Cookie is a small piece of data sent by a server to a browser and
stored on the user's computer while the user is browsing. Cookies
are produced and shared between the browser and the server using the HTTP
Header.
It
Allows server store and retrieve data from the client, It Stored in a file on
the client side and maximum size of cookie that can stored is limited upto 4K
in any web browser. Cookies have short time period because they have expiry
date and time as soon as browser closed.
Example- when you visit YouTube and search for
Bollywood songs, this gets noted in your browsing history, the next time you
open YouTube on your browser, the cookies reads your browsing history and you
will be shown Bollywood songs on your YouTube homepage
Creating cookie
The setcookie()
function is used for the cookie to be sent along with the rest of the HTTP
headers.
When
developer creates a cookie, with the function setcookie, he must specify atleast three arguments. These arguments
are setcookie(name, value, expiration);
Cookie Attributes
1. Name:
Specifies the name of the cookie
2. Value: Specifies the value of the cookie
3. Secure: Specifies whether or not the cookie should only be
transmitted over a secure HTTPS connection. TRUE indicates that the cookie will
only be set if a secure connection exists. Default is FALSE
4. Domain:
Specifies the domain name of the cookie. To make the cookie available on all
subdomains of example.com, set domain to "example.com". Setting it to
www.example.com will make the cookie only available in the www subdomain
5. Path: Specifies the server path of the cookie. If set to
"/", the cookie will be available within the entire domain. If set to
"/php/", the cookie will only be available within the php directory
and all sub-directories of php. The default value is the current directory that
the cookie is being set in
6. HTTPOnly: If
set to TRUE the cookie will be accessible only through the HTTP protocol (the
cookie will not be accessible by scripting languages). This setting can help to
reduce identity theft through XSS attacks. Default is FALSE
7. Expires:
Specifies when the cookie expires. The value: time ()+86400*30, will set the
cookie to expire in 30 days. If this parameter is omitted or set to 0, the
cookie will expire at the end of the session (when the browser closes). Default
is 0
Necessity of Cookies
Cookies can be
used for various purposes –
§ Identifying Unique Visitors.
§ Http is a stateless protocol; cookies
permit us to track the state of the application using small files stored on the
user’s computer.
§ Recording the time each user spends on a website.
Type of cookies
Session Cookie
This type of cookies dies
when the browser is closed because they are stored in browser’s memory. They’re
used for e-commerce websites so user can continue browsing without losing what he
put in his cart. If the user visits the website again after closing the browser
these cookies will not be available. It is safer, because no developer
other than the browser can access them.
Persistent Cookie
These
cookies do not depend on the browser session because they are stored in a file
of browser computer. If the user closes the browser and then access the website
again then these cookies will still be available. The lifetime of these cookies
are specified in cookies itself (as expiration time). They are less secure.
Third Party Cookie
A cookie set by a domain
name that is not the domain name that appears in the browser address bar these
cookies are mainly used for tracking user browsing patterns and/or finding the
Advertisement recommendations for the user.
Secure Cookie
A secure cookie can only
be transmitted over an encrypted connection.
A cookie is made secure by adding the secure flag to the cookie. Browsers which support the secure flag will only send
cookies with the secure flag when the request is going to a HTTPS page.
HTTP Only Cookie
It informs the
browser that this particular cookie should only be accessed by the server. Any
attempt to access the cookie from client script is strictly prohibited. This is an important security protection for session
cookies.
Zombies Cookie
A
zombie cookie is an HTTP cookie that is recreated after deletion. Cookies are
recreated from backups stored outside the web browser's dedicated cookie
storage.
Sessions
PHP session: when
any user made any changes in web application like sign in or out, the server
does not know who that person on the system is. To shoot this problem PHP
session introduce which store user information to be used across several web
pages.
Session
variables hold information about one single user, and are exist to all pages in
one application.
Example: login ID user
name and password.
Session ID
PHP code generates a unique identification in the form of
hash for that specific session which is a random string of 32 hexadecimal
numbers such as 5f7dok65iif989fwrmn88er47gk834 is known as PHPsessionID.
