” phase of packet Crafting operation.
This ICMP message type also uses to test the strength of IDS and Firewall
against ICMP smurf Dos Attack.
Capturing ICMP-Type0
packet through IDS
Advantage of install snort through apt respiratory is
that, it is quick and easy to install in your system as well as it contains
predefine set of rule files related to every type of network traffic either
TCP/UDP or ICMP.
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP echo Reply packet is
found in network. This rule also works against Smurf Dos attack in which ICMP
echo reply/response traffic is received on target’s network without sending
genuine ICMP request packet from target’s network to other network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when IDS received any matching packets defined in file of
rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given below image you
can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP Echo Reply” packets
from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to destination 192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type0
packet through Wireshark
Now Last phase is Packet Analysis which is also
last mode of operation of packet crafting process where received packet is
analysis using packet analysis tool. Here we had use wireshark for capturing
incoming traffic. From given below image you can observe that wireshark has
captured exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet
Assembly and packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message type packet
and other information.
From given below
image you can perceive that our ICMP Type 0 is successfully sent on target
machine.
Message TYPE 1 ICMP
Packet Crafting
So the Packet Assembly phase and Packet Editing phase for
ICMP packet crafting is almost same as above only the difference is make in
change ICMP message through which connection will be established with target
network.
Since we want to send traffic through message type 1 packets
for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type -1 Reserved from given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network which known as “packet playing” phase of
packet Crafting operation.
Capturing ICMP-Type1
packet through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP unassigned type 1 packet
is found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when IDS received any matching packets
defined in file of rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given
below image you can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP
unassigned type 1” packets from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to destination
192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type1
packet through Wireshark
From given below image you can observe that wireshark has captured
exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet Assembly and
packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message type “Reserved” packets and other information.
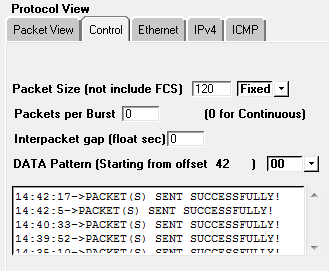
When the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 1 is successfully sent on target machine.
Message TYPE 2 ICMP
Packet Crafting
Again the Packet Assembly phase and Packet Editing phase
for ICMP packet crafting is almost same as above only the difference is make in
change ICMP message through which connection will be established with target
network.
Since we want to send traffic through only message type 2
packets for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 2 Reserved from given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button for sending packet on
target’s network.
Capturing ICMP-Type2
packet through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP unassigned type 2 packet
is found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when again our IDS received any matching
packets defined in its file of rules then generate an alert for captured
packet. From given below image you can observe that an alert is generated by
snort for “ICMP unassigned type 2” packets from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to
destination 192.168.1.107.
Here also
the wireshark has captured exactly same information as per our prediction and
fetch same details which we had bind in packet during packet Assembly and
packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message “Reserved” packet and
other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 2 is successfully sent on target machine.
Now we want to send traffic through message
type 3 packets for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 3 Destination Unreachable from
given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is
ready to send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network.
Capturing ICMP-Type3
packet through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP Destination
Unreachable Network Unreachable packet
when found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
As said above so when IDS received any matching packets
defined in file of rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given
below image you can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP
Destination Unreachable Network Unreachable” packets from source address
192.168.1.1.2 to destination 192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type3
packet through Wireshark
From given below image you can observe that wireshark has captured
exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet Assembly and
packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message type “Destination
Unreachable” (Network Unreachable) packet and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 3 is successfully sent on target machine.
So the Packet Assembly phase and Packet Editing
phase for ICMP packet crafting is almost same as above only the difference is
make in change ICMP message through which connection will be established with
target network.
Since we want to send traffic through message
type 4 packets for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 4 Source Quench from given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is
ready to send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network which known as “packet playing” phase of
packet Crafting operation.
Capturing ICMP-Type4 packet
through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP Source Quench packet
when found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when IDS received any matching packets defined in file of
rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given below image you
can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP Source Quench”
packets from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to destination 192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type4
packet through Wireshark
Here also the wireshark has captured exactly same information as
per our prediction and fetch same details which we had bind in packet during
packet Assembly and packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message
type “Source quench” packet and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 4 is successfully sent on target machine.
