Security
Onion is a Linux distro for intrusion detection, network security monitoring,
and log management. It’s based on Ubuntu and contains Snort, Suricata, Bro,
OSSEC, Sguil, Squert, ELSA, Xplico, NetworkMiner, and many other security
tools. The easy-to-use Setup wizard allows you to build an army of distributed
sensors for your enterprise in minutes!
Security
Onion effortlessly merges collectively two main roles i.e. complete packet
capture another Network-based [NIDS] and host-based intrusion detection systems
[HIDS].
There
are some Analysis tool are available that also work as real time program by
capturing network packets.
NIDS:
Snort or Suricata and Bro as network intrusion
detection for fingerprints and identifiers that contest identified malicious,
abnormal otherwise suspicious traffic.
HIDS:
Security Onion
offers OSSEC for host-based intrusion detection.
Sguil: It is the crucial Security Onion tool for network security analysts.
Sguil's main component is an intuitive
GUI that gives access to real-time events, session data, and raw packet captures.
Squert: It is a web application that is
used to query and view event data stored in a Sguil database.
ELSA: Enterprise Log Search and Archive is a
three-tier log receiver, archiver, indexer, and web frontend for incoming
syslog.
Let’s start!!
Create VM for
Security Onion installation
Open
vmware, select option “creates new virtual machine”, now for install from
wizard select second option:
Install
disc image file in order to browser iso file of security onion.
Then click on next.
Now
select 2nd option “Linux” for guest operating
system and select version “ubuntu”. Then
click on next and next as per your requirements.
Select bridges
connection and enable the check box for replicate
connection for network adapter setting. Similarly add one more network adapter
and also select bridges connection for 2nd
adapter
Then click
on finish.
Installation
It will start booting the vm automatically, now for SECURITY
ONION
At welcome screen; Select
language and click "Continue". Here we had chosen English as
preferred language.
Read the content and then click on "Continue".
Choose the radio button for “Erase the disk and install Security
Onion” to begin installation and click “Install Now”
Click on “Continue” then it will proceed for disk
partitions.
Check your location, without holdup, select your time
zone and then click on “Continue”.
Choose keyboard layout “English (US)” and then click on
“Continue”.
Now crate your profile by giving yours detail as given
below:
Enter your name:
Ignite
Enter your
computer’s name: Ignite-pc
Select a username:
Ignite
Enter a password:
1234
Click "Continue"
Now it may take some time in installation, but
after that when installation is complete. Click "Restart Now"
for new installation.
Security onion configuration 1st
part
In order to configure security onion as real time system for
NIDS and HIDS we have divided configuration setting in two parts.
Now enter your username and password for login as shown in
given below image.
At Desktop screen you
have can see setup icon; click on “setup” icon for configuration of
network interface.
Configure 1st network
adapter for management interface
Click on “setup” icon present at desktop to configure
security onion on your system.
Click "Yes, Continue"
Click "Yes” to configure /etc/network/interface now
as shown in given below image.
Choose eth0 as
network interface should be the management interface as shown in given below
image.
Choose Static addressing for eth0 utilization as shown in
given below image.
Enter a static IP for your management interface as shown in
given image.
Enter subnet mask of for static addressing as shown in given
below image.
Enter gateway as shown in given below image.
Enter DNs server IP it can be 192.168.1.1 or 8.8.8.8 or can
be both separated by spaces.
Enter you local domain name as shown in given below image.
Configure 2nd
network adapter for sniffing interface
Click "Yes” to configure sniffing interfaces now as
shown in given below image.
Choose eth1 as
network interface should be used for sniffing interface.
Network configuration is completed
now click “Yes Reboot”
Security onion
configuration 2nd part
Now once it gets restarted then again click on “setup” icon
for further configuration of security onion setup as real-time machine. Then
click “yes, Continue”
Since we had already configure network interface therefore
click on “yes, Skip network configuration”
Select “Stable setup” which will configure ELSA; then Click
OK
Enter password for username used while you want to login
into Sguil, Squert and ELSA a shown in given below image.
Now again next
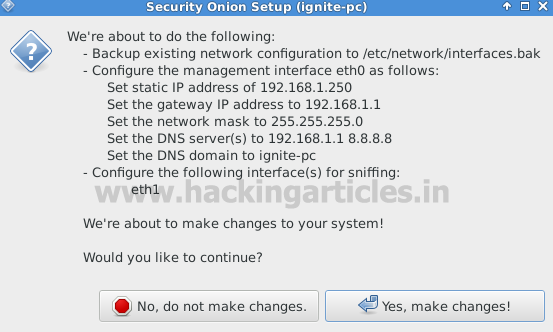
dialoge box will display brief detain for configuration setting. Click on “yes,
proceed with changes”
Here it will proceed for stopping all NSM services which
manages all network services from creation to deletion.
Security Onion configuration is now completed. You will see
it will launch icon for SGUIL, Squert and ELSA. Now click on squil icon and
then enter username and password to login into sguil.
Select network eth1
to be monitor as shown in given below image and click on “start SGUIL”
Great!!
Now analysis your network traffic will real-time machine