A session
ID or token is a unique
number which is used to identify a user that has
logged into a website. Session ID is stored inside server, it is assigns
to a specific user for the duration of that user's visit (session). The session
ID can
be stored as a cookie, form field, or URL.
Explanation:
Now
let’s have a look over this picture and see what this picture says:
In
given picture we can clearly see there are three components inside it: HTTP Client, HTTP server and Database
(holding session ID).
Step1:
client send request to server via POST or GET.
Step2:
session Id created on web server. Server save session ID into database and
using set-cookie function send session ID to the client browser as response.
Step3: cookie
with session ID stored on client browser is send back to server where server
matches it from database and sends response as HTTP 200 OK.
Session hijacking
As we
know different users have unique session ID when an attacker sniff the session via
man-in-middle attack or via XSS and steal session ID or session token this is
called session hijacking. When attacker sends the stealing session ID to web
server, server match that ID from database stored session ID. If they both
matched to each other then the server reply with HTTP 200 OK and attacker get successfully access without submitting
proper Identification.
Session hijacking tutorial
For this
tutorial I have targeted DVWA, here cookie name is dvwa Session.
Note: session ID for this page will change
every time when we will close the browser.
Now
capture the browser request using burp
suite.
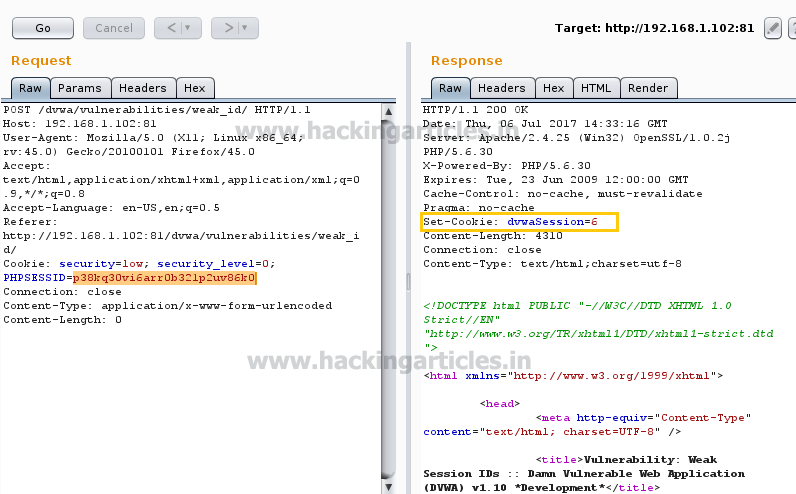
From given image we can see the cookie holds PHPSESSID P38kq30vi6arr0b321p2uv86k0;
now send this intercepted data into repeater to observe its response.
In response you can see the highlighted data show set –cookie: dvwaSession =1 more over HTTP
200 OK response from server side.
According to developer each time a new sessionID will
generate by server each time, but attacker sniff this session ID P38kq30vi6arr0b321p2uv86k0 for
unauthorized login.
Next time
we receive another session id when data is intercepted through burp suite i.e. PHPSESSID= gutnu601knp4qsrgfdb4ad0te3, again send this intercepted data into repeater to observe its response.
But
before we perceive its response, replace
new PHPSESSID from old PHPSESSID.
From given image you can observe we have replaced the SESSION
ID and then generate its response in which set –cookie: dvwaSession =6 and HTTP 200 OK response from server side.
Now
change the value inside intercepted data and then forward this request to the
server.
Session Vs cookies
|
Session
|
Cookies
|
|
Data are stored on Server
|
Data are stored in Client’s Browser
|
|
Sessions Data are more secure because
they never travel on every HTTPRequest
|
Travel with each and Every HTTP
request
|
|
You can store Objects (Store Large
Amount of Data)
|
You can store strings type (Max File
Size 4 kb)
|
|
Session Cannot be used for Future
Reference
|
Cookies are mostly used for future
reference
|