This is a very handy little application. It’s been developed
by the QEMU team. The software is very useful when dealing with virtualization,
Qemu-img is available for both windows and Linux. Its function is to give you
the ability to change the format of a given virtual disk file to the majority
of the popular virtual disk formats that are used across platforms. Let’s say
you are using virtual box in Windows and want to migrate the virtual disk to be
used on a mac, in parallels, you can use this simple program to achieve this
with minimum effort.
Our purpose of writing about this today is slightly
different from Qemu-img’s mainstream usage, we want to focus on how we can use
this application to convert a virtual disk image, whole or split into a .raw file that can be used with most of
the popular forensic frameworks that are available.
Let’s start up Qemu-img on our Linux machine
At the terminal prompt type “qemu-img –h”
This will show you all the options that can be used with
qemu-img,
Right at the end of the information that is presented after
the command given above is used, we can see all the formats supported by this
application.
Here is a list of all the formats that are compatible with
Qemu-img
Now let’s see how this application comes in handy for use in
forensics.
In a situation where a virtual disk is part of the
acquisition and further dedicated analysis is required, the virtual disc can be
converted into .raw format.
Let’s begin.
Since our goal is to analyze the virtual disk, we are using
the image file from Windows 7 installed on VMWare. The file in question is in .vmdk format.
Just a heads up, when you convert a virtual disk file to a .raw file, the size of the converted
file can be quite big, so make sure you have enough space.
Here is our .vmdk
file
For ease of use, we have placed the .vmdk file in a folder named Qmeu
on the desktop. The terminal is
opened from within the folder.
At the terminal prompt type “qemu-img convert -f vmdk -O raw Windows\ 7.vmdk win7.raw”
A breakdown of the command that we just gave:
qemu-img convert is invoking the convert function of
qemu-img.
-f is the format
of the input file, which in this case is .vmdk
-O is the format
of the output file that we want, a .raw
file.
Windows\ 7.vmdk is
the name of the input file that we have in our folder.
win7.raw is the
name we have given the output file with its file extension.
Give it a few minutes and check the folder, you will find
the converted file.
As you can see, the size of the .raw file is 10.7 GB and the
size of the .vmdk file was 6.0 GB, that’s quite a jump in size!
We can now use Foremost
to carve the .raw file to see what’s
inside.
At the terminal type “foremost
-t jpeg,png -i win7 -o output”
With this command we are carving the .raw file for .jpeg and .png files which will be collected in a
folder named output. If you have any
doubts about foremost you can refer this
article.
As you can see, our .raw file has been successfully carved, the results are visible
below.
We have successfully carved a .raw file made from a virtual disk, now let’s mount the .raw file to view its contents. We will
be using a Windows for this operation.
Now we will mount this .raw file using FTK Imager to
see its contents. The image mounting option can be found under the File menu. Navigate to the .raw file from within the mounting
menu.
Select Mount, leave
the other options as they are and the file will appear on the Mapped Image List.
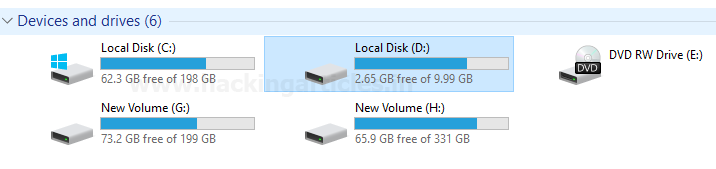
Next we navigate to My
Computer and we can see that the .raw
has been mounted as a partition.
The windows file system can be seen within and explored for
content.
Qemu-img is a very simple application with a high potential.
It can be a very valuable tool in your forensic toolkit due to its large list
of compatible formats. It will make sure that the format of the acquired image
does not keep you from using your forensic tool of choice to run your
investigation or carve out data.
We hope you enjoy using this tool.
Have fun and stay ethical.
About The Author
Abhimanyu Dev is a Certified Ethical Hacker, penetration
tester, information security analyst and researcher. Connect with him here