Message TYPE 5 ICMP
Packet Crafting
We want to send traffic through message type 5 packets
for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 5 Redirect from given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network.
Capturing ICMP-Type5 packet
through IDS
As given in below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP redirect net packet when
found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
Again as per our prediction wireshark has
captured exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet
Assembly and packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message type “redirect”
packet and other information.
From given below
image you can perceive that our ICMP Type 5 is successfully sent on target
machine.
So the
Packet Assembly phase and Packet Editing phase for ICMP packet crafting is
almost same as above only the difference is make in change ICMP message through
which connection will be established with target network.
Here now
next we want to send traffic through message type 6 packets for establishing
connection with target network therefore select Type 6 for Alternate Host Address from given list.
Once
everything is edited then your packet is ready to send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for sending packet on target’s
network.
Capturing ICMP-Type6 packet
through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP Alternate
Host Address packet is found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when IDS received any matching packets defined in file of
rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given below image you
can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP Alternate Host Address”
packets from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to destination 192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type6
packet through Wireshark
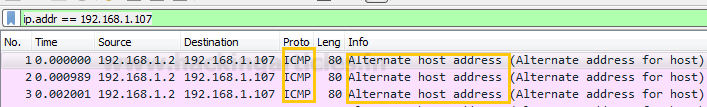
From given below image you can observe that wireshark has captured
exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet Assembly and
packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP message type “Alternate Host Address” packet and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 6 is successfully sent on target machine.
Message TYPE 7 ICMP
Packet Crafting
Again Repeat the same and send traffic through message
type 7 packets for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 7 for Unassigned
from given list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network.
From given below image you can observer that
inside the file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for
capturing the traffic of ICMP Alternate Host Address packet is found in
network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing
given below command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
Therefore when IDS received any matching packets described
in file of rules then it will generate an alert for captured packet. From given
below image you can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP
unassigned type 7” packets from source address 192.168.1.1.2 to destination
192.168.1.107.
Wireshark
has captured exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet
Assembly and packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP unknown message
type “obsolete or malformed” packet and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 7 is successfully sent on target machine.
Message TYPE 8 ICMP
Packet Crafting
Since we want to send traffic through message type 8 packets
for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 8 for ICMP echo Request from given list.
This step is very useful because it will craft a packet
will send ICMP Request packet on target’s network to test the strength of IDS
and Firewall.
Infinite packet ICMP Request packet is consider as ICMP
Flood or Ping of Death Attack when sent only network therefore we can check our
IDS and Firewall Strength against such DOS attack through this packet
crafting.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network.
Capturing ICMP-Type8 packet
through IDS
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP Ping
packet is found in network. As we know ICMP echo Request packet is
consider as Ping request packet which sends request to a network IP for
establishing connection with it.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
Analysis ICMP-Type8
packet through Wireshark
From given below image you can observe that wireshark has captured
Ping packet for ICMP Echo request as described above, exactly same information
which we had bind in packet such as ICMP protocol, ICMP Ping request message packet
and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 8 is successfully sent on target machine.
Message TYPE 9 ICMP
Packet Crafting
Now at last we want to send traffic through message type
9 packets for establishing connection with target network therefore select Type 9 for router Advertisement from given
list.
Once everything is edited then your packet is ready to
send on target network. Click on play button given in menu bar for
sending packet on target’s network.
From given below image you can observer that inside the
file “icmp-info rules” an alert rule is already implemented for capturing the
traffic of ICMP router Advertisement packet is
found in network.
Now turn on IDS mode of snort by executing given below
command in terminal:
sudo snort -A console -q -u
snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf -i eth0
So when IDS received any matching packets defined in file of
rules then generate an alert for captured packet. From given below image you
can observe that an alert is generated by snort for “ICMP router Advertisement” packets from source address
192.168.1.1.2 to destination 192.168.1.107.
Analysis ICMP-Type9
packet through Wireshark
From given below image you can observe that wireshark has captured
exactly same information which we had bind in packet during packet Assembly and
packet Editing mode such as ICMP protocol, ICMP P ICMP router Advertisement message packet and other information.
Again when the tester will click on Stop button, he will receive the status of sent packet either as
successful or as failed.
From given below image you can perceive that our ICMP
Type 9 is successfully sent on target machine.